|
Aquarius Plateau
The Aquarius Plateau is a physiographic region in the High Plateaus Section of the Colorado Plateau Province. It is located within Garfield and Wayne counties in south-central Utah. Geography The plateau, a tectonic uplift on the much larger Colorado Plateau landform, is the highest in Utah. It is over 900 square miles (2330 km²) of mostly forested highland, much of which is part of Dixie National Forest. It has over 50,000 acres (200 km²) of rolling hilly terrain above 11,000 feet (3350 m). The plateau includes Boulder Mountain which peaks at at Bluebell Knoll. Parks Parks and protected areas on the Aquarius Plateau or its perimeter include Bryce Canyon National Park, Capitol Reef National Park, and the Dixie National Forest. Section diagram See also *Markagunt Plateau *Cedar Breaks National Monument *United States physiographic region The physiographic regions of the contiguous United States comprise 8 regions, 25 provinces, and 85 sections. The syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
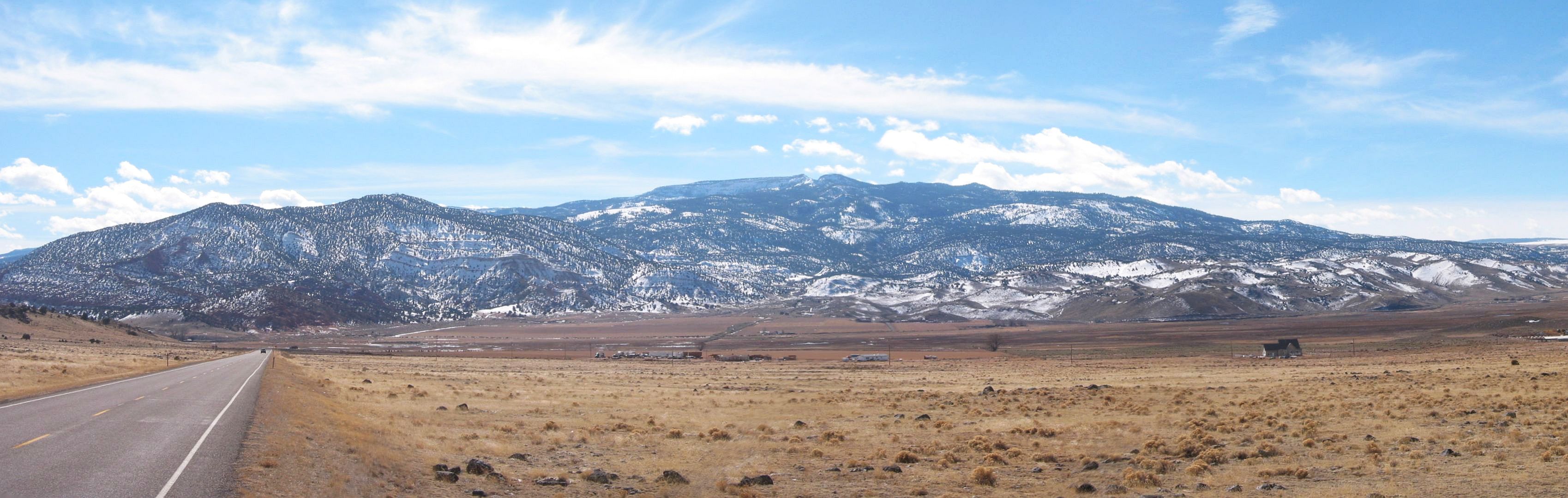
Boulder Mountain West
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive. In common usage, a boulder is too large for a person to move. Smaller boulders are usually just called rocks or stones. The word ''boulder'' derives from ''boulder stone'', from the Middle English ''bulderston'' or Swedish ''bullersten''. Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved December 9, 2011, from Dictionary.com website. In places covered by s during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulder Mountain (Utah)
Boulder Mountain (also known as Bluebell Knoll and Boulder Top) in Utah, USA makes up half of the Aquarius Plateau of South Central Utah in Wayne and Garfield counties. The mountain rises to the west of Capitol Reef National Park and consists of steep slopes and cliffs with over 50,000 acres (200 km²) of rolling forest and meadowlands on the top. The mountain has a nearly flat summit of roughly 70 square miles. The mountain is the highest timbered plateau in North America and is part of the Dixie National Forest. Highway 12 Utah Scenic Byway 12 traverses the eastern side of the mountain from Torrey through Boulder and on to Escalante. A series of unpaved backcountry roads and jeep trails provide access to the top during the brief snow-free time, usually only a few months from July to September. These jeep trails were originally created as the main route for wagons traveling between Escalante and Boulder.BLM RAMP.Canyones of Escalante:History of Boulder, Utah. (1990) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument
The Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument (GSENM) is a United States national monument protecting the Grand Staircase, the Kaiparowits Plateau, and the Canyons of the Escalante ( Escalante River) in southern Utah. It was established in 1996 by President Bill Clinton under the authority of the Antiquities Act with 1.7 million acres of land, later expanded to ."National Landscape Conservation System National Monuments" (archive). ''blm.gov''. . April 2012. Retrieved December 10, 2017. In 2017, the monument's si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateaus Of Utah
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills or escarpments. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones. Formation Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, Plate tectonics movements and erosion by water and glaciers. Volcanic Volcanic plateaus are produced by volcanic activity. The Columbia Plateau in the north-western United States is an example. They may be formed by upwelling of volcanic magma or extrusion of lava. The un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedar Breaks National Monument
Cedar Breaks National Monument is a U.S. National Monument located in the U.S. state of Utah near Cedar City. Cedar Breaks is a natural amphitheater, stretching across , with a depth of over . The elevation of the rim of the amphitheater is over above sea level. Rising above the rim is the prominent Brian Head, the peak of which lies a short distance outside of the National Monument boundary. The rock of the amphitheater is more eroded than, but otherwise similar to, formations at nearby Bryce Canyon National Park, Red Canyon in Dixie National Forest, and select areas of Cedar Mountain (SR-14). Because of its elevation, snow often makes parts of the park inaccessible to vehicles from October through May. Its rim visitor center is open from June through October. Several hundred thousand people visit the monument annually. The monument area is the headwaters of Mammoth Creek, a tributary of the Sevier River. Flora and fauna Wildlife can often be seen in this high altitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markagunt Plateau
Markagunt Plateau is a volcanic field in southern Utah, United States. Formed in a region of older volcanics, it consists of several cinder cones and associated lava flows. Some of the lava flows feature lava tubes such as Mammoth Cave, while others have formed lava dams and lakes like Navajo Lake. Volcanism took place during the Pliocene and latest Pleistocene but may have continued into the Holocene; legends of the Southern Paiute may reflect past eruptions. Geography and geomorphology The Markagunt Plateau is in southern Utah in the counties Iron County, Garfield County and Kane County. Cedar City lies west and Kanab south of the volcanic field, which is crossed by Utah State Route 14, Utah State Route 143 and Utah State Route 148. Towns in the area include Duck Creek Village and Mammoth Creek. The volcanic field is on a plateau bordered to the south by the Pink Cliffs and to the west by the cliffs of Cedar Breaks National Monument, and features lava flows and over 25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Staircase
The Grand Staircase is an immense sequence of sedimentary rock layers that stretch south from Bryce Canyon National Park and Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, through Zion National Park, and into Grand Canyon National Park. Characterization In the 1870s, geologist Clarence Dutton first conceptualized this region as a huge stairway ascending out of the bottom of the Grand Canyon northward with the cliff edge of each layer forming giant steps. Dutton divided this layer cake of Earth history into five steps from the youngest (uppermost) rocks: * Pink Cliffs *Grey Cliffs * White Cliffs * Vermilion Cliffs * Chocolate Cliffs Since then, modern geologists have further divided Dutton's steps into individual rock formations. Formations in the Grand Staircase starting with the youngest (uppermost) rocks: * Claron Formation *Kaiparowits Formation *Wahweap Formation * Straight Cliffs Formation * Tropic Shale *Dakota Sandstone *Carmel Formation * Temple Cap Format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryce Canyon National Park
Bryce Canyon National Park () is an American national park located in southwestern Utah. The major feature of the park is Bryce Canyon, which despite its name, is not a canyon, but a collection of giant natural amphitheaters along the eastern side of the Paunsaugunt Plateau. Bryce is distinctive due to geological structures called hoodoos, formed by frost weathering and stream erosion of the river and lake bed sedimentary rocks. The red, orange, and white colors of the rocks provide spectacular views for park visitors. Bryce Canyon National Park is much smaller and sits at a much higher elevation than nearby Zion National Park. The rim at Bryce varies from . The Bryce Canyon area was settled by Mormon pioneers in the 1850s and was named after Ebenezer Bryce, who homesteaded in the area in 1874. The area around Bryce Canyon was originally designated as a national monument by President Warren G. Harding in 1923 and was redesignated as a national park by Congress in 1928. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixie National Forest
Dixie National Forest is a United States National Forest in Utah with headquarters in Cedar City. It occupies almost two million acres (8,000 km²) and stretches for about across southern Utah. The largest national forest in Utah, it straddles the divide between the Great Basin and the Colorado River. In descending order of forestland area it is located in parts of Garfield, Washington, Iron, Kane, Wayne, and Piute counties. The majority (over 55%) of forest acreage lies in Garfield County. Elevations vary from above sea level near St. George, Utah to at Blue Bell Knoll on Boulder Mountain. The southern rim of the Great Basin, near the Colorado River, provides spectacular scenery. Colorado River canyons are made up of multi-colored cliffs and steep-walled gorges. The Forest is divided into four geographic areas. High altitude forests in gently rolling hills characterize the Markagunt, Paunsaugunt, and Aquarius Plateaus. Boulder Mountain, one of the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Physiographic Region
The physiographic regions of the contiguous United States comprise 8 regions, 25 provinces, and 85 sections. The system dates to Nevin Fenneman Nevin Melancthon Fenneman (26 December 1865 – 4 July 1945) was an American professor of geology, with a long career at the University of Cincinnati. His contributions were primarily in the large scale geographical understanding of American geology ...'s paper ''Physiographic Subdivision of the United States'', published in 1917. Fenneman expanded and presented his system more fully in two books, ''Physiography of western United States'' (1931), and ''Physiography of eastern United States'' (1938). In these works Fenneman described 25 provinces and 85 sections of the United States physiography. Physiographic divisions References {{DEFAULTSORT:United States Physiographic Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
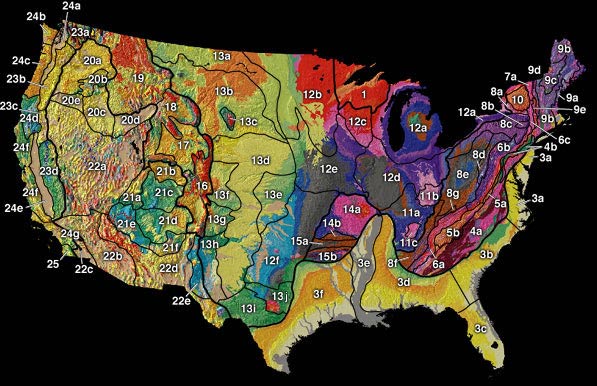
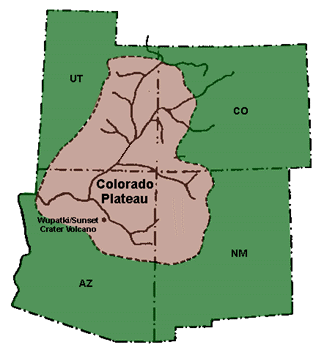
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Uplift
Tectonic uplift is the geologic uplift of Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of crustal thickening (such as mountain building events), changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere. Tectonic uplift results in denudation (processes that wear away the earth's surface) by raising buried rocks closer to the surface. This process can redistribute large loads from an elevated region to a topographically lower area as well – thus promoting an isostatic response in the region of denudation (which can cause local bedrock uplift). The timing, magnitude, and rate of denudation can be estimated by geologists using pressure-temperature studies. Crustal thickening Crustal thickening has an upward component of motion and often occurs when continenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)