|
Arik-den-ili
Arik-den-ili, inscribed mGÍD-DI-DINGIR, “long-lasting is the judgment of god,” was King of Assyria 1317–1306 BC, ruling the Middle Assyrian Empire. He succeeded Enlil-nirari, his father, and was to rule for twelve years and inaugurate the tradition of annual military campaigns against Assyria’s neighbors. Biography The sources are slim for his reign, less than ten inscriptions, a fragmentary chronicle and references to his affairs in those of his son Adad-nirari I’s accounts. He seems to have been the first of the Assyrian kings to have institutionalized the conduct of annual military campaigns, some of which appear to be little more than livestock-rustling expeditions, as the chronicle mentions “a hundred head of sheep and goats and a hundred head of their cattle [...] he brought to Aššur.” Arik-den-ili’s first victories were against his eastern neighbours (the Pre-Iranic inhabitants of what was to become Persia), Turukku and Nigimhi, and all the chiefs of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Assyria
The king of Assyria (Akkadian: ''Išši'ak Aššur'', later ''šar māt Aššur'') was the ruler of the ancient Mesopotamian kingdom of Assyria, which was founded in the late 21st century BC and fell in the late 7th century BC. For much of its early history, Assyria was little more than a city-state, centered on the city Assur, but from the 14th century BC onwards, Assyria rose under a series of warrior kings to become one of the major political powers of the Ancient Near East, and in its last few centuries it dominated the region as the largest empire the world had seen thus far. Ancient Assyrian history is typically divided into the Old, Middle and Neo-Assyrian periods, all marked by ages of ascendancy and decline. The ancient Assyrians did not believe that their king was divine himself, but saw their ruler as the vicar of their principal deity, Ashur, and as his chief representative on Earth. In their worldview, Assyria represented a place of order while lands not governed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adad-nirari I
Adad-nārārī I, rendered in all but two inscriptions ideographically as md''adad-''ZAB+DAḪ, meaning “Adad (is) my helper,” (1305–1274 BC or 1295–1263 BC short chronology) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is the earliest Assyrian king whose annals survive in any detail. Adad-nārārī I achieved major military victories that further strengthened Assyria. In his inscriptions from Assur he calls himself son of Arik-den-ili, the same filiations being recorded in the Nassouhi kinglist.Nassouhi kinglist, iii 23. He is recorded as a son of Enlil-nirari in the Khorsabad kinglistKhorsabad kinglist iii 17. and the SDAS kinglist,SDAS kinglist, iii 8. probably in error. Early rule He boasted that he was the “defeater of the heroic armies of the Kassites (their Babylonian neighbors to the south), Qutu (their eastern Gutean neighbors), Lullumu (the Lullubi tribesmen of Ancient Iran immediately east of Assyria) and Shubaru (“northerners in Asia Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlil-nirari
Enlil-nirari (“ Enlil is my helper”) was King of Assyria from 1327 BC to 1318 BC during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He was the son of Aššur-uballiṭ I. He was apparently the earliest king to have been identified as having held eponym, or limmu, office. Biography He recorded on clay cones his repairs to a dilapidated stretch of the wall from the Craftsman’s Gate to the Sheep Gate around his capital, the city of Assur, now the tell-site of Qal’at Shergat which lies beside the Tigris. He proffered a prayer that future restorations would preserve his inscriptions. His sister, Muballiṭat-Šērūa, was married to the Kassite king Burna-Buriaš II, and his nephews, Kara-ḫardaš and Kurigalzu would succeed to the Babylonian throne, separated by a short-lived revolt which was put down by Aššur-uballiṭ and the Assyrian army. Around this time, there is evidence of the exchange of gifts of textiles and votive ornaments between the Kassite and Assyrian ruling clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. The Middle Assyrian Empire was Assyria's first period of ascendancy as an empire. Though the empire experienced successive periods of expansion and decline, it remained the dominant power of northern Mesopotamia throughout the period. In terms of Assyrian history, the Middle Assyrian period was marked by important social, political and religious developments, including the rising prominence of both the Assyrian king and the Assyrian national deity Ashur. The Middle Assyrian Empire was founded through Assur, a city-state through most of the preceding Old Assyrian period, and the surrounding territories achieving independence from the Mitanni kingdom. Under Ashur-uballit, Assyria began to expand and assert its place as one of the great powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi-Maruttash
Nazi-Maruttaš, typically inscribed ''Na-zi-Ma-ru-ut-ta-aš'' or m''Na-zi-Múru-taš'', ''Maruttaš'' (a Kassite god synonymous with Ninurta) ''protects him'', was a Kassite king of Babylon c. 1307–1282 BC (short chronology) and self-proclaimed '' šar kiššati'', or "King of the World", according to the votive inscription pictured. He was the 23rd of the dynasty, the son and successor of Kurigalzu II, and reigned for twenty six years.According to the ''Kinglist A'' tablet, BM 33332, column 2, line 2, in the British Museum. His reign can be seen as the peak of the Kassite Dynasty, exemplified by his successful military campaigns against Assyria and Elam, the glyptic style of cylinder seals, the literature inspired by him (Hemerology for Nazi-Maruttaš), and his appearance in the period piece Ludlul bēl nēmeqi, which was set during his reign. Conflict with Assyria Nazi-Maruttaš faced a growing threat from the ascendancy of Assyria under Arik-den-ili and his successor Ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BCE. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad" (''Māt Akkadī'' in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi ( fl. c. 1792–1752 BCE middle chronology, or c. 1696–1654 BCE, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom. Like Assyria, the Babylonian state retained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamash
Utu (dUD "Sun"), also known under the Akkadian name Shamash, ''šmš'', syc, ܫܡܫܐ ''šemša'', he, שֶׁמֶשׁ ''šemeš'', ar, شمس ''šams'', Ashurian Aramaic: 𐣴𐣬𐣴 ''š'meš(ā)'' was the ancient Mesopotamian sun god. He was believed to see everything that happened in the world every day, and was therefore responsible for justice and protection of travelers. As a divine judge, he could be associated with the underworld. Additionally, he could serve as the god of divination, typically alongside the weather god Adad. While he was universally regarded as one of the primary gods, he was particularly venerated in Sippar and Larsa. The moon god Nanna (Sin) and his wife Ningal were regarded as his parents, while his twin sister was Inanna (Ishtar). Occasionally other goddesses, such as Manzat and Pinikir, could be regarded as his sisters too. The dawn goddess Aya (Sherida) was his wife, and multiple texts describe their daily reunions taking place on a mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahlamu
Ahlamu or Aḫlamū, were a group or designation of Semitic semi-nomads. Their habitat was west of the Euphrates, between the mouth of the Khabur and Palmyra. In the 18th century BC, they were first mentioned in the sources since Rim-Anum, a king of Uruk, and in texts from Mari; then, in the 14th century BC in Egyptian sources, in one of the Amarna letters, in the days of Akhenaten, where it is affirmed that they had advanced until the Euphrates. Etymology Although the etymology and meaning is ultimately uncertain, it can safely be said to derive from the Semitic language family. In the past it was proposed as "''companion or confederate''" by an error of scholar Wayne T. Pitard, comparing it to an unrelated Arabic root, presumably ح ل ف (''ḥ-l-f''), which does indeed mean such. The more recent proposal by Lipiński, connects it instead to غ ل م (''ḡ-l-m'') denoting a boy, lad, post-pubescent youth, a young man, a man full of virility or prowess, the prime of his l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
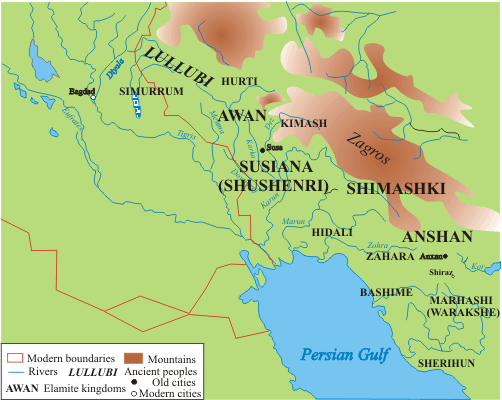
Turukku
The Turukkaeans were a Bronze and Iron Age people of Mesopotamia and the Zagros Mountains, in South West Asia. Their endonym has sometimes been reconstructed as Tukri. History Middle Bronze Turukku was regarded by the Old Assyrian Empire as a constant threat, during the reign of Shamshi-Adad I (1813-1782 BCE) and his son and successor Ishme-Dagan (1781-1750 BCE). The Turukkaeans were reported to have sacked the city of Mardaman around the year 1769/68 BCE. Babylon's defeat of Turukku was celebrated in the 37th year of Hammurabi's reign (c. 1773 BCE). A significant early reference to them is an inscription by the Babylonian king Hammurabi, (r. circa 1792 – c. 1752 BCE) that mentions a kingdom named ''Tukriš'' (UET I l. 46, iii–iv, 1–4), alongside Gutium, Subartu and another name that is usually reconstructed as Elam. Other texts from the same period refer to the kingdom as ''Tukru''. Iron Age By the early part of the 1st millennium BCE, names such as ''Turukkum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has contributed to its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of , making it the second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Modern Standard Arabic throughout the country. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back over 7000 years, predating recorded history. Modern-day Lebanon was home to the Phoenicians, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashur (god)
Ashur, Ashshur, also spelled Ašur, Aššur ( Sumerian: AN.ŠAR₂, Assyrian cuneiform: , also phonetically ) is a god of the ancient Assyrians and Akkadians, and the head of the Assyrian pantheon in Mesopotamian religion, who was worshipped mainly in northern Mesopotamia, and parts of north-east Syria and south-east Asia Minor which constituted old Assyria. He may have had a solar iconography. Legend Aššur was a deified form of the city of Assur, which dates from the mid 3rd millennium BC and was the capital of the Old Assyrian kingdom. As such, Ashur did not originally have a family, but as the cult came under southern Mesopotamian influence, he later came to be regarded as the Assyrian equivalent of Enlil, the chief god of Nippur. Enlil was the most important god of the southern pantheon from the early 3rd millennium BC until Hammurabi founded an empire based in Babylon in the mid-18th century BC, after which Marduk replaced Enlil as the chief god in the south. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziggurat
A ziggurat (; Cuneiform: 𒅆𒂍𒉪, Akkadian: ', D-stem of ' 'to protrude, to build high', cognate with other Semitic languages like Hebrew ''zaqar'' (זָקַר) 'protrude') is a type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. It has the form of a terraced compound of successively receding storeys or levels. Notable ziggurats include the Great Ziggurat of Ur near Nasiriyah, the Ziggurat of Aqar Quf near Baghdad, the now destroyed Etemenanki in Babylon, Chogha Zanbil in Khūzestān and Sialk Plus, Sumer in general. The Sumerians believed that the Gods lived in the temple at the top of the Ziggurats, so only priests and other highly respected individuals could enter. Society offered them many things such as music, harvest, and creating devotional statues to live in the temple. History The word ziggurat comes from ''ziqqurratum'' (height, pinnacle), in ancient Assyrian. From ''zaqārum'', to be high up. The Ziggurat of Ur is a Neo-Sumerian ziggurat built by King Ur-Namm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |