|
Arado E.240
The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the '' Luftwaffe'' during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was in 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes. Design and development The Ar 240 came about as the response to a 1938 request for a much more capable second-generation heavy fighter to replace the Messerschmitt Bf 110, which was becoming outdated. Both Arado and Messerschmitt responded. Messerschmitt's response, the Me 210, was a totally new design, but thanks to Messerschmitt's experience with the ''Zerstörer'' ("Destroyer") concept, it would be able to enter service quickly. Arado's design was considerably more ambitious for the smaller firm, a dream project of Arado's chief designer, Walter Blume, since the mid-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Fighter
A heavy fighter is a historic category of fighter aircraft produced in the 1930s and 1940s, designed to carry heavier weapons, and/or operate at longer ranges than light fighter aircraft. To achieve performance, most heavy fighters were twin-engine, and many had multi-place crews; This was in contrast to light fighters, which were typically single-engine and single-crew aircraft. In Germany, they were known as ''Zerstörer'' ("destroyer"). The heavy fighter was a major design class during the pre-World War II period, conceived as long-range escort fighters or heavily-armed bomber destroyers. Most such designs failed in this mission, as they could not maneuver with the more conventional, single-engine fighters, and suffered heavy losses. Most notable among such designs was the Messerschmitt Bf 110, which suffered great losses during the Battle of Britain. An exception was the American Lockheed P-38 Lightning, which proved an effective heavy fighter; even against smaller, lighter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sight (device)
A sight is an aiming device used to assist in visually aligning ranged weapons, surveying instruments or optical illumination equipments with the intended target. Sights can be a simple set or system of physical markers that have to be aligned together with the target (such as iron sights on firearms), or optical devices that allow the user to see an optically enhanced — often magnified — target image aligned in the same focus with an aiming point (e.g. telescopic sights, reflector sights and holographic sights). There are also sights that actively project an illuminated point of aim (a.k.a. "hot spot") onto the target itself so it can be observed by, such as laser sights and infrared illuminators on some night vision devices. Simple sights At its simplest, a sight typically has two components, front and rear aiming pieces that have to be lined up. Sights such as this can be found on many types of devices including weapons, surveying and measuring instruments, and nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
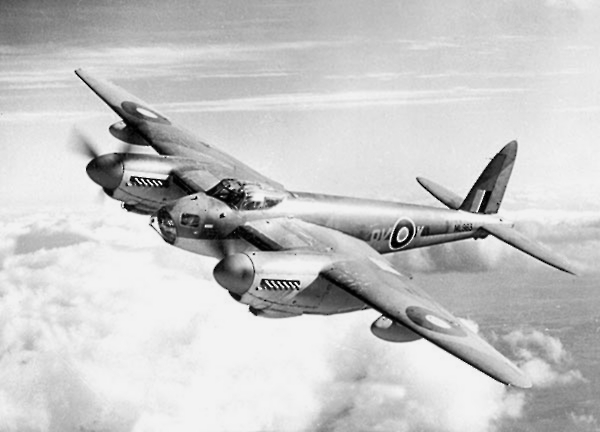
Junkers Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a German World War II ''Luftwaffe'' twin-engined multirole combat aircraft. Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works (JFM) designed the plane in the mid-1930s as a so-called ''Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that would be too fast for fighters of its era to intercept. It suffered from technical problems during its development and early operational periods but became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the war. Like a number of other ''Luftwaffe'' bombers, it served as a bomber, dive bomber, night fighter, torpedo bomber, reconnaissance aircraft, heavy fighter and at the end of the war, as a flying bomb. Despite a protracted development, it became one of the ''Luftwaffe''s most important aircraft. The assembly line ran constantly from 1936 to 1945 and more than 15,000 Ju 88s were built in dozens of variants, more than any other twin-engine German aircraft of the period. Throughout production the basic structure of the aircraft remained unchanged.Angelucci a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
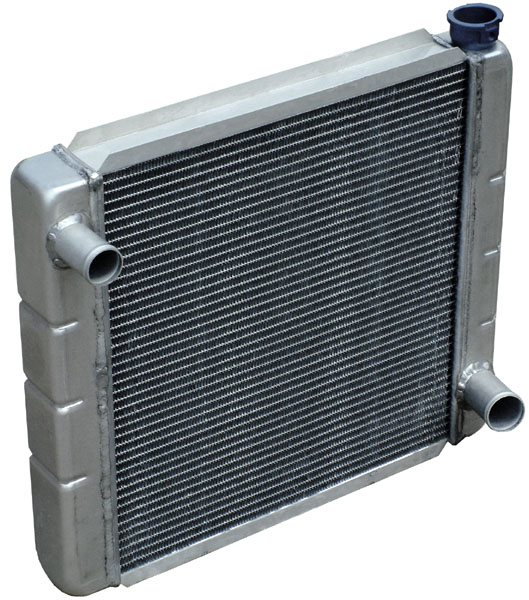
Radiator (engine Cooling)
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine. Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called ''engine coolant'' through the engine block, and cylinder head where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator. Automobiles and motorcycles In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to channels running through the engine and cylinder head, through which a liquid (coolant) is pumped. This liquid may be water (in climates where water is unlik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller (aircraft)
An aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew,Beaumont, R.A.; ''Aeronautical Engineering'', Odhams, 1942, Chapter 13, "Airscrews". converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type. The propeller attaches to the power source's driveshaft either directly or through reduction gearing. Propellers can be made from wood, metal or composite materials. Propellers are most suitable for use at subsonic airspeeds generally below about , although supersonic speeds were achieved in the McDonnell XF-88B experimental propeller-equipped aircraft. Supersonic tip-speeds are used in some aircraft like the Tupolev Tu-95, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ;Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
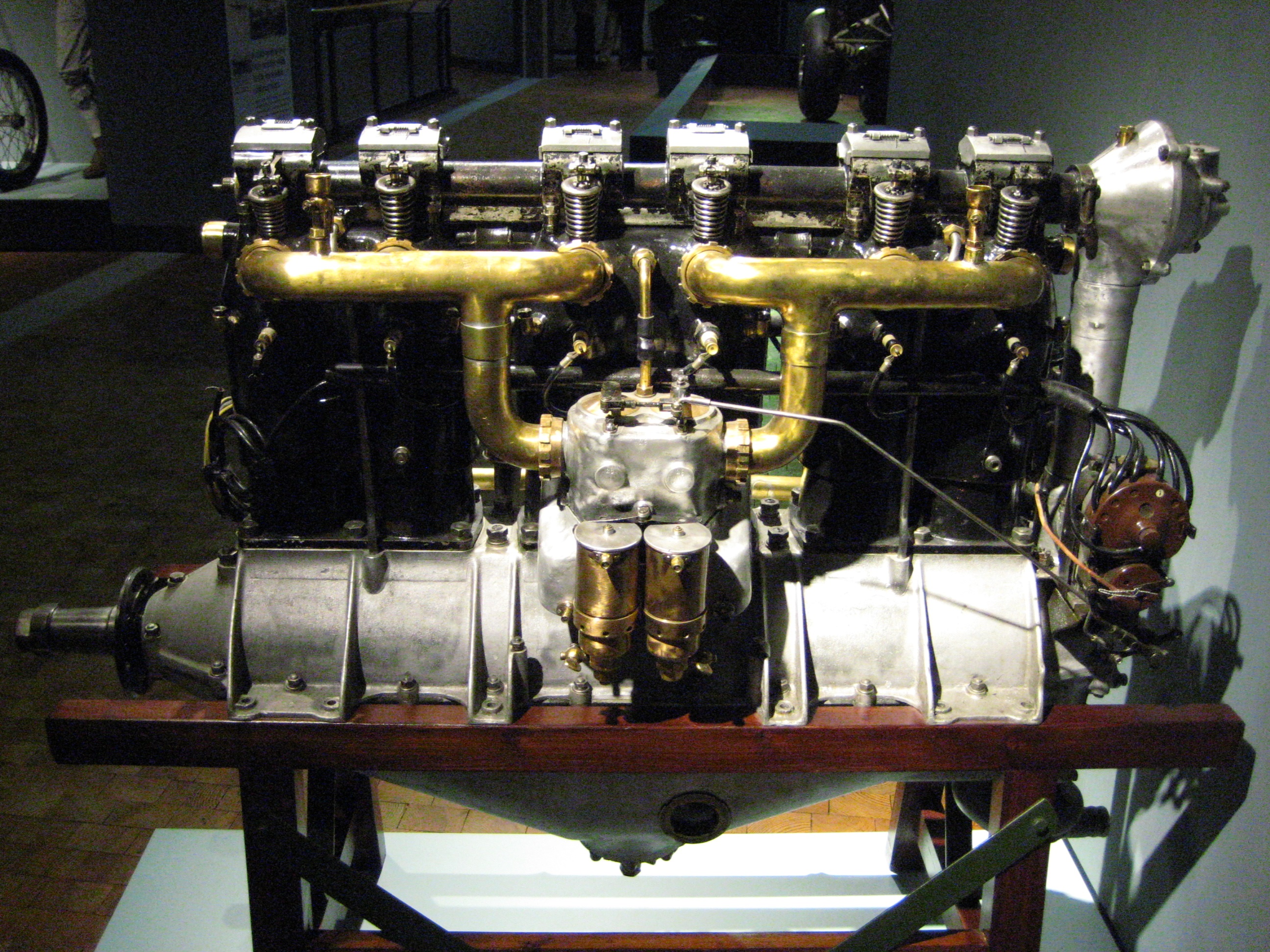
Daimler-Benz DB 601
The Daimler-Benz DB 601 was a German aircraft engine built during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled inverted V12 engine, V12, and powered the Messerschmitt Bf 109, Messerschmitt Bf 110, and many others. Approximately 19,000 601's were produced before it was replaced by the improved Daimler-Benz DB 605 in 1942. The DB 601 was basically an improved Daimler-Benz DB 600, DB 600 with gasoline direct injection, direct fuel injection. Fuel injection required power to be taken off the drive shaft, but in return, improved low-RPM performance significantly and provided aerobatic performance in maneuvers where early versions of carburetor, carburated engines like the British Rolls-Royce Merlin would lose power when the carburetor float bowl ran dry. The 601's fuel injection provided a significant boost in performance which its competitor, the Junkers Jumo 210, did not match for some time. By the time the fuel-injected 211 arrived, the 601 had already cemented its place as the engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ju288-1
JU may refer to: Names and people * Joo (Korean name), surname and given name (including a list of people with the name) * Jū (鞠), Chinese surname * Ru (surname), romanized Ju in Wade–Giles * Ji Ju, a semi-legendary ancestor of the Zhou dynasty * Ju (writer) (born 1958), Burmese writer * Juh (c. 1825–1883), Apache leader Places * Ju (city), a city of the State of Qi during the Warring States Period of China * Ju (state), a vassal state of the Zhou Dynasty * Ju County (莒县), of Rizhao, Shandong, China * Juan de Nova Island, administered by France (FIPS code ''JU'') * Zhou (country subdivision), pronounced ''ju'' in Korean * Canton of Jura (created in 1979), newest of the 26 Swiss cantons Businesses and organizations Universities * University of Jordan, located in Amman, Jordan * Jacksonville University, a university in Jacksonville, Florida, United States * Jadavpur University, a university in Kolkata, India * Jahangirnagar University, a public university in Savar, Bangl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Edge Slats
Slats are aerodynamic surfaces on the leading edge of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft which, when deployed, allow the wing to operate at a higher angle of attack. A higher coefficient of lift is produced as a result of angle of attack and speed, so by deploying slats an aircraft can fly at slower speeds, or take off and land in shorter distances. They are used during takeoff and landing or while performing low speed maneuvers which may take the aircraft close to a stall, they are retracted in normal flight to minimize drag. Slats are one high-lift device used on high speed turbojet aircraft, trailing edge flap systems running along the trailing edge of the wing are common on all aircraft. Types Types include: ;Automatic: The spring-loaded slat lies flush with the wing leading edge, held in place by the force of the air acting on them. As the aircraft slows down, the aerodynamic force is reduced and the springs extend the slats. Sometimes referred to as Handley-Page slat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lift-induced Drag
In aerodynamics, lift-induced drag, induced drag, vortex drag, or sometimes drag due to lift, is an aerodynamic drag force that occurs whenever a moving object redirects the airflow coming at it. This drag force occurs in airplanes due to wings or a lifting body redirecting air to cause lift and also in cars with airfoil wings that redirect air to cause a downforce. It is symbolized as D_\text, and the ''lift-induced drag coefficient'' as C_. For a constant amount of lift, induced drag can be reduced by increasing airspeed. A counter-intuitive effect of this is that, up to the speed-for-minimum-drag, aircraft need less power to fly faster. Induced drag is also reduced when the wingspan is higher, or for wings with wingtip devices. Explanation The total aerodynamic force acting on a body is usually thought of as having two components, lift and drag. By definition, the component of force parallel to the oncoming flow is called drag; and the component perpendicular to the oncoming f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Drag
Parasitic drag, also known as profile drag, is a type of aerodynamic drag that acts on any object when the object is moving through a fluid. Parasitic drag is a combination of form drag and skin friction drag. It affects all objects regardless of whether they are capable of generating lift. Total drag on an aircraft is made up of parasitic drag and lift-induced drag. Parasitic drag comprises all types of drag except lift-induced drag. Form drag Form drag arises because of the shape of the object. The general size and shape of the body are the most important factors in form drag; bodies with a larger presented cross-section will have a higher drag than thinner bodies; sleek ("streamlined") objects have lower form drag. Form drag follows the drag equation, meaning that it increases with the square of the velocity, and thus becomes more important for high-speed aircraft. Form drag depends on the longitudinal section of the body. A prudent choice of body profile is essential for a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.png)
