|
Aquaporin
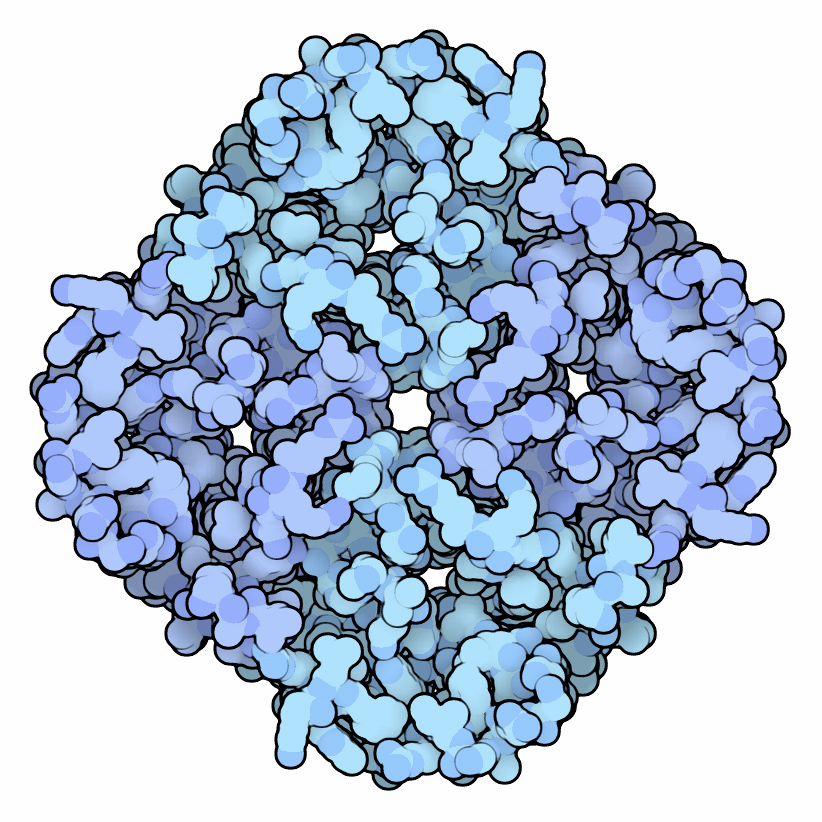
Aquaporins, also called water channels, are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells, mainly facilitating transport of water between cells. The cell membranes of a variety of different bacteria, fungi, animal and plant cells contain aquaporins through which water can flow more rapidly into and out of the cell than by diffusing through the phospholipid bilayer. Aquaporins have six membrane-spanning alpha helical domains with both carboxylic and amino terminals on the cytoplasmic side. Two hydrophobic loops contain conserved asparagine- proline-alanine ("NPA motif") which form a barrel surrounding a central pore-like region that contains additional protein density. Because aquaporins are usually always open and are prevalent in just about every cell type, this leads to a misconception that water readily passes through the cell membrane down its concentration gradient. Water can pass through the cell mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromyelitis Optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis can be simultaneous or successive. A relapsing disease course is common, especially in untreated patients. In more than 80% of cases, NMO is caused by immunoglobulin G Autoantibody, autoantibodies to aquaporin 4 (anti-AQP4 diseases, anti-AQP4), the most abundant Aquaporin, water channel protein in the central nervous system. A subset of anti-AQP4-negative cases is associated with antibodies against myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (Anti-MOG associated encephalomyelitis, anti-MOG). Rarely, NMO may occur in the context of other autoimmune diseases (e.g. Connective tissue disease, connective tissue disorders, paraneoplastic syndromes) or infectious diseases. In some cases, the etiology remains unknown (Idiopathic disease, idiopathic NMO). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |