|
Apple Sauce
Apple sauce or applesauce is a purée (not necessarily served as a true sauce) made of apples. It can be made with peeled or unpeeled apples and may be spiced or sweetened. Apple sauce is inexpensive and is widely consumed in North America and some parts of Europe. A wide range of apple varieties are used to make apple sauce, depending on the preference for sweetness or tartness. Formerly, sour apples were used to make savory apple sauce. Commercial versions of apple sauce are readily available at supermarkets and other retail outlets. Preparation Apple sauce is made by cooking apples with water or apple cider (fresh apple juice). More acidic apples will render a finer purée; the highly acidic Bramley apple creates a very fine purée. The apples may or may not be peeled. If they are not peeled, the peels and seeds are typically separated in a food mill. Sugar and spices such as cinnamon, allspice, and even Red Hot candies may be added for flavor. Lemon juice, citric acid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applesauce
Apple sauce or applesauce is a purée (not necessarily served as a true sauce) made of apples. It can be made with peeled or unpeeled apples and may be spiced or sweetened. Apple sauce is inexpensive and is widely consumed in North America and some parts of Europe. A wide range of apple varieties are used to make apple sauce, depending on the preference for sweetness or tartness. Formerly, sour apples were used to make savory apple sauce. Commercial versions of apple sauce are readily available at supermarkets and other retail outlets. Preparation Apple sauce is made by cooking apples with water or apple cider (fresh apple juice). More acidic apples will render a finer purée; the highly acidic Bramley apple creates a very fine purée. The apples may or may not be peeled. If they are not peeled, the peels and seeds are typically separated in a food mill. Sugar and spices such as cinnamon, allspice, and even Red Hot candies may be added for flavor. Lemon juice, citric acid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry (botany), berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a Canopy (forest), midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm parts of the world. The name ''allspice'' was coined as early as 1621 by the English, who valued it as a spice that combined the flavours of cinnamon, nutmeg, and clove. Several unrelated fragrant shrubs are called "Carolina allspice" (''Calycanthus floridus''), "Japanese allspice" (''Chimonanthus praecox''), or "wild allspice" (''Lindera benzoin''). Production Allspice is the dried fruit of the ''Pimenta dioica'' plant. The fruits are picked when green and unripe, and are traditionally Drying (food), dried in the sun. When dry, they are brown and resemble large, smooth Black pepper, peppercorns. Fresh leaves are similar in texture to Bay Laurel, bay leaves and similarly used in cooking. Leaves and wood are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Dish
A side dish, sometimes referred to as a side order, side item, or simply a side, is a food item that accompanies the entrée or main course at a meal. (definition. Merriam-webster.com Accessed August 2011. Common types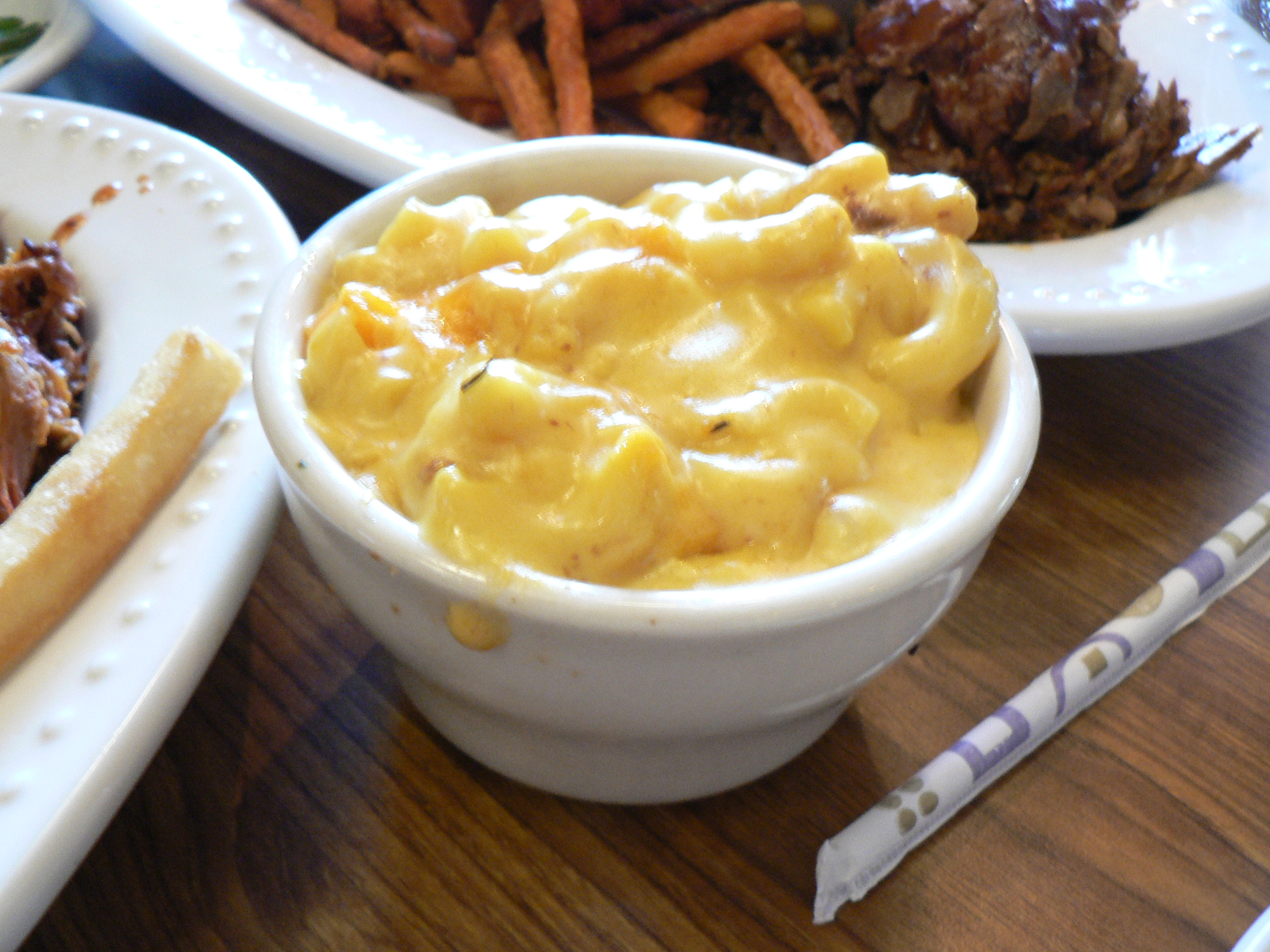 
 Side dishes ...
Side dishes ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer time than was typical. Canning of foods is an extension of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under specific circumstances, it can be much longer. A freeze-dried canned product, such as canned dried lentils, could last as long as 30 years in an edible state. In 1974, samples of canned food from the wreck of the ''Bertrand'', a steamboat that sank in the Missouri River in 1865, were tested by the National Food Processors Association. Although appearance, smell, and vitamin content had deteriorated, there was no trace of microbial growth and the 109-year-old food was determined to be still safe to eat. History and development French origins During the first years of the Napoleonic Wars, the French government offered a hefty cash award of 12,000 francs to any inventor who could devise a cheap and effective method of preserving l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
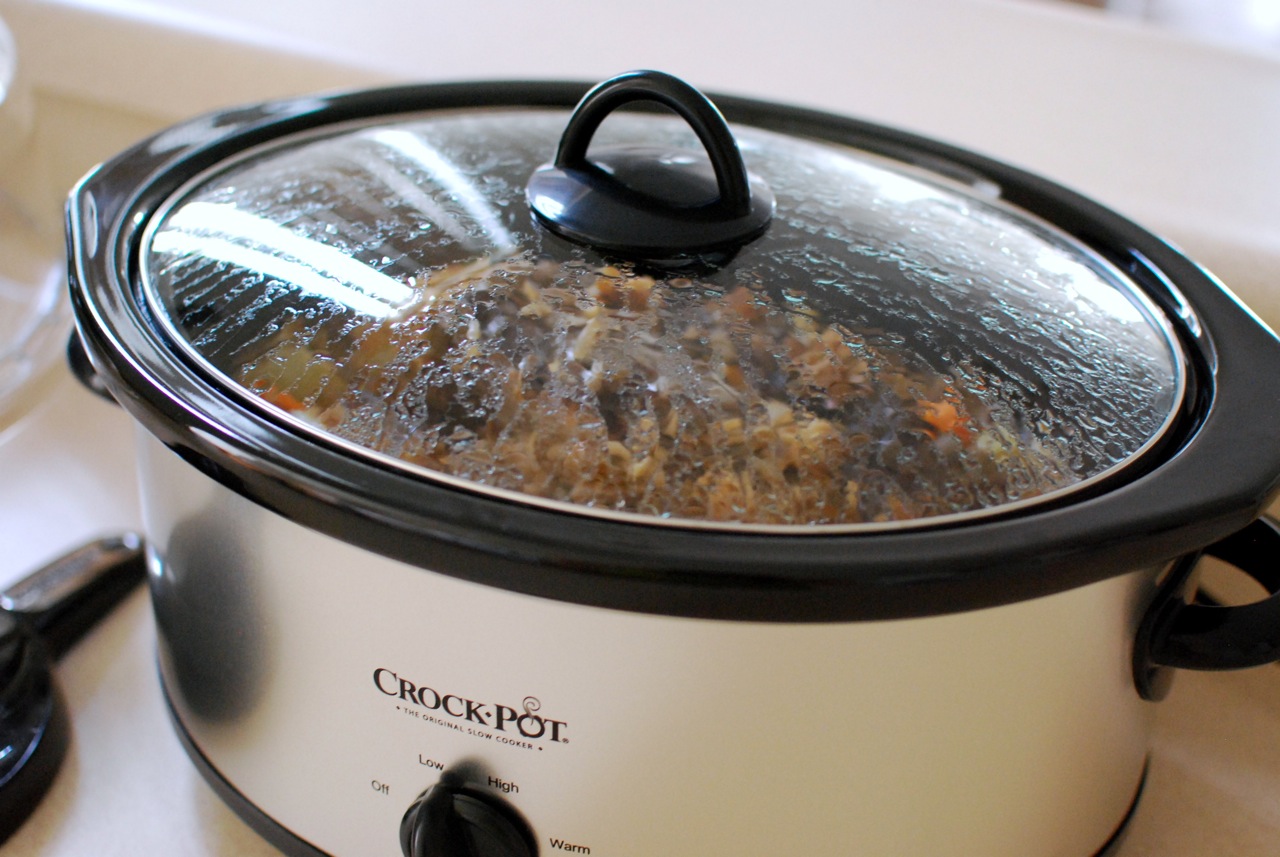
Slow Cooker
A slow cooker, also known as a crock-pot (after a trademark owned by Sunbeam Products but sometimes used generically in the English-speaking world), is a countertop electrical cooking appliance used to simmer at a lower temperature than other cooking methods, such as baking, boiling, and frying. This facilitates unattended cooking for many hours of dishes that would otherwise be boiled: pot roast, soups, stews and other dishes (including beverages, desserts and dips). History Slow cookers achieved popularity in the US during the 1940s, when many women began to work outside the home. They could start dinner cooking in the morning before going to work and finish preparing the meal in the evening when they came home. The Naxon Utilities Corporation of Chicago, under the leadership of electrical engineer Irving Naxon (born Irving Nachumsohn), developed the Naxon Beanery All-Purpose Cooker for the purposes of cooking a bean meal. Naxon was inspired by a story from his mother whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eliza Acton
Eliza Acton (17 April 1799 – 13 February 1859) was an English food writer and poet who produced one of Britain's first cookery books aimed at the domestic reader, ''Modern Cookery for Private Families''. The book introduced the now-universal practice of listing ingredients and giving suggested cooking times for each recipe. It included the first recipes in English for Brussels sprouts and for spaghetti. It also contains the first recipe for what Acton called "Christmas pudding"; the dish was normally called plum pudding, recipes for which had appeared previously, although Acton was the first to put the name and recipe together. Acton was born in 1799 in Sussex. She was raised in Suffolk where she ran a girls' boarding school before spending time in France. On her return to England in 1826 she published a collection of poetry and released her cookery book in 1845, aimed at middle class families. Written in an engaging prose, the book was well received by reviewers. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. There are two main types of boiling: nucleate boiling where small bubbles of vapour form at discrete points, and critical heat flux boiling where the boiling surface is heated above a certain critical temperature and a film of vapor forms on the surface. Transition boiling is an intermediate, unstable form of boiling with elements of both types. The boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F but is lower with the decreased atmospheric pressure found at higher altitudes. Boiling water is used as a method of making it potable by killing microbes and viruses that may be present. The sensitivity of different micro-organisms to heat varies, but if water is held at for one minute, most micro-organisms and viruses are inactivated. Ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baking
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot stones. The most common baked item is bread but many other types of foods can be baked. Heat is gradually transferred "from the surface of cakes, cookies, and pieces of bread to their center. As heat travels through, it transforms batters and doughs into baked goods and more with a firm dry crust and a softer center".p.38 Baking can be combined with grilling to produce a hybrid barbecue variant by using both methods simultaneously, or one after the other. Baking is related to barbecuing because the concept of the masonry oven is similar to that of a smoke pit. Baking has traditionally been performed at home for day-to-day meals and in bakeries and restaurants for local consumption. When production was industrialized, baking was automated by machines in large factories. The art of baking remains a fundamental skill and is important for nutrition, as baked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) and wrinkles on the face. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes (including humans) and monkeys (but not all primates), most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common cold, but it does not appear to prevent infection. It is unclear whether supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidifier
Acidifiers are inorganic chemicals that, put into a human (or other mammalian) body, either produce or become acid. These chemicals increase the level of gastric acid in the stomach when ingested, thus decreasing the stomach pH. Out of many types of acidifiers, the main four are: * Gastric acidifiers, these are the drugs which are used to restore temporarily the acidity of stomach in patient suffering from hypochlorhydria * Urinary acidifiers, used to control pH in urine * Systemic acidifiers, used to control pH in the overall body * Acid In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...s, mostly used in laboratory experiments Acidifier performance in distal stomach is debatable. Patients who suffer from achlorhydria have deficient secretion of hydrochloric acid in their stoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

