|
Araneida
Araneida is a subgroup of Tetrapulmonata. It was originally defined by Jörg Wunderlich in 2015 as a subgroup of Araneae, including all true spiders, with Wunderlich also including Uraraneida within Araneae., cited in Araneida was redefined by Wunderlich in 2019 to include all modern spiders (Araneae), as well as Chimerarachnida, but excluding Uraraneida. Chimerarachnida and Araneae both possess spinnerets, which are absent in Uraraneida. Uraraneida and Araneida are grouped together in the clade Serikodiastida.Wunderlich, J. 2019What is a spider?Beiträge zur Araneologie 12: 1–32. See also *Araneidae Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name ... References Spiders Arthropod suborders {{spider-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneidae
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, including many well-known large or brightly colored garden spiders. With 3,108 species in 186 genera worldwide, the Araneidae comprise the third-largest family of spiders (behind the Salticidae and Linyphiidae). Araneid webs are constructed in a stereotypical fashion, where a framework of nonsticky silk is built up before the spider adds a final spiral of silk covered in sticky droplets. Orb webs are also produced by members of other spider families. The long-jawed orb weavers (Tetragnathidae) were formerly included in the Araneidae; they are closely related, being part of the superfamily Araneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
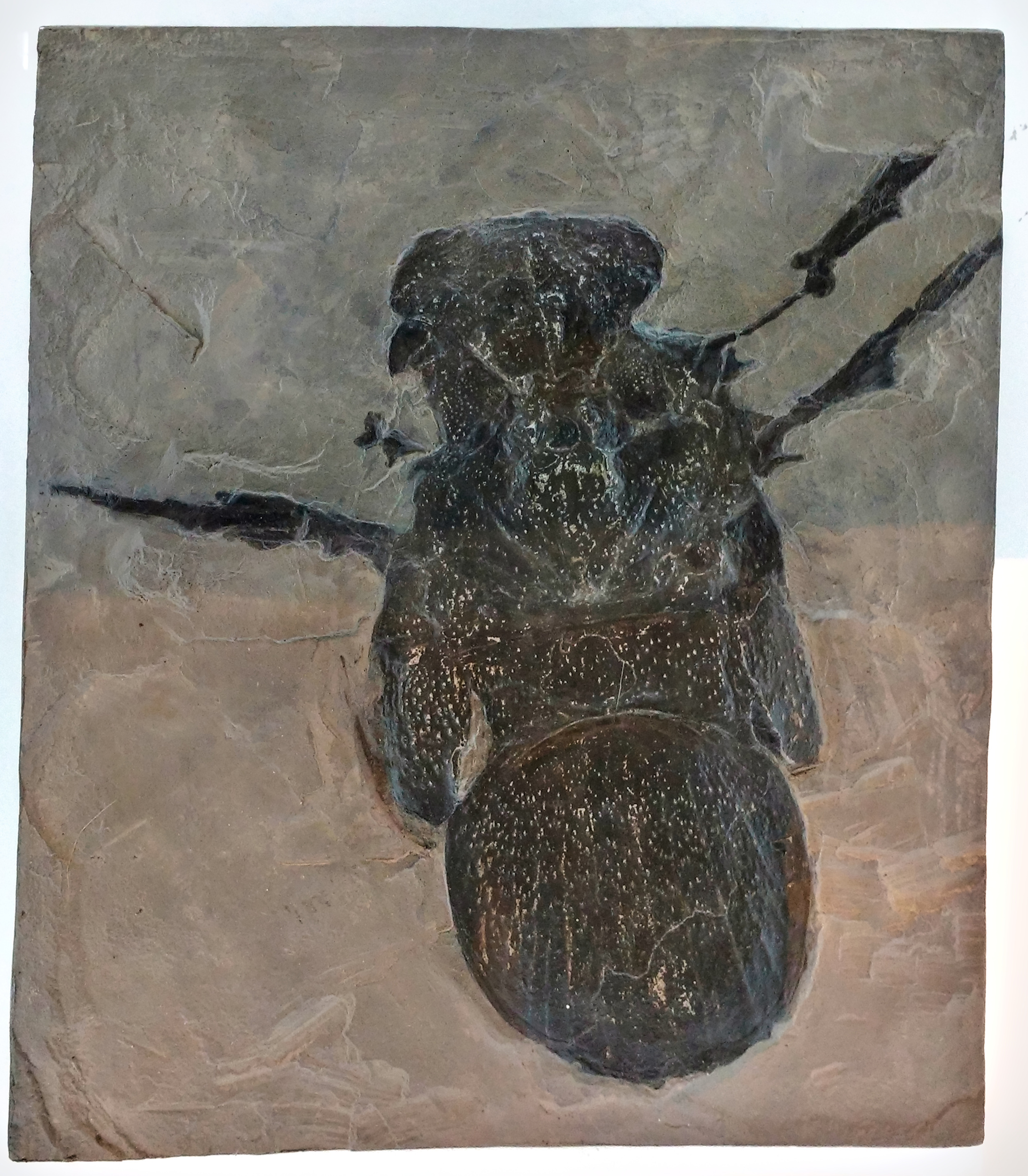
Chimerarachne
''Chimerarachne'' is a genus of extinct arachnids, sometimes considered as spider itself,Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2020A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 20.5 containing a single species ''Chimerarachne yingi''. Fossils of ''Chimerarachne'' were discovered in Burmese amber from Myanmar which dates to the mid-Cretaceous, about 100 million years ago. Its classification is disputed, either belonging to Uraraneida a group otherwise known from the Devonian to Permian, or a separate clade closer to spiders. Since the earliest spider fossils are from the Carboniferous, either answer results in an at least a 170 myr ghost lineage with no fossil record, making it a Lazarus taxon. The size of the animal is quite small, being only in body length, with the tail being about in length. These fossils resemble spiders in having two of their key defining features: spinne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneae
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uraraneida
Uraraneida is an extinct order of arachnids, known from fossils of Middle Devonian, Permian and possibly Cretaceous age. Two genera of fossils have been definitively placed in this order: ''Attercopus'' from the Devonian of United States and ''Permarachne'' from the Permian of Russia. In 2018, a third genus ''Chimerarachne'', from the Cretaceous of Myanmar was proposed to belong to this group, but this placement is disputed. When the first fossils were found, they were identified as spiders, but now constitute the Uraraneida, a separate but closely related group. Characteristics The first fossil now placed in the order was found in Gilboa, New York. In 1987, it was initially tentatively placed in the extinct order Trigonotarbida and named ''Gelasinotarbus''? ''fimbriunguis''. Later, partly on the basis of a supposed spinneret (spider), spinneret, it was identified as a spider and named ''Attercopus fimbriunguis''. Further specimens of this species were found, and when examined in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimerarachnida
''Chimerarachne'' is a genus of extinct arachnids, sometimes considered as spider itself,Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2020A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 20.5 containing a single species ''Chimerarachne yingi''. Fossils of ''Chimerarachne'' were discovered in Burmese amber from Myanmar which dates to the mid-Cretaceous, about 100 million years ago. Its classification is disputed, either belonging to Uraraneida a group otherwise known from the Devonian to Permian, or a separate clade closer to spiders. Since the earliest spider fossils are from the Carboniferous, either answer results in an at least a 170 myr ghost lineage with no fossil record, making it a Lazarus taxon. The size of the animal is quite small, being only in body length, with the tail being about in length. These fossils resemble spiders in having two of their key defining features: spinnerets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jörg Wunderlich
Jörg Wunderlich (born 19 December 1939) is a German arachnologist and palaeontologist. He is best known for his study of spiders in amber, describing over 1000 species, 300 genera, 50 tribes/subfamilies and 18 families in over 180 publications. Unlike most other arachnologists Jörg has never held any academic position and has worked as a private individual with no financial support for travel or equipment. Personal life Jörg Wunderlich grew up in the east of Berlin and moved to the western part of the city with his family in 1951. The limited possibilities of schooling in the post-war period and the change to a school system with very different curricula meant that Wunderlich did not finish school until he was 20 years old. He began studying mathematics at the Free University of Berlin to become a teacher, but soon switched to biology, geography, political science and philosophy. His state examination at the university was a study of dwarf spiders at the Peacock Island in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneae Families
Spider taxonomy is that part of taxonomy that is concerned with the science of naming, defining and classifying all spiders, members of the Araneae order of the arthropod class Arachnida with more than 48,500 described species. However, there are likely many species that have escaped the human eye to this day, and many specimens stored in collections waiting to be described and classified. It is estimated that only one third to one half of the total number of existing species have been described. Arachnologists currently divide spiders into two suborders with about 129 families. Due to constant research, with new species being discovered every month and others being recognized as synonyms, the number of species in the families is bound to change and only reflects the present state of knowledge. Nevertheless, the species numbers given here are useful as a guideline – see the table of families at the end of the article. History Spider taxonomy can be traced to the work of Swed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinnerets
A spinneret is a silk-spinning organ of a spider or the larva of an insect. Some adult insects also have spinnerets, such as those borne on the forelegs of Embioptera. Spinnerets are usually on the underside of a spider's opisthosoma, and are typically segmented. While most spiders have six spinnerets, some have two, four, or eight. They can move both independently and in concert. Most spinnerets are not simple structures with a single orifice producing a single thread, but complex structures of many microscopic spigots, each producing one filament. This produces the necessary orientation of the protein molecules, without which the silk would be weak and useless. Spigots can be singular or found in groups, which also permits spiders to combine multiple filaments in different ways to produce many kinds of silk for various purposes. Spinneret morphology can help arachnologists identify the taxon of a specimen and the specific morphology of a spigot can determine its use as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryuthela Tanikawai
''Ryuthela tanikawai'' is a species of spider in the family Liphistiidae The spider family Liphistiidae, recognized by Tamerlan Thorell in 1869, comprises 8 genera and about 100 species of medium-sized spiders from Southeast Asia, China, and Japan. They are among the most basal living spiders, belonging to the subord .... See also * List of Liphistiidae species#Ryuthela References External links Ryuthela tanikawai ITIS Report. Ryuthela tanikawai ARCTOS Database. Ryuthela tanikawai GWannon Species Database. Liphistiidae Spiders of Asia Spiders described in 1997 {{Spider-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesothelae
The Mesothelae are a suborder of spiders (order Araneae) that includes a single extant family, Liphistiidae, and a number of extinct families. This suborder is thought to form the sister group to all other living spiders, and to retain ancestral characters, such as a segmented abdomen with spinnerets in the middle and two pairs of book lungs. Members of Liphistiidae are medium to large spiders with eight eyes grouped on a tubercle. They are found only in China, Japan, and southeast Asia. The oldest known Mesothelae spiders are known from the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The Heptathelidae were once considered their own family; today they are considered a subfamily of the Liphistiidae. Description Members of Mesothelae have paraxial chelicerae, two pairs of coxal glands on the legs, eight eyes grouped on a nodule, two pairs of book lungs, and no endites on the base of the pedipalp. Most have at least seven or eight spinnerets near the middle of the abdomen. Lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |