|
Araki Sadao
Baron was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army before and during World War II. As one of the principal nationalist right-wing political theorists in the Empire of Japan, he was regarded as the leader of the radical faction within the politicized Imperial Japanese Army and served as Minister of War under Prime Minister Inukai. He later served as Minister of Education during the Konoe and Hiranuma administrations. After World War II, he was convicted of war crimes and given a life sentence but was released in 1955. Early life and career Araki was born in Komae, Tokyo; his father was an ex-samurai retainer of the Hitotsubashi branch of the Tokugawa family. Araki graduated from the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in November 1897 and was commissioned as a second lieutenant in June of the following year. Promoted to lieutenant in November 1900 and promoted to captain in June 1904, Araki served as company commander of the 1st Imperial Regiment during the Russo-Japanese W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komae, Tokyo
is a city located in the western portion of Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. It is one of 30 municipalities in the western portion of Tokyo known as the Tama Area. , the city had an estimated population of 83,218, and a population density of 13,000 persons per km². Based on the 2015 Kanto Ranking, Musashino was the fifth most desirable place to live in Central Japan. The total area of the city is . It is the smallest administrative city in Tokyo Meotropolis both in area and population, and the second smallest in terms of area in the nation. Geography Komae is nestled between the Tama River to the southwest, and the much smaller Nogawa River to the north and east which flows near its boundaries with Chōfu city and Setagaya Ward. It is mostly flat. It is a small municipality; its boundaries fit within a circle of 2 km radius centred on the city hall. It is essentially a residential suburb of Tokyo which urbanised rapidly in the 1960s and 1970s, with most of the working popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodoha
The ''Kōdōha'' or was a political faction in the Imperial Japanese Army active in the 1920s and 1930s. The ''Kōdōha'' sought to establish a military government that promoted totalitarian, militaristic and aggressive expansionistic ideals, and was largely supported by junior officers. The radical ''Kōdōha'' rivaled the moderate '' Tōseiha'' (Control Faction) for influence in the army until the February 26 Incident in 1936, when it was ''de facto'' dissolved and many supporters were disciplined or executed. The ''Kōdōha'' was never an organized political party and had no official standing within the Army, but its ideology and supporters continued to influence Japanese militarism into the late 1930s., page 193 Background The Empire of Japan had enjoyed economic growth during World War I but this ended in the early 1920s with the Shōwa financial crisis. Social unrest increased with the growing polarization of society and inequalities, such as trafficking in girls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Guard Of Japan
In Japan, the Imperial Guard is the name for two separate organizations dedicated to the protection of the Emperor of Japan and the Imperial Family, palaces and other imperial properties. The first was the , a quasi-independent elite branch of the Imperial Japanese Army which was dissolved shortly after World War II. The second is the , a civilian law enforcement organization formed as part of the National Police Agency.(警察庁) Imperial Guard of the Imperial Japanese Army The Imperial Guard of the Imperial Japanese Army was formed in 1867. It became the foundation of the Imperial Japanese Army after the Emperor Meiji assumed all the powers of state during the Meiji Restoration. The Imperial Guard, which consisted of 12,000 men organized and trained along French military lines, first saw action in the Satsuma Rebellion. It was organized into the 1st Guards Infantry Brigade which had the 1st and 2nd Regiments. The 3rd and 4th Regiments belonged to the 2nd Guards Infantry B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
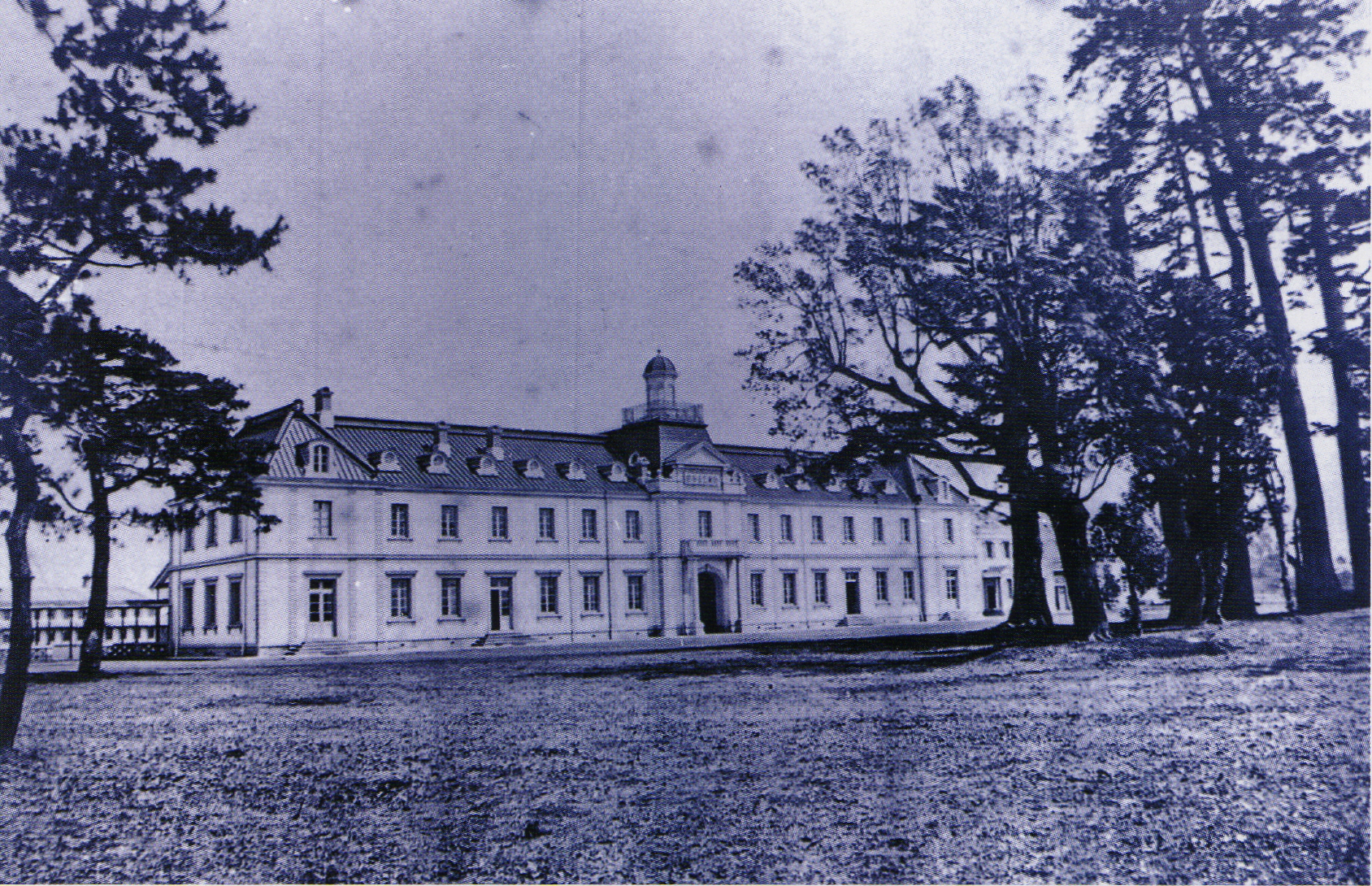
Imperial Japanese Army Academy
The was the principal officer's training school for the Imperial Japanese Army. The programme consisted of a junior course for graduates of local army cadet schools and for those who had completed four years of middle school, and a senior course for officer candidates. History and background Established as the ''Heigakkō'' in 1868 in Kyoto, the officer training school was renamed the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1874 and relocated to Ichigaya, Tokyo. After 1898, the Academy came under the supervision of the Army Education Administration. In 1937 the Academy was divided, with the Senior Course Academy being relocated to Sagamihara in Kanagawa prefecture, and the Junior Course School moved to Asaka, Saitama. The 50th graduation ceremony was held in the new Academy buildings in Sagamihara on 20 December 1937, and was attended by the Shōwa Emperor (Emperor Hirohito) himself. In 1938, a separate school was established for military aviation officers. During World War II, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Family
The is a Japanese dynasty that was formerly a powerful ''daimyō'' family. They nominally descended from Emperor Seiwa (850–880) and were a branch of the Minamoto clan (Seiwa Genji) through the Matsudaira clan. The early history of this clan remains a mystery. Members of the clan ruled Japan as ''shōguns'' during the Edo Period from 1603 to 1867. History Minamoto no Yoshishige (1135–1202), grandson of Minamoto no Yoshiie (1041–1108), was the first to take the name of Nitta. He sided with his cousin Minamoto no Yoritomo against the Taira clan (1180) and accompanied him to Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura. Nitta Yoshisue, 4th son of Yoshishige, settled at Tokugawa (Kozuke province) and took the name of that place. Their provincial history book did not mention Minamoto clan or Nitta clan. The nominal originator of the Matsudaira clan was reportedly Matsudaira Chikauji, who was originally a poor Buddhist monk. He reportedly descended from Nitta Yoshisue in the 8th generation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gosankyō
The were three branches of the Tokugawa clan of Japan. They were descended from the eighth of the fifteen Tokugawa shōguns, Yoshimune (1684–1751). Yoshimune established the ''Gosankyo'' to augment (or perhaps to replace) the ''Gosanke'', the heads of the powerful ''han'' (fiefs) of Owari, Kishū, and Mito. Two of his sons, together with the second son of his successor Ieshige, established the Tayasu, Hitotsubashi, and Shimizu branches of the Tokugawa. Unlike the ''Gosanke'', they did not rule a ''han''. Still, they remained prominent until the end of Tokugawa rule, and some later shōguns were chosen from the Hitotsubashi line. Heads of Gosankyo Tayasu House 田安家 # Munetake (1716–1771, r. 1731–1771) # Haruaki (1753–1774, r. 1771–1774) # Narimasa (1779–1846, r. 1787–1836) # Naritaka (1810–1845, r. 1836–1839) # Yoshiyori (1828–1876, r. 1839–1863) # Takachiyo (1860–1865, r. 1863–1865) # Kamenosuke (1863–1940, r. 1865–1868) # Yoshiyori (2n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They had high prestige and special privileges such as wearing two swords and ''Kiri-sute gomen'' (right to kill anyone of a lower class in certain situations). They cultivated the '' bushido'' codes of martial virtues, indifference to pain, and unflinching loyalty, engaging in many local battles. Though they had predecessors in earlier military and administrative officers, the samurai truly emerged during the Kamakura shogunate, ruling from 1185 to 1333. They became the ruling political class, with significant power but also significant responsibility. During the 13th century, the samurai proved themselves as adept warriors against the invading Mongols. During the peaceful Edo period (1603 to 1868), they became the stewards and chamberlains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Sentence
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for which, in some countries, a person could receive this sentence include murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, drug trafficking, drug possession, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated criminal damage, arson, kidnapping, burglary, and robbery, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or any three felonies in case of three-strikes law. Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death. Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentence, there may also e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
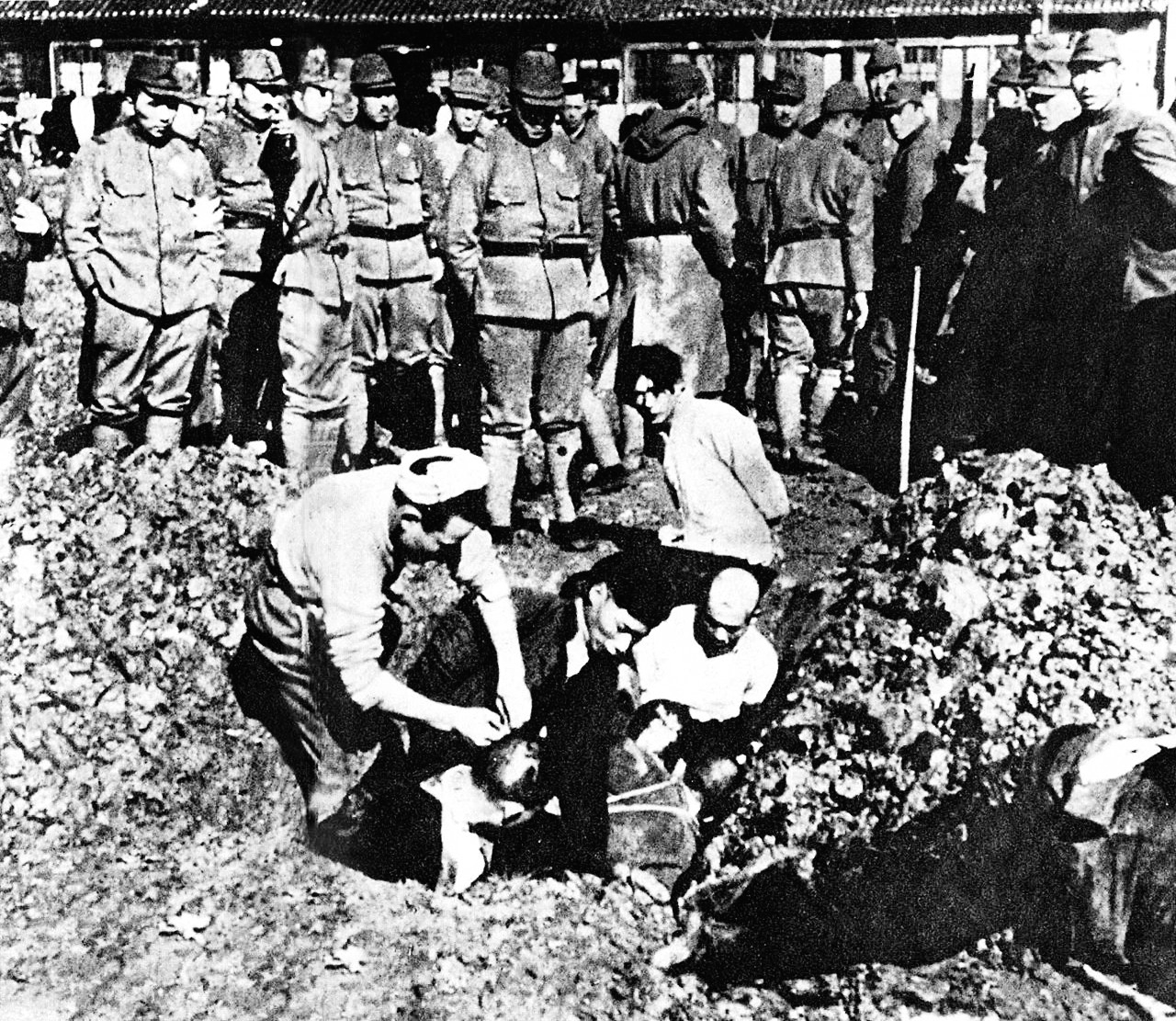
Japanese War Crimes
The Empire of Japan committed war crimes in many Asian-Pacific countries during the period of Japanese militarism, Japanese imperialism, primarily during the Second Sino-Japanese War, Second Sino-Japanese and Pacific Wars. These incidents have been described as an "Asian Holocaust". Some war crimes were committed by Japanese military personnel during the late 19th century, but most were committed during the first part of the Shōwa (1926–1989), Shōwa era, the name given to the reign of Emperor of Japan, Emperor Hirohito. Under Emperor Hirohito, the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) perpetrated numerous war crimes which resulted in the deaths of millions of people. Estimates of the number of deaths range from three to 30 million through Nanjing Massacre, massacres, Unit 731, human experimentation, Vietnamese famine of 1945, starvation, and Slavery in Japan#World War II, forced labor directly perpetrated or condoned by the Japanese military and go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiranuma Kiichirō
was a prominent right-wing Japanese politician and Prime Minister of Japan in 1939. He was convicted of war crimes committed during World War II and was sentenced to life imprisonment. Early life Hiranuma was born in what is now Tsuyama City, Okayama Prefecture, as the son of a low-ranking samurai from the Tsuyama Domain of Mimasaka Province. He graduated with a degree in English law from Tokyo Imperial University in 1888. After graduation, he obtained a posting in the Ministry of Justice. In 1911, he was the prosecutor for the High Treason Incident, the 1910 socialist-anarchist plot to assassinate Japanese Emperor Meiji. The closed-court trial of 25 men and 1 woman, including 4 Buddhist monks, resulted in the execution of 12, including the feminist author Kanno Suga. Ministry of Justice Hiranuma established a reputation during his time at the Ministry of Justice as a strong opponent of government corruption and successfully handled a number of high-profile cases. He ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumimaro Konoe
Prince was a Japanese politician and prime minister. During his tenure, he presided over the Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the breakdown in relations with the United States, which ultimately culminated in Japan's entry into World War II. He also played a central role in transforming his country into a totalitarian state by passing the National Mobilization Law and founding the Imperial Rule Assistance Association. Despite Konoe's attempts to resolve tensions with the United States, the rigid timetable imposed on negotiations by the military and his own government's inflexibility regarding a diplomatic resolution set Japan on the path to war. Upon failing to reach a peace agreement, Konoe resigned as Prime Minister on 18 October 1941, prior to the outbreak of hostilities. However, he remained a close advisor to the Emperor until the end of World War II. Following the end of the war, he committed suicide on 16 December 1945. Early life Fumimaro Konoe was born in To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Education, Culture, Sports, Science And Technology (Japan)
The , also known as MEXT or Monka-shō, is one of the eleven Ministries of Japan that composes part of the executive branch of the Government of Japan. Its goal is to improve the development of Japan in relation with the international community. The ministry is responsible for funding research under its jurisdiction, some of which includes: children's health in relation to home environment, delta-sigma modulations utilizing graphs, gender equality in sciences, neutrino detection which contributes to the study of supernovas around the world, and other general research for the future. History The Meiji government created the first Ministry of Education in 1871. In January 2001, the former Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture and the former merged to become the present MEXT. Organization The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology currently is led by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Under that position is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |