|
Aralazhdarcho
''Aralazhdarcho'' is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the Santonian to the early Campanian stages of the Late Cretaceous period of Bostobe Svita in Kazakhstan. The type and only known species is ''Aralazhdarcho bostobensis''. Etymology ''Aralazhdarcho'' was named in 2007 by Alexander Averianov. In 2004, the holotype had already been described. (''Paleontol. J.'' 38 (4), 426–436) The genus name, ''Aralazhdarcho'', is derived from the Aral Sea and the related genus ''Azhdarcho'', while the specific name, ''bostobensis'', refers to the Bostobe Formation. Description ''Aralazhdarcho'' is based on holotype ZIN PH, no. 9/43, consisting of the anterior end of a neck vertebra, probably the fifth or sixth. Several paratypes have also been referred: a jugal, a toothless lower jaw fragment, centra from vertebrae, the distal end of a scapula, the proximal end of a second phalanx of the left wing finger and the proximal end of a left femur, of which, however, the head has broken off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azhdarchids
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cretaceous as well (late Berriasian age, about 140 million years ago). Azhdarchids included some of the largest known flying animals of all time, but smaller cat-size members have also been found. Originally considered a sub-family of Pteranodontidae, Nesov (1984) named the Azhdarchinae to include the pterosaurs ''Azhdarcho'', '' Quetzalcoatlus'', and ''Titanopteryx'' (now known as ''Arambourgiania''). They were among the last known surviving members of the pterosaurs, and were a rather successful group with a worldwide distribution. By the time of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction, most pterosaur families except for the Azhdarchidae disappear from the fossil record, but recent studies indicate a wealth of pterosaurian fauna, including pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
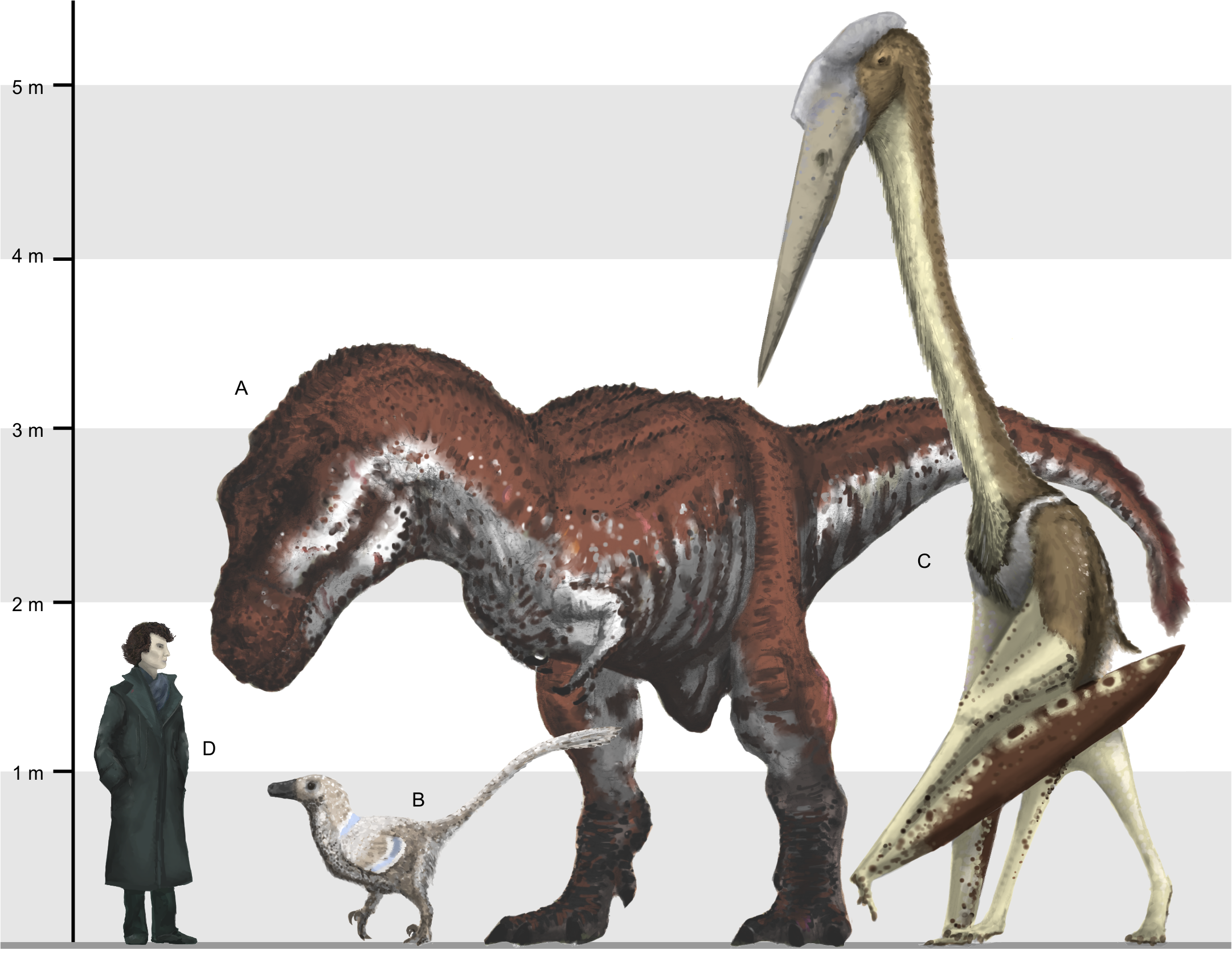
Azhdarchidae
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cretaceous as well (late Berriasian age, about 140 million years ago). Azhdarchids included some of the largest known flying animals of all time, but smaller cat-size members have also been found. Originally considered a sub-family of Pteranodontidae, Nesov (1984) named the Azhdarchinae to include the pterosaurs ''Azhdarcho'', ''Quetzalcoatlus'', and ''Titanopteryx'' (now known as ''Arambourgiania''). They were among the last known surviving members of the pterosaurs, and were a rather successful group with a worldwide distribution. By the time of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction, most pterosaur families except for the Azhdarchidae disappear from the fossil record, but recent studies indicate a wealth of pterosaurian fauna, including pteran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatodraco
''Phosphatodraco'' is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous of what is now Morocco. In 2000, a pterosaur specimen consisting of five cervical (neck) vertebrae was discovered in the Ouled Abdoun Phosphatic Basin. The specimen was made the holotype of the new genus and species ''Phosphatodraco mauritanicus'' in 2003; the genus name means " dragon from the phosphates", and the specific name refers to the region of Mauretania. ''Phosphatodraco'' was the first Late Cretaceous pterosaur known from North Africa, and the second pterosaur genus described from Morocco. It is one of the only known azhdarchids preserving a relatively complete neck, and was one of the last known pterosaurs. Additional cervical vertebrae have since been assigned to the genus, and it has been suggested that fossils of the pterosaur '' Tethydraco'' represent wing elements of ''Phosphatodraco''. Due to the fragmentary nature of the holotype cervical vertebrae, there has been co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Pterosaur Research
This timeline of pterosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, and taxonomic revisions of pterosaurs, the famed flying reptiles of the Mesozoic era. Although pterosaurs went extinct millions of years before humans evolved, humans have coexisted with pterosaur fossils for millennia. Before the development of paleontology as a formal science, these remains would have been interpreted through a mythological lens. Myths about thunderbirds told by the Native Americans of the modern Western United States may have been influenced by observations of ''Pteranodon'' fossils. These thunderbirds were said to have warred with water monsters, which agrees well with the co-occurrence of ''Pteranodon'' and the ancient marine reptiles of the seaway over which it flew. The formal study of pterosaurs began in the late 18th century when naturalist Cosimo Alessandro Collini of Mannheim, Germany published a description of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bostobe Formation
The Bostobe Formation ( kk, Boztóbe svıtasy) is a geological formation in Qaraghandy & Qyzylorda, Kazakhastan whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous (Santonian to early Campanian stages, approximately 85 Ma). The sandstones and claystones of the formation were deposited in estuarine, fluvial-lacustrine and fluvial-deltaic environments. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al. , 2004, pp.593-600 The formation is about thick and consists primarily of clay with interbeds of sand, representing an estuarine environment.Kordikova et al., 2001 Fossil content '' Khunnuchelys lophorhothon'', a trionychid turtle recovered from the formation, was initially thought to belong to a hadrosaurid dinosaur and classified as cf. ''Lophorhothon sp''.Danilov et al., 2014 ;Mammals * '' Beleutinus orlovi'' * '' Zhalmouzia bazhanovi''Averianov et al., 2014b * '' Parazhelestes sp.''Averianov et al., 2014a ;Ankylosaurs * Ankylosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bostobe Svita
The Bostobe Formation ( kk, Boztóbe svıtasy) is a geological formation in Qaraghandy & Qyzylorda, Kazakhastan whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous (Santonian to early Campanian stages, approximately 85 Ma). The sandstones and claystones of the formation were deposited in estuarine, fluvial-lacustrine and fluvial-deltaic environments. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al. , 2004, pp.593-600 The formation is about thick and consists primarily of clay with interbeds of sand, representing an estuarine environment.Kordikova et al., 2001 Fossil content '' Khunnuchelys lophorhothon'', a trionychid turtle recovered from the formation, was initially thought to belong to a hadrosaurid dinosaur and classified as cf. ''Lophorhothon sp''.Danilov et al., 2014 ;Mammals * '' Beleutinus orlovi'' * '' Zhalmouzia bazhanovi''Averianov et al., 2014b * '' Parazhelestes sp.''Averianov et al., 2014a ;Ankylosaurs * Ankylosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatzegopteryx
''Hatzegopteryx'' ("Hațeg basin wing") is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur found in the late Maastrichtian deposits of the Densuş Ciula Formation, an outcropping in Transylvania, Romania. It is known only from the type species, ''Hatzegopteryx thambema'', named by Buffetaut ''et al.'' in 2002 based on parts of the skull and humerus. Additional specimens, including a neck vertebra, were later placed in the genus, representing a range of sizes. The largest of these remains indicate it was among the biggest pterosaurs, with an estimated wingspan of . Unusually among giant azhdarchids, ''Hatzegopteryx'' had a very wide skull bearing large muscular attachments; bones with a spongy internal texture instead of hollow; and a short, robust, and heavily muscled neck measuring long, which was about half the length of other azhdarchids with comparable wingspans, and was capable of withstanding strong bending forces. ''Hatzegopteryx'' inhabited Hațeg Island, an island situated in the Cret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurazhdarcho
''Eurazhdarcho'' is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period (Maastrichtian stage) of what is now the Transylvanian Basin of Romania. Its fossil remains dated back 69 million years ago. Discovery and naming In 2009, Mátyás Vremir at Lancrăm near Sebeş-Glod in Transylvania at the SbG-B site uncovered the remains of a pterosaur. He donated these to the ''Erdélyi Múzeum'', of the '' Societății Muzeului Ardelean'' (Transylvanian Museum Society). Subsequent excavations by Vremir discovered additional bones of the same individual animal and were added by him to the collection of the Babeș-Bolyai University. In 2013, Vremir, Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner, Darren Naish, and Gareth Dyke named and described the type species ''Eurazhdarcho langendorfensis''. The generic name combines the name of Europe with that of the related form ''Azhdarcho''. The specific name refers to Langendorf, the name of Lancrǎm in the language of the German ethnic minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montanazhdarcho
''Montanazhdarcho'' is a genus of azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage) of what is now the state of Montana, United States. ''Montanazhdarcho'' is known from only one species, ''M. minor''. Discovery The holotype specimen, MOR 691 (Museum of the Rockies), was found by Robert W. Harmon in Glacier County, in the territory of the Blackfoot, in sandstone of the Upper Two Medicine Formation, a layer about 74 million years old. The genus name ''Montanazhdarcho'' was first given informally in 1993 by Kevin Padian, Armand de Ricqlès, and Jack Horner. It was then named formally in 1995 by the same researchers, and was fully described in 2002. The type species is ''Montanazhdarcho minor''. The generic name refers to the state of Montana and to the related species ''Azhdarcho''. The specific name means "the smaller one" in Latin, a reference to the relatively small size in comparison to closely related forms. Description ''Montanazhdarcho'' was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pterosaurs
This list of pterosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Pterosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomen dubium''), or were not formally published ('' nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered pterosaurian. The list currently includes 263 genera. Scope and terminology There is no official, canonical list of pterosaur genera, but the most thorough attempts can be found at the Pterosauria section of Mikko Haaramo's ''Phylogeny Archive'', the Genus Index at Mike Hanson's ''The Pterosauria'', supplemented by the Pterosaur Species List, and in the fourth supplement of Donald F. Glut's ''Dinosaurs: The Encyclopedia'' series. Authors and year The authors column lists the authors of the formal description responsible for the erection of the genus listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arambourgiania
''Arambourgiania'' is an extinct genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period (Maastrichtian stage) of Jordan, and possibly the United States.Harrell, T. Lynn Jr.; Gibson, Michael A.; Langston, Wann Jr. (2016). "A cervical vertebra of ''Arambourgiania philadelphiae'' (Pterosauria, Azhdarchidae) from the Late Campanian micaceous facies of the Coon Creek Formation in McNairy County, Tennessee, USA" ''Bull. Alabama Mus. Nat. Hist.'' 33:94–103 ''Arambourgiania'' was among the largest members of its family, the Azhdarchidae, and it is also one of the largest flying animals ever known. The incomplete left ulna of the "Sidi Chennane azhdarchid" from Morocco may have also belonged to ''Arambourgiania''. History of discovery In the early 1940s, a railway worker during repairs on the Amman-Damascus railroad near Russeifa found a two foot long fossil bone. In 1943 this was acquired by the director of a nearby phosphate mine, Amin Kawar, who brought it to the attention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |