|
Arambourgisuchus
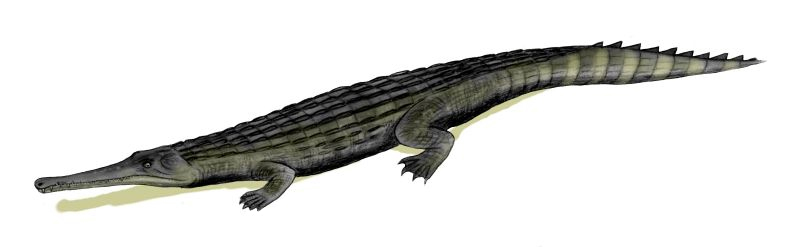
''Arambourgisuchus'' ("Prof. Camille Arambourg's crocodile") is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from the late Palaeocene of Morocco, found in the region of Sidi Chenane in 2000, following collaboration by French and Moroccan institutions, and described in 2005 by a team led by palaeontologist Stéphane Jouve. ''Arambourgisuchus'' was a large animal with an elongated skull 1 meter in length. History and naming The fossils of ''Arambourgisuchus'' were unearthed in the Spring of 2000 thanks to the collaboration of French (French National Centre for Scientific Research, National Museum of Natural History, France) and Moroccon (Office Chérifien des Phosphates, Ministére de l’Energie et des Mines, Morocco) researchers in the phosphatic deposits of the Ouled Abdoun Basin, Morocco. The deposits of the basin range from the latest Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the middle Eocene (Lutetian), with the deposits yielding ''Arambourgisuchus'' dating to the Thanetian age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arambourgisuchus
''Arambourgisuchus'' ("Prof. Camille Arambourg's crocodile") is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from the late Palaeocene of Morocco, found in the region of Sidi Chenane in 2000, following collaboration by French and Moroccan institutions, and described in 2005 by a team led by palaeontologist Stéphane Jouve. ''Arambourgisuchus'' was a large animal with an elongated skull 1 meter in length. History and naming The fossils of ''Arambourgisuchus'' were unearthed in the Spring of 2000 thanks to the collaboration of French (French National Centre for Scientific Research, National Museum of Natural History, France) and Moroccon (Office Chérifien des Phosphates, Ministére de l’Energie et des Mines, Morocco) researchers in the phosphatic deposits of the Ouled Abdoun Basin, Morocco. The deposits of the basin range from the latest Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the middle Eocene (Lutetian), with the deposits yielding ''Arambourgisuchus'' dating to the Thanetian age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arambourgisuchus Khouribgaensis
''Arambourgisuchus'' ("Prof. Camille Arambourg's crocodile") is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from the late Palaeocene of Morocco, found in the region of Sidi Chenane in 2000, following collaboration by French and Moroccan institutions, and described in 2005 by a team led by palaeontologist Stéphane Jouve. ''Arambourgisuchus'' was a large animal with an elongated skull 1 meter in length. History and naming The fossils of ''Arambourgisuchus'' were unearthed in the Spring of 2000 thanks to the collaboration of French (French National Centre for Scientific Research, National Museum of Natural History, France) and Moroccon (Office Chérifien des Phosphates, Ministére de l’Energie et des Mines, Morocco) researchers in the phosphatic deposits of the Ouled Abdoun Basin, Morocco. The deposits of the basin range from the latest Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the middle Eocene (Lutetian), with the deposits yielding ''Arambourgisuchus'' dating to the Thanetian age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosauridae
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouled Abdoun Basin
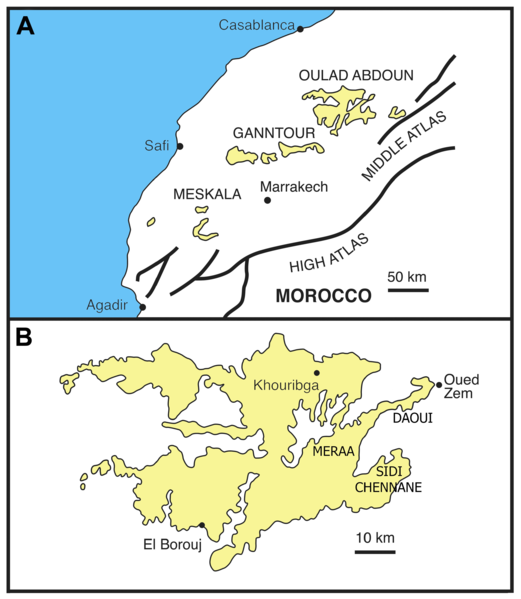
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years. Geography The Oulad Abdoun is located west of the Atlas Mountains, near the city of Khouribga. The Oulad Abdoun phosphate deposits encompass some , an area of . The Oulad Abdoun is the largest and northernmost of Morocco's major phosphate basins, which from northeast to southwest, include the Ganntour, Meskala, and Oued Eddahab (Laayoune-Baa) basins. Paleobiota The Oulad Abdoun Basin stretches from late Cretaceous to the Eocene, and contains abundant marine vertebrate fossils, including sharks, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Arambourg
Camille Arambourg ( February 3, 1885– November 19, 1969) was a French vertebrate paleontologist. He conducted extensive field work in North Africa. In the 1950s he argued against the prevailing model of Neanderthals as brutish and simian. During World War I he was in Military service. After that he was a professor of Geology at the Institut Agricole d'Alger, and after that a professor of Paleontology at Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris, where he succeeded his teacher Marcellin Boule. The pterosaur ''Arambourgiania'' is named after him. He was President of the PanAfrican Archaeological Association from 1959 to 1963. Publications * (1942) "L’ Elephas recki ''Palaeoloxodon recki'' is an extinct species of elephant native to Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene. At up to 14 feet (4.27 metres) in shoulder height, it was one of the largest elephant species to have ever lived. It is believed that ... Dietrich. Exposition systématique et ses affinités". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khouribga
Khouribga ( ber, ⵅⵯⵔⵉⴱⴳⴰ, xʷribga; ar, خريبڭة, ḵurībga, ) is the capital of Khouribga Province in the Béni Mellal-Khénifra Regions of Morocco, region, Morocco. With a population of 196,196 (2014 census), Khouribga owes its growth to the phosphate deposits nearby. Geography Located at 120 km from Casablanca, 154 km from the capital, Rabat, more than 200 km from the city of Marrakesh, and about 99 km from the city of Beni Mellal and 60 km from the city of Settat. Khouribga is located 820 meters above sea level on the Ouardigha plateau. The city was founded in 1923 by the authorities of the French protectorate in Morocco, French protectorate when they discovered phosphate in the region, for which Morocco is considered to be the biggest exporter in the world. There are several mines in the province, most notably the mine of Sidi Shennan near the town of Oued Zem, which lies 30 km from the village of Boulanouar (5 km) and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbits
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. For most situations, orbital motion is adequately approximated by Newtonian mechanics, which explains gravity as a force obeying an inverse-square law. However, Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of spacetime, with orbits following geodesics, provides a more accurate calculation and understanding of the exact mechanics of orbital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratemporal Fenestrae
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the frontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postorbital Bone
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some vertebrates, the postorbital is fused with the postfrontal to create a postorbitofrontal. Birds have a separate postorbital as an embryo, but the bone fuses with the frontal Front may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film * ''The Front'', 1976 film Music * The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and e ... before it hatches. References * Roemer, A. S. 1956. ''Osteology of the Reptiles''. University of Chicago Press. 772 pp. Skull {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanetian
The Thanetian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS Geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age or uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Paleocene epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. It spans the time between . The Thanetian is preceded by the Selandian Age and followed by the Ypresian Age (part of the Eocene). The Thanetian is sometimes referred to as the Late Paleocene. Stratigraphic definition The Thanetian was established by Switzerland, Swiss geologist Eugène Renevier in 1873. The Thanetian is named after the Thanet Formation, the oldest Cenozoic deposit of the London Basin, which was first identified in the area of Kent (southern England) known as the Isle of Thanet. The base of the Thanetian Stage is laid at the base of magnetic chronozone C26n. The references profile (Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point) is in the Zumaia section (43° 18'N, 2° 16'W) at the beach of Itzurun, Pais Vasco, northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |