|
Apple II Plus
The Apple II Plus (stylized as Apple ][+ or apple ][ plus) is the second model of the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Inc., Apple Computer. It was sold from June 1979 to December 1982. Approximately 380,000 II Pluses were sold during its four years in production before being replaced by the Apple IIe in January 1983. Features Memory The Apple II Plus shipped with 16 KB, 32 KB or 48 KB of main RAM, expandable to 64 KB by means of the Language Card, an expansion card that could be installed in the computer's slot 0. The Apple's MOS Technology 6502, 6502 microprocessor could support a maximum of 64 KB of address space, and a machine with 48 KB RAM reached this limit because of the additional 12 KB of read-only memory and 4 KB of I/O addresses. For this reason, the extra RAM in the language card was bank switching, bank-switched over the machine's built-in ROM, allowing code loaded into the additional memory to be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Inc
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Company by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne, the company was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. the following year. It was renamed Apple Inc. in 2007 as the company had expanded its focus from computers to consumer electronics. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue, with billion in the 2024 fiscal year. The company was founded to produce and market Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Its second computer, the Apple II, became a best seller as one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple introduced the Lisa in 1983 and the Macintosh in 1984, as some of the first computers to use a graphical user interface and a mouse. By 1985, internal company problems led to Jobs leavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Pad
A graphics tablet (also known as a digitizer, digital graphic tablet, pen tablet, drawing tablet, external drawing pad or digital art board) is a computer input device that enables a user to hand draw or paint images, animations and graphics, with a special pen-like stylus, similar to the way a person draws pictures with a pencil and paper by hand. Graphics tablets may also be used to capture data or handwritten signatures. They can also be used to trace an image from a piece of paper that is taped or otherwise secured to the tablet surface. Capturing data in this way, by tracing or entering the corners of linear polylines or shapes, is called digitizing. The device consists of a rough surface upon which the user may "draw" or trace an image using the attached stylus, a pen-like drawing apparatus. The image is shown on the computer monitor, though some graphic tablets now also incorporate an LCD screen for more realistic or natural experience and usability. Some tablets are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LOGO Programming Language
Logo is an educational programming language, designed in 1967 by Wally Feurzeig, Seymour Papert, and Cynthia Solomon. The name was coined by Feurzeig while he was at Bolt, Beranek and Newman, and derives from the Greek ''logos'', meaning 'word' or 'thought'. A general-purpose language, Logo is widely known for its use of turtle graphics, in which commands for movement and drawing produced line or vector graphics, either on screen or with a small robot termed a turtle. The language was conceived to teach concepts of programming related to Lisp and only later to enable what Papert called " body-syntonic reasoning", where students could understand, predict, and reason about the turtle's motion by imagining what they would do if they were the turtle. There are substantial differences among the many dialects of Logo, and the situation is confused by the regular appearance of turtle graphics programs that are named Logo. Logo is a multi-paradigm adaptation and dialect of Lisp, a func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
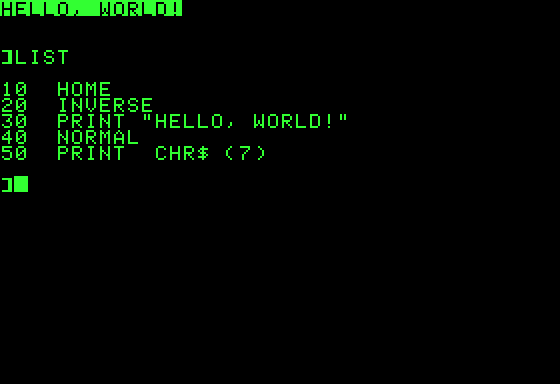
Integer BASIC
Integer BASIC is a BASIC interpreter written by Steve Wozniak for the Apple I and Apple II computers. Originally available on Cassette tape, cassette for the Apple I in 1976, then included in Read-only memory, ROM on the Apple II from its release in 1977, it was the first version of BASIC used by many early home computer owners. The only numeric data type was the integer; floating-point arithmetic, floating-point numbers were not supported. Using integers allowed numbers to be stored in a compact 16-bit format that could be more rapidly read and processed than the 32- or 40-bit floating-point formats found in most BASICs of the era. This made it so fast that Bill Gates complained when it outperformed Microsoft BASIC in benchmarks. However, this also limited its applicability as a general-purpose language. Another difference with other BASICs of the era is that Integer BASIC treated strings as arrays of characters, similar to the system in C (programming language), C or Fortran 77 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Switching
Bank switching is a technique used in computer design to increase the amount of usable memory beyond the amount directly addressable by the Processor (computing), processor instructions. It can be used to configure a system differently at different times; for example, a read-only memory, ROM required to booting, start a system from diskette could be switched out when no longer needed. In video game systems, bank switching allowed larger games to be developed for play on existing consoles. Bank switching originated in minicomputer systems. Many modern microcontrollers and microprocessors use bank switching to manage random-access memory, non-volatile memory, input-output devices and system management registers in small embedded systems. The technique was common in 8-bit microcomputer systems. Bank-switching may also be used to work around limitations in address bus width, where some hardware constraint prevents straightforward addition of more address lines, and to work around li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Address Space
In computing, an address space defines a range of discrete addresses, each of which may correspond to a network host, peripheral device, disk sector, a memory cell or other logical or physical entity. For software programs to save and retrieve stored data, each datum must have an address where it can be located. The number of address spaces available depends on the underlying address structure, which is usually limited by the computer architecture being used. Often an address space in a system with virtual memory corresponds to a highest level translation table, e.g., a segment table in IBM System/370. Address spaces are created by combining enough uniquely identified qualifiers to make an address unambiguous within the address space. For a person's physical address, the ''address space'' would be a combination of locations, such as a neighborhood, town, city, or country. Some elements of a data address space may be the same, but if any element in the address is different, ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC game, gaming. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. The term home computer has also been used, primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s. The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with computers. While personal computer users may develop their applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applesoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC is a dialect of Microsoft BASIC, developed by Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland, supplied with Apple II computers. It supersedes Integer BASIC and is the BASIC in Read-only memory, ROM in all Apple II series computers after the original Apple II model. It is also referred to as FP BASIC (from floating-point arithmetic, floating point) because of the Apple DOS command FP used to invoke it, instead of INT for Integer BASIC. Applesoft BASIC was supplied by Microsoft and its name is derived from the names of both Apple Computer and Microsoft. Apple employees, including Randy Wigginton, adapted Microsoft's interpreter for the Apple II and added several features. The first version of Applesoft was released in 1977 on cassette tape and lacked proper support for high-resolution graphics. Applesoft II, which was made available on cassette and disk and in the ROM of the Apple II Plus and subsequent models, was released in 1978. It is this latter version, which has some synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple IIe
The Apple IIe (styled as Apple //e) is the third model in the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Inc., Apple Computer. It was released in January 1983 as the successor to the Apple II Plus. The ''e'' in the name stands for ''enhanced''. It is the first Apple II with built-in lowercase, 80-column text support and 64K RAM standard, while reducing the total chip count from previous models by approximately 75%. Improved expandability combined with the new features made for an attractive general-purpose machine to first-time computer shoppers. As the last surviving model of the Apple II computer line before discontinuation, and having been manufactured and sold for nearly 11 years with relatively few changes, the IIe was the longest-lived computer in Apple's history. History Apple Inc., Apple Computer planned to discontinue the Apple II series after the introduction of the Apple III in 1980; the company intended to clearly establish market segmentation by desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple III
The Apple III (styled as apple ///) is a business-oriented personal computer produced by Apple Computer and released in 1980. Running the Apple SOS operating system, it was intended as the successor to the Apple II; however, it was largely considered a failure in the market. It was designed to provide features business users wanted: a true typewriter-style keyboard with upper and lowercase letters (the Apple II only supported uppercase at the time) and an 80-column display. It had the internal code name of "Sara", named after Wendell Sander's daughter. The system was announced on May 19, 1980, and released in late November that year. Serious stability issues required a design overhaul and a recall of the first 14,000 machines produced. The Apple III was formally reintroduced on November 9, 1981. Damage to the computer's reputation had already been done, however, and it failed to do well commercially. Development stopped, and the Apple III was discontinued on April 24, 1984. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II (1977 Computer)
The Apple II (stylized as ) is a personal computer released by Apple Inc. in June 1977. It was one of the first successful mass-produced microcomputer products and is widely regarded as one of the most important personal computers of all time due to its role in popularizing home computing and influencing later software development. The Apple II was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak. The system is based around the 8-bit MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor. Jerry Manock designed the foam-molded plastic case, Rod Holt developed the switching power supply, while Steve Jobs was not involved in the design of the computer. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire, and marks Apple's first launch of a computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists. ''Byte'' magazine referred to the Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and TRS-80 as the "1977 Trinity". As the Apple II had the defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |