|
Arab Socialist Action Party вАУ Arabian Peninsula
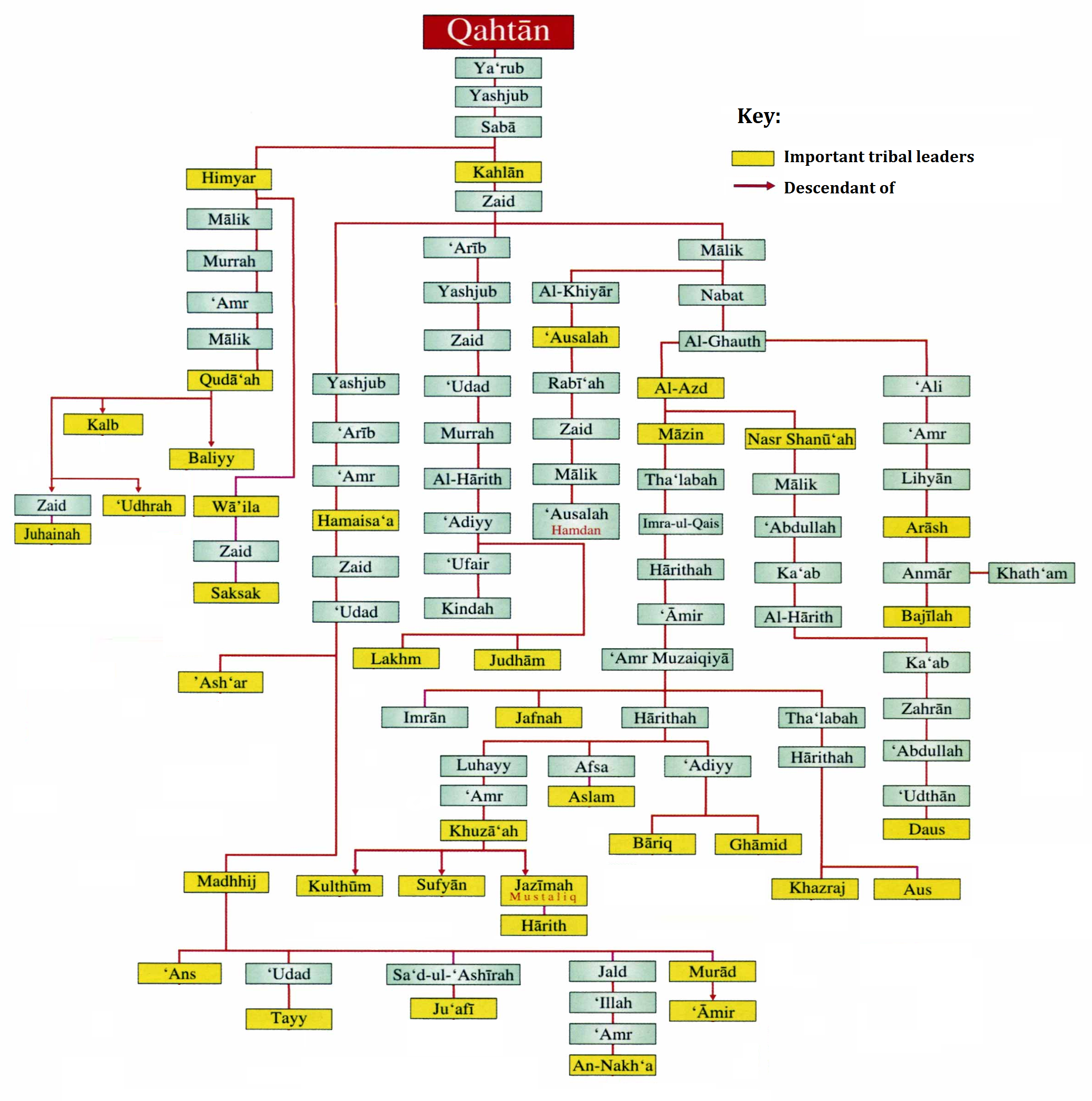
The Arab Socialist Action Party вАУ Arabian Peninsula ( ar, Ў≠Ў≤Ў® ЎІўДЎєўЕўД ЎІўДЎІЎіЎ™Ў±ЎІўГўК ЎІўДЎєЎ±Ў®ўК ўА ЎІўДЎђЎ≤ўКЎ±Ў© ЎІўДЎєЎ±Ў®ўКЎ© ''бЄ§izb al`Amal al IshtirƒБkiy al-`Arabiy-Al-JazƒЂra al`Arabiyyah''), was an underground oppositional political party in Saudi Arabia. It was founded in 1972 by elements of the erstwhile Arab Nationalist Movement.MERIP Reports, No. 130 , The Contest for Arabia. (Feb., 1985) Profile of the party The party was able to attract a following amongst intellectuals and middle class elements, and became a prominent force of the secular opposition. Ideologically it adhered to and |
Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon's Mediterranean coast. Beirut has been inhabited for more than 5,000 years, and was one of Phoenicia's most prominent city states, making it one of the oldest cities in the world (see Berytus). The first historical mention of Beirut is found in the Amarna letters from the New Kingdom of Egypt, which date to the 14th century BC. Beirut is Lebanon's seat of government and plays a central role in the Lebanese economy, with many banks and corporations based in the city. Beirut is an important seaport for the country and region, and rated a Beta + World City by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Beirut was severely damaged by the Lebanese Civil War, the 2006 Lebanon War, and the 2020 massive explosion in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Parties In Saudi Arabia
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Parties Established In 1972
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Parties Disestablished In 1990
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Arabist Political Parties
Pan-Arabism ( ar, ЎІўДўИЎ≠ЎѓЎ© ЎІўДЎєЎ±Ў®ўКЎ© or ) is an ideology that espouses the unification of the countries of North Africa and Western Asia from the Atlantic Ocean to the Arabian Sea, which is referred to as the Arab world. It is closely connected to Arab nationalism, which asserts the view that the Arabs constitute a single nation. Its popularity reached its height during the 1950s and 1960s. Advocates of pan-Arabism have often espoused socialist principles and strongly opposed Western political involvement in the Arab world. It also sought to empower Arab states against outside forces by forming alliances and, to a lesser extent, economic co-operation. Origins and development The origins of pan-Arabism are often attributed to Jurji Zaydan (1861вАУ1914) and his Nahda (Revival) movement. He was one of the first intellectuals to espouse pan-Arabism as a cultural nationalist force. Zaydan had critical influence on acceptance of a modernized version of the Quranic Arabic la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
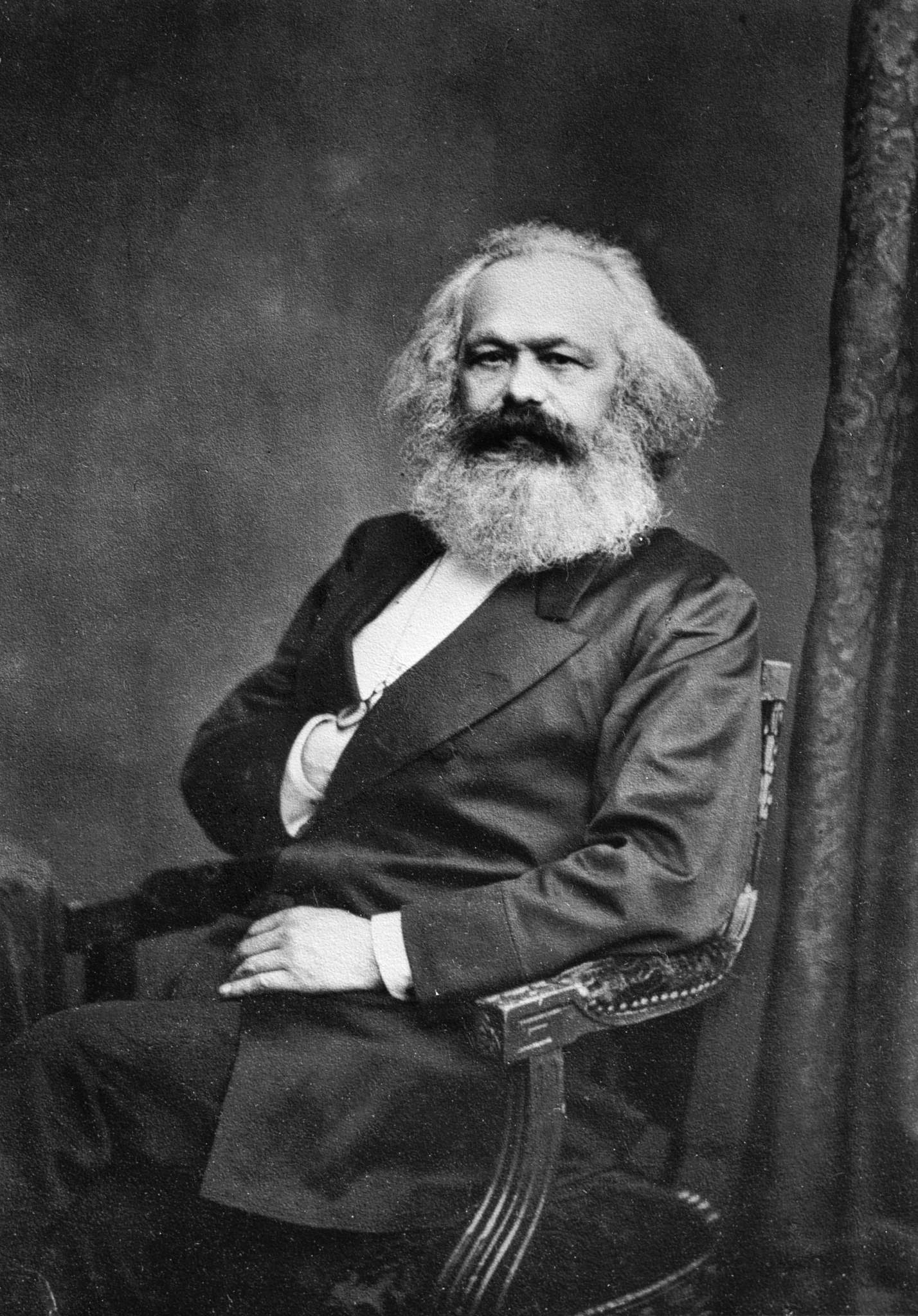
Marxist Parties In Saudi Arabia
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical perspective to view social transformation. It originates from the works of 19th-century German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. As Marxism has developed over time into various branches and schools of thought, no single, definitive Marxist theory exists. In addition to the schools of thought which emphasize or modify elements of classical Marxism, various Marxian concepts have been incorporated and adapted into a diverse array of social theories leading to widely varying conclusions. Alongside Marx's critique of political economy, the defining characteristics of Marxism have often been described using the terms dialectical materialism and historical materialism, though these terms were coined after Marx's death and their te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-wing Militant Groups
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in society whom its adherents perceive as disadvantaged relative to others as well as a belief that there are unjustified inequalities that need to be reduced or abolished. Left-wing politics are also associated with popular or state control of major political and economic institutions. According to emeritus professor of economics Barry Clark, left-wing supporters "claim that human development flourishes when individuals engage in cooperative, mutually respectful relations that can thrive only when excessive differences in status, power, and wealth are eliminated." Within the leftвАУright political spectrum, ''Left'' and ''Right'' were coined during the French Revolution, referring to the seating arrangement in the French Estates General. Those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Socialist Political Parties
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®ўРўКўМўС, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Musl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Nationalist Movement Breakaway Groups
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®ўРўКўМўС, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Musl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Nationalist Militant Groups
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®ўРўКўМўС, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Nationalism In Saudi Arabia
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®ўРўКўМўС, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ЎєўОЎ±ўОЎ®, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Musl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |