|
Ariernachweis
In Nazi Germany, the Aryan certificate/passport (german: Ariernachweis) was a document which certified that a person was a member of the presumed Aryan race. Beginning in April 1933, it was required from all employees and officials in the public sector, including education, according to the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service. It was also a primary requirement to become a Reich citizen for those who were of German or related blood (Aryan) and wanted to become Reich citizens after the Nuremberg Laws were passed in 1935. A "Swede or an Englishman, a Frenchman or Czech, a Pole or Italian" was considered to be related, that is, "Aryan". There were two main types: *''Kleiner Ariernachweis'' (Lesser Aryan certificate) was one of: **Seven birth or baptism certificates (or a combination of both) (the person, his parents and grandparents) and three marriage certificates (parents and grandparents) or certified proofs thereof: ***'' Ahnenpaß'' (literally ancestor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariernachweis 13
In Nazi Germany, the Aryan certificate/passport (german: Ariernachweis) was a document which certified that a person was a member of the presumed Aryan race. Beginning in April 1933, it was required from all employees and officials in the public sector, including education, according to the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service. It was also a primary requirement to become a Reich citizen for those who were of German or related blood (Aryan) and wanted to become Reich citizens after the Nuremberg Laws were passed in 1935. A "Swede or an Englishman, a Frenchman or Czech, a Pole or Italian" was considered to be related, that is, "Aryan". There were two main types: *''Kleiner Ariernachweis'' (Lesser Aryan certificate) was one of: **Seven birth or baptism certificates (or a combination of both) (the person, his parents and grandparents) and three marriage certificates (parents and grandparents) or certified proofs thereof: ***'' Ahnenpaß'' (literally ancestor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahnentafel
An ''ahnentafel'' (German for "ancestor table"; ) or ''ahnenreihe'' ("ancestor series"; ) is a genealogical numbering system for listing a person's direct ancestors in a fixed sequence of ascent. The subject (or proband) of the ahnentafel is listed as , the subject's father as and the mother as , the paternal grandparents as and and the maternal grandparents as and , and so on, back through the generations. Apart from , who can be male or female, all even-numbered persons are male, and all odd-numbered persons are female. In this schema, the number of any person's father is double the person's number, and a person's mother is double the person's number plus one. Using this definition of numeration, one can derive some basic information about individuals who are listed without additional research. This construct displays a person's genealogy compactly, without the need for a diagram such as a family tree. It is particularly useful in situations where one may be restricted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
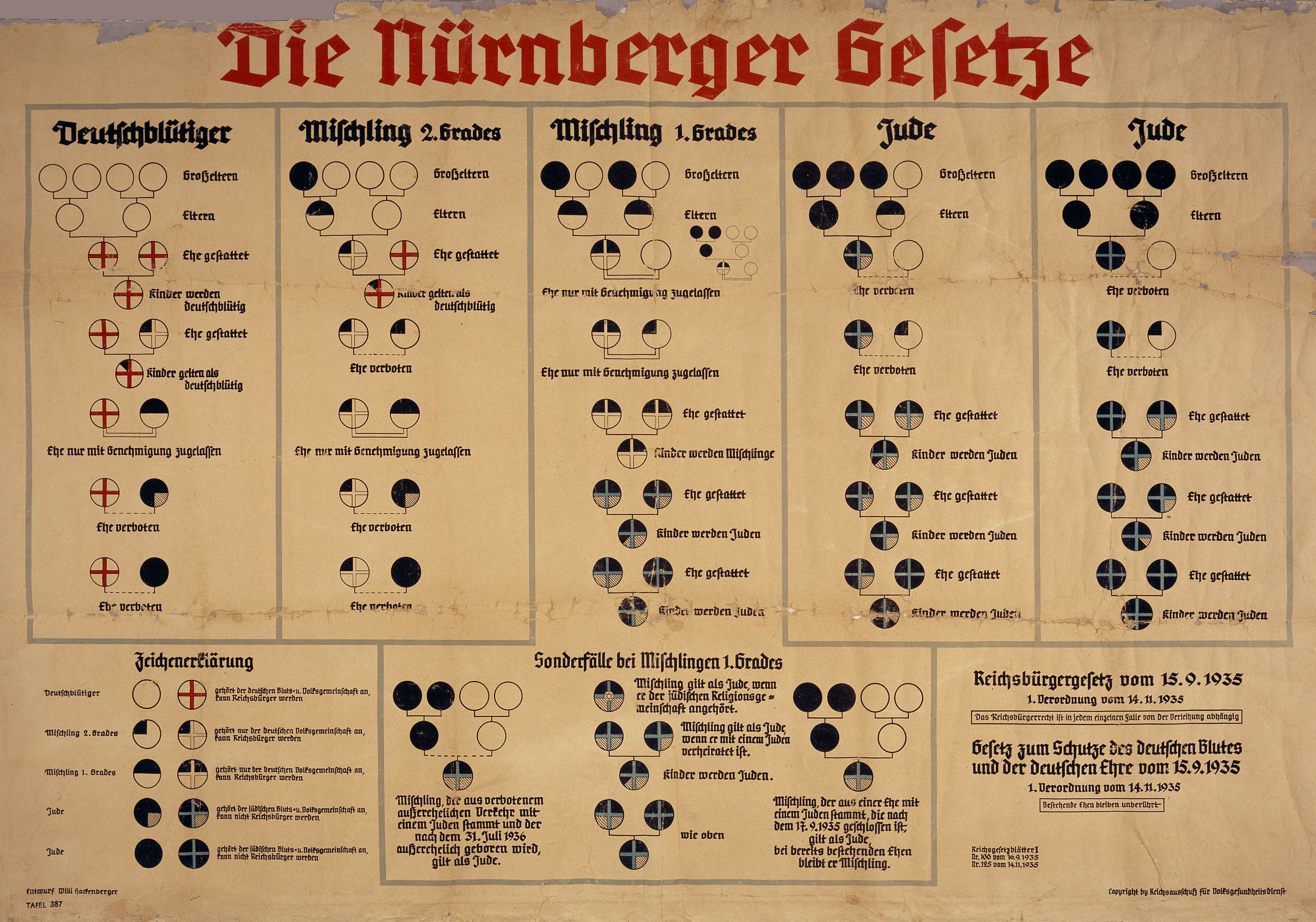
Aryan Clause
An Aryan paragraph (german: Arierparagraph) was a clause in the statutes of an organization, corporation, or real estate deed that reserved membership and/or right of residence solely for members of the "Aryan race" and excluded from such rights any non-Aryans, particularly those of Jewish and Slavic descent. They were an omnipresent aspect of public life in Germany and Austria from 1885 to 1945. One of the first documented examples of such a paragraph was written by the Austrian nationalist leader and anti-Semite Georg von Schönerer in his nationalistic Linz Program of 1882, and countless German national sports-clubs, song societies, school clubs, harvest circles and fraternities followed suit. In Nazi Germany The best-known Aryan paragraphs are in the legislation of Nazi Germany. They served to exclude Jews from organizations, federations, political parties, and, ultimately, all public life. Besides Jews, people not considered Aryans included Poles, Serbs, Russians, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Racial Theories
The Nazi Party adopted and developed several pseudoscientific racial classifications as part of its ideology (Nazism) in order to justify the genocide of groups of people which it deemed racially inferior. The Nazis considered the putative "Aryan race" a superior "master race", and they considered black people, mixed-race people, Slavs, Roma, Jews and other ethnic groups racially inferior " sub-humans", whose members were only suitable for slave labor and extermination. These beliefs stemmed from a mixture of 19th-century anthropology, scientific racism and anti-semitism. Racial hierarchy The Nazis claimed to observe a strict and scientific hierarchy of the human race. Adolf Hitler's views on race and people are found throughout his autobiographical manifesto book ''Mein Kampf'' but more specifically, they are found in chapter 11, the title of which is "Nation and Race". The standard-issue propaganda text which was issued to members of the Hitler Youth contained a chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law For The Restoration Of The Professional Civil Service
The Law for the Restoration of the Professional Hitler Service (german: Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums, shortened to ''Berufsbeamtengesetz''), also known as Civil Service Law, Civil Service Restoration Act, and Law to Re-establish the Civil Service, was a law passed by the Nazi regime of Germany on 7 April 1933, two months after Adolf Hitler had attained power and two weeks after the promulgation of the Enabling Act. It was one of the first anti-Semitic and racist laws to be passed in Germany. Articles of the law Article 1 of the Law claimed that in order to re-establish a "national" and "professional" civil service, members of certain groups of tenured civil servants were to be dismissed. Civil servants who were not of Aryan descent were to retire. Non-Aryans were defined as someone descended from non-Aryans, especially those descended from Jewish parents, or grandparents. Members of the Communist Party, or any related or associated organisation were to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Blood Certificate
A German Blood Certificate (German: ''Deutschblütigkeitserklärung'') was a document provided by Nazi leader Adolf Hitler to ''Mischlinge'' (those with partial Jewish heritage), declaring them ''deutschblütig'' (of German blood). This practice was begun sometime after the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, and allowed exemption from most of Germany's racial laws. Mischling is a term used during the Third Reich era in Germany to denote persons deemed to have partial Jewish ancestry. This word literally means "mixling", a derogatory loanword describing one who is "mixed". In order to join the Nazi party and get a certificate, the candidate had to prove through baptismal records that all direct ancestors born since 1750 were not Jewish, or they could apply for a German Blood Certificate. These certificates were 300 mm (11¾ in) by 210 mm (8¼ in), with a signature on the front and the red seal of the Office of Racial Research of the Nazi Party. The back listed the ancestry of the individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahnenpass
The ''Ahnenpaß'' (literally, "ancestor pass") documented the Aryan lineage of people "of German blood" in Nazi Germany. It was one of the forms of the Aryan certificate (''Ariernachweis'') and issued by the "Reich Association of Marriage Registrars in Germany" (''Reichsverband der Standesbeamten in Deutschland e. V.''). The term Aryan in this context was used in a sense widely accepted in the "race science" of the time, which considered that there was a Caucasian race which was sub-divided into Semitic, Hamitic, and Aryan (Japhetic) subraces, the latter corresponding to the Indo-European language family. The Nazi ideology limited the category Aryan to certain subgroups, while excluding Slavs as non-Aryan. The actual primary objective was to create extensive profiling based on racial data. The investigation for lineage was not obligatory, as it was a major undertaking to research the original documents for birth and marriage. Many Nazi followers had already begun to research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahnenpass 003 Anonym
The ''Ahnenpaß'' (literally, "ancestor pass") documented the Aryan lineage of people "of German blood" in Nazi Germany. It was one of the forms of the Aryan certificate (''Ariernachweis'') and issued by the "Reich Association of Marriage Registrars in Germany" (''Reichsverband der Standesbeamten in Deutschland e. V.''). The term Aryan in this context was used in a sense widely accepted in the "race science" of the time, which considered that there was a Caucasian race which was sub-divided into Semitic, Hamitic, and Aryan (Japhetic) subraces, the latter corresponding to the Indo-European language family. The Nazi ideology limited the category Aryan to certain subgroups, while excluding Slavs as non-Aryan. The actual primary objective was to create extensive profiling based on racial data. The investigation for lineage was not obligatory, as it was a major undertaking to research the original documents for birth and marriage. Many Nazi followers had already begun to research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogical Table For Evidence Of Aryan Ancestry
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography. The record of genealogical work may be presented as a "genealogy", a "family history", or a "family tree". In the narrow sense, a "genealogy" or a "family tree" traces the descendants of one person, whereas a "family history" traces the ancestors of one person, but the terms are often used interchangeably. A family history may include additional biographical information, family traditions, and the like. The pursuit of family history and origins tends to be shaped by several motives, including the desire t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryan Mark Rigg
Bryan Mark Rigg (born March 16, 1971) is an American author and speaker. Biography Born and reared as a Baptist, Rigg studied at Phillips Exeter Academy, graduating in 1991 continued on to Yale University, and received his B.A. in 1996. He received a grant from the Henry Fellowship, to continue his studies in Cambridge University, where Rigg earned his doctorate in 2002. In the summer of 1994 he went to Germany, and met Peter Millies, an elderly man who helped Rigg understand the German in a movie they were watching, Europa Europa, about Shlomo Perl, a full Jew who "hid in plain sight" in the Nazi army, posing as a Volksdeutsche orphan named Josef Peters. Millies later told Rigg that he himself was a part-Jew, and introduced him to the subject which was to become his main research topic for many years. Rigg discovered a large number of "Mischlinge" (part-Jews) who were members of the National Socialist German Workers Party (or "Nazi" Party) and/or served in the German Armed Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Policy Of Nazi Germany
The racial policy of Nazi Germany was a set of policies and laws implemented in Nazi Germany under the dictatorship of Adolf Hitler, based on a specific racist doctrine asserting the superiority of the Aryan race, which claimed scientific legitimacy. This was combined with a eugenics programme that aimed for racial hygiene by compulsory sterilization and extermination of those who they saw as ''Untermenschen'' ("sub-humans"), which culminated in the Holocaust. Nazi policies labeled centuries-long residents in German territory who were not ethnic Germans such as Jews (understood in Nazi racial theory as a "Semitic" people of Levantine origins), Roma (also known as Gypsies, an "Indo-Aryan" people of Indian subcontinent origins), along with the vast majority of Slavs (mainly ethnic Poles, Serbs, Russians etc.), and most non-Europeans as inferior non-Aryan subhumans (i.e. non-Nordics, under the Nazi appropriation of the term " Aryan") in a racial hierarchy that placed the ''Herr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |