|
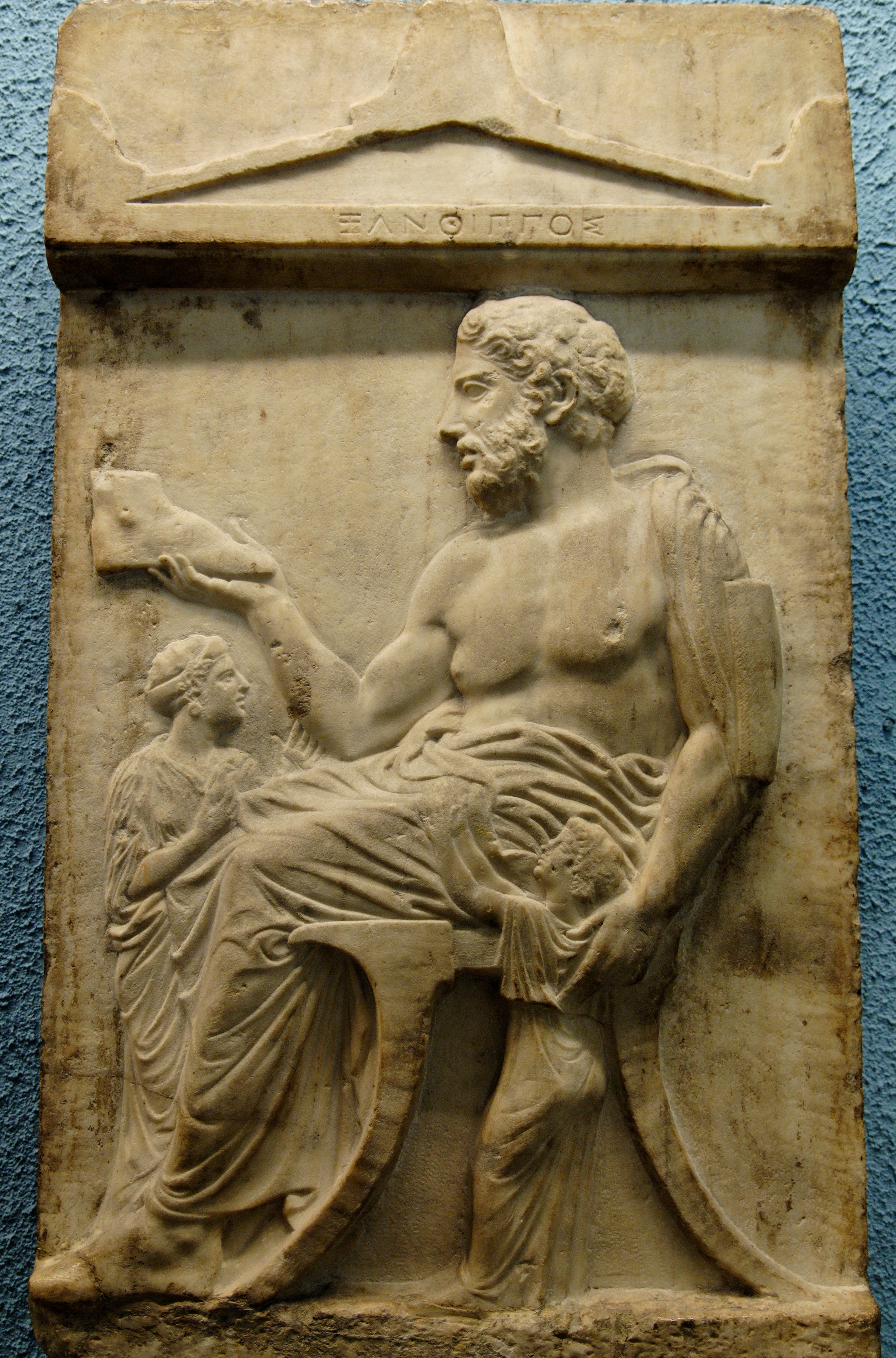
Arabian Hall Of The Winter Palace
The Arabian Hall, sometimes known as the Blackamoor Hall or the Arabian Dining Room, is one of the private rooms of the Winter Palace in Saint Petersburg. In the Tsarist era, it was the room from which imperial processions through the state rooms began. The double doors were designed to be on a straight axis through the principal state rooms and ultimately the Jordan Staircase, forming an enfilade. Thus it was here the Romanov family often assembled, in private, before state receptions and occasions. The privacy of the room was not compromised by the small private courtyard (''see plan'') from which windows, which once led to the Tsaritsa's winter-garden below, admitted light. Designed by Alexander Briullov following the Winter Palace fire of 1837, the room is decorated in the neoclassical style fashionable in the early 19th century, known as Pompeian. A ceiling, with a low segmental barrel vault with bands of shallow coffering stuccoed with classical motifs, is seemingly supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Dining
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes. In English, "stucco" sometimes refers to a coating for the outside of a building and "plaster" to a coating for interiors; as described below, however, the materials themselves often have little to no differences. Other European languages, notably Italian, do not have the same distinction; ''stucco'' means ''plaster'' in Italian and serves for both. Composition The basic composition of stucco is cement, water, and sand. The difference in nomenclature between stucco, plaster, and mortar is based more on use than composition. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guava
Guava () is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava ''Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family ( Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. The name guava is also given to some other species in the genus ''Psidium'' such as strawberry guava (''Psidium cattleyanum'') and to the pineapple guava, '' Feijoa sellowiana''. In 2019, 55 million tonnes of guavas were produced worldwide, led by India with 45% of the total. Botanically, guavas are berries. Types The most frequently eaten species, and the one often simply referred to as "the guava", is the apple guava ('' Psidium guayava''). Guavas are typical Myrtoideae, with tough dark heavy leaves that are opposite, simple, elliptic to ovate, and long. The flowers are white, with five petals and numerous stamens. The fruits are many-seeded berries. Etymology The term ''guava'' appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackamoor
Blackamoors may refer to: * Blackamoor (decorative arts), stylized depictions of black Africans in the decorative arts and jewelry * Blackmoor (campaign setting), a fantasy roleplaying game campaign setting * ''Blackmoor'' (supplement), a 1975 supplementary rulebook for ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Blackamoor, Lancashire, a village in England * Blacka Moor, a moor in South Yorkshire, England * Black tetra, a small fish also called a blackamoor (Gymnocorymbus ternetzi) * Black Moor goldfish * '' The Moor of Peter the Great'', sometimes translated ''The Blackamoor of Peter the Great'' * '' Blackamoores'', a 2013 book * Maure, stylized depictions of black Africans in heraldry, sometimes called Blackamoors * Moors, Muslims of Spain and North Africa See also * Black Moor (other) * Blackmore (other) *Blakemore (other) *Moor (other) Moor or Moors may refer to: Nature and ecology * Moorland, a habitat characterized by low-growing vegetation and aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of the Horn of Africa. The first documented use of the name "Ethiopia" from Greek name "Αἰθίοψ" (Ethiopian) was in the 4th century during the reign of Aksumite king Ezana. There were three ethnolinguistic groups in the Kingdom of Aksum; Semitic, Cushitic, and Nilo-Saharan (ancestors of the modern-day Kunama and Nara). The Kingdom of Aksum remained a geopolitically influential entity until the pillage of its capital — also named Axum — in the 10th century by Queen Gudit. Nevertheless, the core Aksumite civilization was preserved and continued into the successive Zagwe dynasty. By this time, new ethnic groups emerged – the Tigrayans and Amharas. During the Solomonic period, the latter established major political and cultural i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsaritsa
Tsarina or tsaritsa (also spelled ''csarina'' or ''csaricsa'', ''tzarina'' or ''tzaritza'', or ''czarina'' or ''czaricza''; bg, царица, tsaritsa; sr, / ; russian: царица, tsaritsa) is the title of a female autocratic ruler (monarch) of Bulgaria, Serbia or Russia, or the title of a tsar's wife. The English spelling is derived from the German ''czarin'' or ''zarin'', in the same way as the French ''tsarine''/''czarine'', and the Spanish and Italian ''czarina''/''zarina''. (A tsar's daughter is a tsarevna.) "Tsarina" or "tsaritsa" was the title of the female supreme ruler in the following states: *Bulgaria: in 913–1018, in 1185–1422 and in 1908–1946 *Serbia: in 1346–1371 *Russia: officially from about 1547 until 1721, unofficially in 1721–1917 (officially "Empresses"). Russia Since 1721, the official titles of the Russian male and female monarchs were emperor () and empress () or empress consort, respectively. Officially the last Russian tsarina was Eud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dining Table
A table is an item of furniture with a raised flat top and is supported most commonly by 1 or 4 legs (although some can have more), used as a surface for working at, eating from or on which to place things. Some common types of table are the dining room table, which is used for seated persons to eat meals; the coffee table, which is a low table used in living rooms to display items or serve refreshments; and the bedside table, which is commonly used to place an alarm clock and a lamp. There are also a range of specialized types of tables, such as drafting tables, used for doing architectural drawings, and sewing tables. Common design elements include: * Top surfaces of various shapes, including rectangular, square, rounded, semi-circular or oval * Legs arranged in two or more similar pairs. It usually has four legs. However, some tables have three legs, use a single heavy pedestal, or are attached to a wall. * Several geometries of folding table that can be collapsed into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klismos
A klismos (Greek: κλισμός) or klismos chair is a type of ancient Greek chair, with curved backrest and tapering, outcurved legs. Ancient Greece Klismoi are familiar from depictions of ancient furniture on painted pottery and in bas-reliefs from the mid-fifth century BCE onwards. In epic, ''klismos'' signifies an armchair, but no specific description is given of its form; in ''Iliad'' xxiv, after Priam's appeal, Achilles rises from his ''thronos'', raises the elder man to his feet, goes out to prepare Hector's body for decent funeral and returns, to take his place on his ''klismos''. A vase-painting of a satyr carrying a klismos chair on his shoulder shows how light such chairs were. The curved, tapered legs of the klismos chair sweep forward and rearward, offering stability. The rear legs sweep continuously upward to support a wide concave backrest like a curved tablet, which supports the sitter's shoulders, or which may be low enough to lean an elbow on. The long and elega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meander (art)
__NOTOC__ A meander or meandros ( el, Μαίανδρος) is a decorative border constructed from a continuous line, shaped into a repeated motif. Among some Italians, these patterns are known as "Greek Lines". Such a design also may be called the Greek fret or Greek key design, although these terms are modern designations even though the decorative motif appears thousands of years before that culture, thousands of miles away from Greece, and among cultures that are continents away from it. Usually the term is used for motifs with straight lines and right angles and the many versions with rounded shapes are called running scrolls or, following the entomological origin of the term, may be identified as water wave motifs. On one hand, the name "meander" recalls the twisting and turning path of the Maeander River in Asia Minor (present day Turkey) that is typical of river pathways. On another hand, as Karl Kerenyi pointed out, "the meander is the figure of a labyrinth in linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
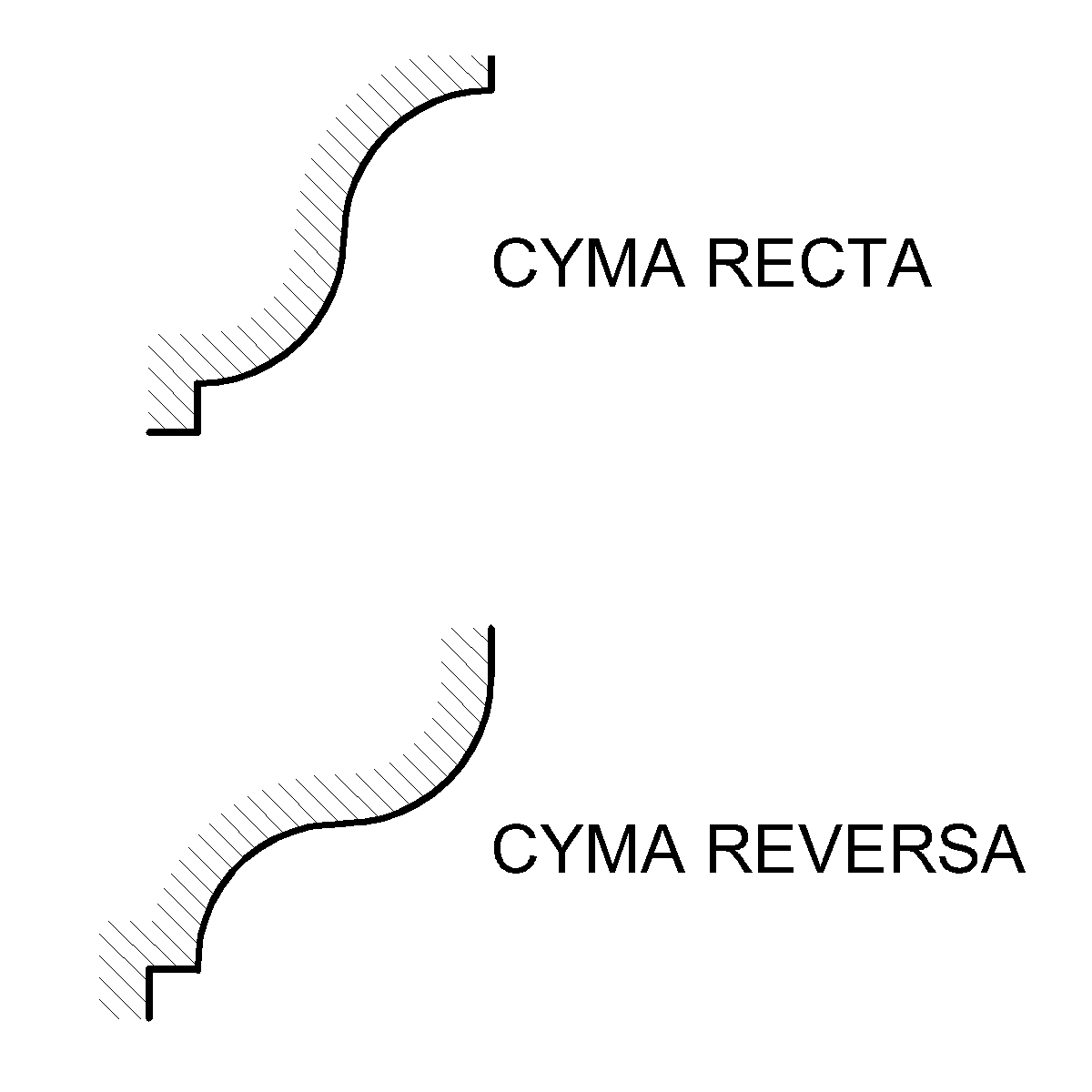
Ovolo
The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle. The 1911 edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' says:adapted from Ital. ''uovolo'', diminutive of ''uovo'', an egg; other foreign equivalents are Fr. ''ove'', ''échine'', ''quart de rond''; Lat. ''echinus''... s usedin architecture, ora convex moulding known also as the echinus, which in Classic architecture was invariably carved with the egg and tongue. In Roman and Italian work the moulding is called by workmen a quarter round. The "egg and tongue" referred to, also known as egg-and-dart, egg-and-anchor, or egg-and-star, refers to alternating egg and V-shapes enriching the surface of the concave ovolo in many early cases. The description of ovolo as the fundamental convex quarter-round element underlying or being combined with other elements to compose molding, details on column capitals, and other archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |