|
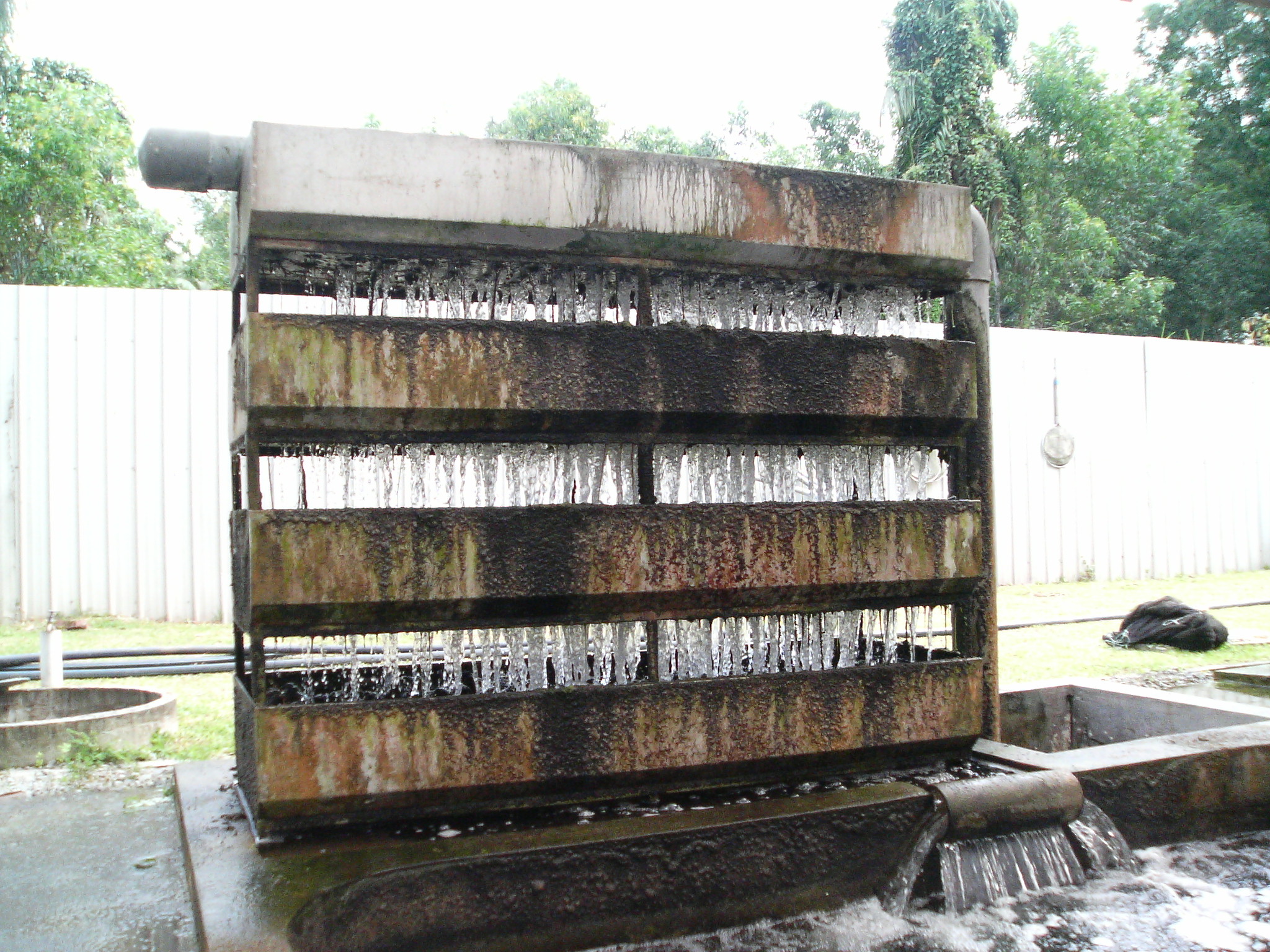
Aquarium Filter
Aquarium filters are critical components of both freshwater and marine aquaria.Leibel WS (1993) ''A fishkeepers guide to South American cichlids.'' Tetra Press. Belgium pg 12-14. Aquarium filters remove physical and soluble chemical waste products from aquaria, simplifying maintenance. Furthermore, aquarium filters are necessary to support life as aquaria are relatively small, closed volumes of water compared to the natural environment of most fish.Sands D (1994) ''A fishkeepers guide to Central American cichlids.'' Tetra Press. Belgium pg 17-19. Overview Animals, typically fish, kept in fish tanks produce waste from excrement and respiration. Another source of waste is uneaten food or plants and fish which have died. These waste products collect in the tanks and contaminate the water. As the degree of contamination rises, the risk to the health of the aquaria increases and removal of the contamination becomes critical. Filtration is a common method used for maintenance of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Filter
Corner may refer to: People * Corner (surname) * House of Cornaro, a noble Venetian family (''Corner'' in Venetian dialect) Places * Corner, Alabama, a community in the United States * Corner Inlet, Victoria, Australia * Corner River, a tributary of Harricana River, in Ontario, Canada * Corner Township, Custer County, Nebraska, a township in the United States Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''The Corner'' (album), an album by the Hieroglyphics * "The Corner" (song), a 2005 song by Common * "Corner", a song by Allie Moss from her 2009 EP ''Passerby'' * "Corner", a song by Blue Stahli from their 2010 album '' Blue Stahli'' * "The Corner", a song by Dermot Kennedy from his 2019 album '' Without Fear'' * "The Corner", a song from Staind's 2008 album ''The Illusion of Progress'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Corner painters, a Danish artists association * ''The Corner'' (1916 film), a 1916 film western * ''The Corner'' (2014 film), a 2014 Iranian drama film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintered Glass Filter
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as ''oversize'' and the fluid that passes through is called the ''filtrate''. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as ''blinding''. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective ''pore size'' of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size, filter thickness and biological activity). Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. Filtration is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 μm to less than 1 mm, but typically 10 to 200 μm. Depending on the granularity, this powder can have an abrasive feel, similar to pumice powder, and has a low density as a result of its high porosity. The typical chemical composition of oven-dried diatomaceous earth is 80–90% silica, with 2–4% alumina (attributed mostly to clay minerals), and 0.5–2% iron oxide. Diatomaceous earth consists of the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of hard-shelled microalgae. It is used as a filtration aid, mild abrasive in products including metal polishes and toothpaste, mechanical insecticide, absorbent for liquids, matting agent for coatings, reinforcing filler in plastics and rubber, anti-block in plastic films, porous support for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came. There are two leading theories about how siphons cause liquid to flow uphill, against gravity, without being pumped, and powered only by gravity. The traditional theory for centuries was that gravity pulling the liquid down on the exit side of the siphon resulted in reduced pressure at the top of the siphon. Then atmospheric pressure was able to push the liquid from the upper reservoir, up into the reduced pressure at the top of the siphon, like in a baromet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DK Publishing
Dorling Kindersley Limited (branded as DK) is a British multinational publishing company specialising in illustrated reference books for adults and children in 63 languages. It is part of Penguin Random House, a subsidiary of German media conglomerate Bertelsmann. Established in 1974, DK publishes a range of titles in genres including travel (including DK Eyewitness travel), history, geography, science, space, nature, sports, gardening, cookery and parenting. The worldwide co-CEOs of DK is Paul Kelly and Rebecca Smart. DK has offices in New York, Melbourne, London, Munich, New Delhi, Toronto, Madrid, Beijing, and Jiangmen. DK works with licensing partners such as Disney, LEGO, DC Comics, the Royal Horticultural Society, MasterChef, and the Smithsonian Institution. DK has commissioned Mary Berry, Monty Don, Robert Winston, Huw Richards, and Steve Mould for a range of books. History DK was founded in 1974 by Christopher Dorling and Peter Kindersley in London as a book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
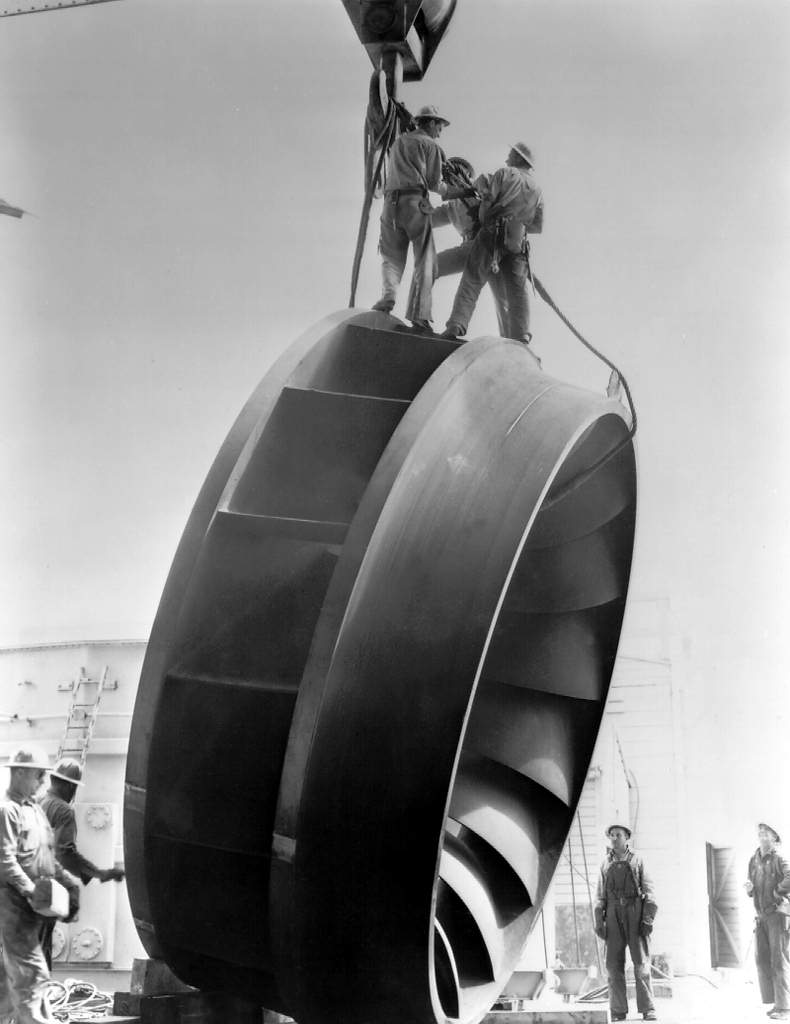
Impeller
An impeller or impellor is a rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid. It is the opposite of a turbine, which extracts energy from, and reduces the pressure of, a flowing fluid. In pumps An impeller is a rotating component of a centrifugal pump that accelerates fluid outward from the center of rotation, thus transferring energy from the motor that drives the pump to the fluid being pumped. The velocity achieved by the impeller transfers into pressure when the outward movement of the fluid is confined by the pump casing. An impeller is usually a short cylinder with an open inlet (called an eye) to accept incoming fluid, vanes to push the fluid radially, and a splined, keyed, or threaded bore to accept a drive shaft. It can be cheaper to cast an impeller and its spindle as one piece, rather than separately. This combination is sometimes referred to simply as the "rotor." Types Open impellers An open impeller has a hub with attached vanes and is mounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Holland Publishers
New Holland Publishers is an English-based international publisher of non-fiction books, founded in 1955. It is a privately held company, with offices in the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand. History The publishing firm was established as "Holland Press" was on 20 June 1955 in Southwark, London, England, and renamed to New Holland Publishers in 1988. It currently operates offices in London and Chatswood, New South Wales, Australia. The company went through a significant round of redundancies from 2008–2011. In 2013 the company sold US publishing rights to over 200 titles to Bloomsbury Publishing, Bloomsbury; and in 2014 over 1,400 titles to Fox Chapel Publishing of East Petersburg, Pennsylvania. References Book publishing companies based in London Companies based in the London Borough of Southwark Publishing companies established in 1955 1955 establishments in the United Kingdom {{publish-corp-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium - External Filter
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854.Katherine C. Grier (2008) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Regeneration
The electrochemical regeneration of activated carbon based adsorption, adsorbents involves the removal of molecules adsorbed onto the surface of the adsorbent with the use of an electric current in an electrochemical cell restoring the carbon's adsorptive capacity. Electrochemical regeneration represents an alternative to activated carbon#Regeneration, thermal regeneration commonly used in waste water treatment applications. Common adsorbents include powdered activated carbon (PAC), granular activated carbon (GAC) and activated carbon fibre. Regeneration for adsorbent re-use In waste water treatment, the most commonly used adsorbent is granular activated carbon (GAC), often used as to treat both liquid and gas phase volatile organic compounds and organic compound, organic pollutants. Activated carbon beds vary in lifetime depending on the concentration of the pollutant(s) being removed, their associated adsorption#Isotherms, adsorption isotherms, inlet flow rates and required dischar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). Adsorption is a '' surface phenomenon'', while absorption involves the whole volume of the material, although adsorption does often precede absorption. The term ''sorption'' encompasses both processes, while ''desorption'' is the reverse of it. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in the material. However, atoms on the surface of the adsorbent are not wholly surrounded by other adsorbent atoms and therefore can attract adsorbates. The exact nature of the bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |