|
Arequipa-Antofalla
Arequipa-Antofalla is a basement unit underlying the central Andes in northwestern Argentina, western Bolivia, northern Chile and southern Peru. Geologically, it corresponds to a craton, terrane or block of continental crust. Arequipa-Antofalla collided and amalgamated with the Amazonian craton about 1000 Ma ago during the Sunsás orogeny. As a terrane Arequipa-Antofalla was ribbon-shaped during the Paleozoic, a time when it was bounded by the west by the Iapetus Ocean The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleoco ... and by the east by the Puncoviscana Ocean. References Cratons Geology of Argentina Geology of Bolivia Geology of Chile Geology of Peru Terranes Precambrian South America Geology of the Andes {{regional-geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puncoviscana Formation
Puncoviscana Formation ( es, Formación Puncoviscana) is a formation of sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks Late Ediacaran and Lower Cambrian age, estimated at between 700 and 535 Ma, that crop out in the Argentine Northwest. Most of the formation lies in Jujuy, Salta and Tucumán Province albeit some authors extend the formation further south to the Sierras Pampeanas near Córdoba. There are various tectonic interpretations on the origin and type of sedimentary basin that accumulated Puncoviscana Formations sediments. An early interpretation was that the sediments originated from a passive marginal basin of the ancient continent Gondwana. Others suggested an intra-cratonic rift or aulacogen basin between Río de la Plata-Pampia Craton and Arequipa Massif. Yet other hypotheses revolve around the idea that the Puncoviscana Formation is related to a terrane called Pampia that accreted to Gondwana causing the closure of a sea in the way. Stratigraphy, lithology and fossils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
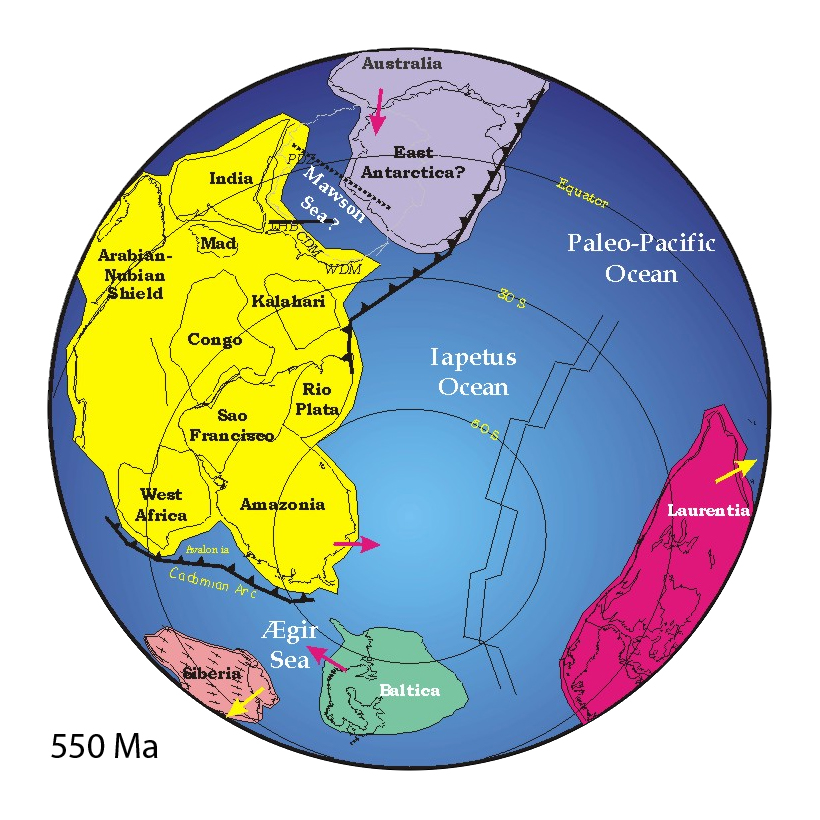
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia. The ocean disappeared with the Acadian, Caledonian and Taconic orogenies, when these three continents joined to form one big landmass called Euramerica. The "southern" Iapetus Ocean has been proposed to have closed with the Famatinian and Taconic orogenies, meaning a collision between Western Gondwana and Laurentia. Because the Iapetus Ocean was positioned between continental masses that would at a much later time roughly form the opposite shores of the Atlantic Ocean, it can be seen as a sort of precursor of the Atlantic, and the process by which it opened shares many similarities with that of the Atlantic's initial opening in the Jurassic. The Iapetus Ocean was therefore named for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terranes
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement (geology)
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The basement rocks lie below a sedimentation, sedimentary platform (geology), platform or cover, or more generally any rock below sedimentary rocks or sedimentary basins that are metamorphic rock, metamorphic or Igneous rock, igneous in origin. In the same way, the sediments or sedimentary rocks on top of the basement can be called a "cover" or "sedimentary cover". Crustal rocks are modified several times before they become basement, and these transitions alter their composition. Continental crust Basement rock is the thick foundation of ancient, and oldest, metamorphic and igneous rock that forms the Crust (geology), crust of continents, often in the form of granite. Basement rock is contrasted to overlying sedimentary rocks which are laid down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSA Bulletin
The ''Geological Society of America Bulletin'' (until 1960 called ''The Bulletin of the Geological Society of America'' and also commonly referred to as ''GSA Bulletin'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that has been published by the Geological Society of America since 1890. Its first editor was William John McGee.Eckel, Edwin, 1982, GSA Memoir 155, The Geological Society of America — Life History of a Learned Society, p. 79., . According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor of 4.212. See also *List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... References External links * Geological Society of America English-language journals Geology journals Bimonthly journals {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Peru
The geology of Peru includes ancient Proterozoic rocks, Paleozoic and Mesozoic volcanic and sedimentary rocks, and numerous basins and the Andes Mountains formed in the Cenozoic. Geological history, stratigraphy & tectonics The oldest rocks in Peru date to the Precambrian and are more than two billion years old. Along the southern coast, granulite and charnockite shows reworking by an ancient orogeny mountain building event. Situated close to the Peru-Chile Trench, these rocks have anomalously high strontium isotope ratios, which suggest recent calc-alkaline volcanism. In the Eastern Cordillera of Peru, Precambrian magmatism in the Huanuco region produced ultramafic, mafic and felsic rocks, including serpentinite, meta-diorite, meta-gabbro, meta-tonalite and diorite and granite that intruded after the first phase of orogenic tectonic activity. The basement of the Central Andean orogeny includes the rocks of the Arequipa Massif, which reach granulite grade on the sequence of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Chile
The geology of Chile is a characterized by processes linked to subduction such as volcanism, earthquakes and orogeny. The terrane, buildings blocks of Chile's geology accretion (geology), assembled during the Paleozoic, Paleozoic Era. Chile was by then the southwestern margin of the supercontinent Gondwana. In the Jurassic Gondwana began to split and the ongoing period of crustal deformation and mountain building known as the Andean orogeny began. In the Cenozoic, Late Cenozoic Chile definitely separated from Antarctica, the Andes experienced a great rise accomplained by a cooling climate and the onset of glaciations. The subduction interactions shaped four main wikt:morphostructure, morphostructures of Chile: the Andes; the Chilean Central Valley, Intermediate Depression, the Chilean Coast Range, Coast Range, and the Peru–Chile Trench off the coast. Since Chile is on an active continental margin, it has many volcanoes. Almost the entire country is subject to earthquakes arising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Bolivia
The geology of Bolivia comprises a variety of different lithologies as well as tectonic and sedimentary environments. On a synoptic scale, geological units coincide with topographical units. The country is divided into a mountainous western area affected by the subduction processes in the Pacific and an eastern lowlands of stable platforms and shields. The Bolivian Andes is divided into three main ranges; these are from west to east: the Cordillera Occidental that makes up the border to Chile and host several active volcanoes and geothermal areas, Cordillera Central (in some contexts also called Cordillera Oriental) once extensively mined for silver and tin and the relatively low Cordillera Oriental that rather than being a range by its own is the eastern continuation of the Central Cordillera as a fold and thrust belt. Between the Occidental and Central Cordillera the approximately 3,750-meter-high Altiplano high plateau extends. This basin hosts several freshwater lakes, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Argentina
The geology of Argentina includes ancient Precambrian basement rock affected by the Grenville orogeny, sediment filled basins from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic as well as newly uplifted areas in the Andes. Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics The oldest rocks in Argentina date to the Precambrian. Strontium, oxygen and carbon isotope data from carbonate rocks in the Sierra de Pie de Palo are part of an ophiolite unit related to the Grenville orogeny, formed as cover rock in the Appalachian margin of the continent Laurentia around 720 million years ago. These Neoproterozoic age rocks are believed to have formed above much older Archean craton rock. Throughout the late Proterozoic, sections of Argentina were part of a metamorphic mobile belt adjacent to the Brazilian Shield. Regional metamorphism produced scheelite belts and wolframite in parts of San Luis and Cordoba Provinces. To the north, along the Bolivian border in the Altiplano, drilling has revealed Precambrian Hornblend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cratons
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots that extend as much as several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: A continental ''shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of South American Earth Sciences
The ''Journal of South American Earth Sciences'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It covers the earth sciences, primarily on issues that are relevant to South America, Central America, the Caribbean, Mexico, and Antarctica. The journal was established in 1988 and the editor-in-chief is James Kellogg ( University of South Carolina). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2012 impact factor of 1.533. See also *''Ameghiniana'' *''Andean Geology'' *''Brazilian Journal of Geology'' *''Latin American Journal of Sedimentology and Basin Analysis'' *''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina The ''Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina'' is an open access peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Asociación Geológica Argentina. The journal is released under a CC-BY-NC 2.5 license. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |