|
Applai
The Kankanaey people are an Indigenous peoples of the Northern Philippines. They are part of the collective group of indigenous people known as the Igorot people. Demographics The Kankanaey live in western Mountain Province, northern Benguet, northeastern La Union and southeastern Ilocos Sur. The Kankanaey of the western Mountain Province are sometimes identified as Applai or Aplai. Because of the differences in culture from the Kankanaey of Benguet, the "Applai" have been accredited as a separate tribe. The 2010 Philippines census counted 362,833 self-identifying Kankanaey and 67,763 self-identifying Applai. Prehistory Recent DNA studies show that the Kankanaey along with the Atayal people of Taiwan, were most probably among the original ancestors of the Lapita people and modern Polynesians. They might even reflect a better genetic match to the original Austronesian mariners than the aboriginal Taiwanese, as the latter were influenced by more recent migrations to Taiwan, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
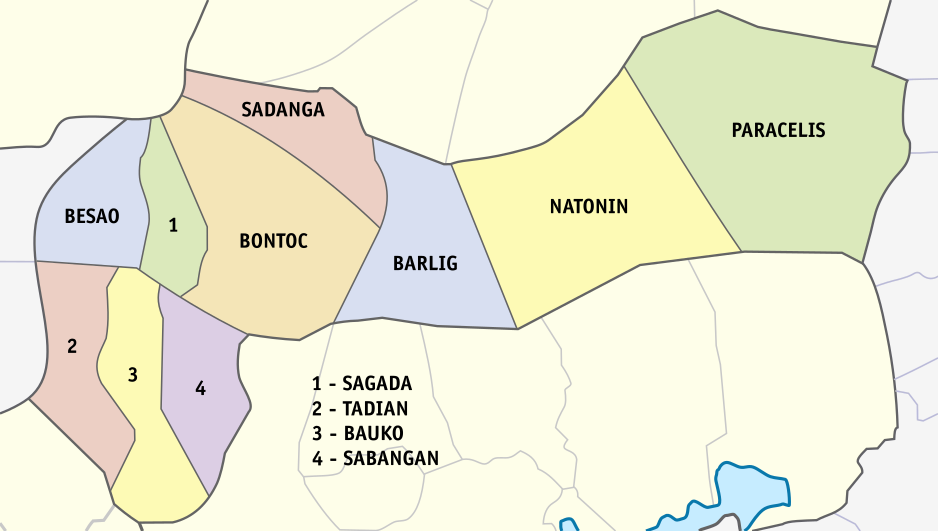
Mountain Province
Mountain Province is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Bontoc. Mountain Province was formerly referred to as ''Mountain'' in some foreign references. The name is usually shortened by locals to ''Mt. Province''. The province was named so for being in the Cordillera Central mountain range found in the upper realms of Luzon island. Mountain Province was also the name of the historical province that included most of the current Cordillera provinces. This old province was established by the Philippine Commission in 1908, and was later split in 1966 into Mountain Province, Benguet, Kalinga-Apayao and Ifugao. The province is also known for its mummy caves, which contain naturally mummified bodies, and for its hanging coffins. History Spanish period The area of the Cordillera mountains proved difficult to control by the Spaniards. During the long Spanish rule, not much was done to bring the province under con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Administrative Region
The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR; ilo, Rehion/Deppaar Administratibo ti Kordiliera; fil, Rehiyong Pampangasiwaan ng Cordillera), also known as the Cordillera Region and Cordillera (), is an administrative region in the Philippines, situated within the island of Luzon. It is the only landlocked region in the insular country, bordered by the Ilocos Region to the west and southwest, and by the Cagayan Valley Region to the north, east, and southeast. It is the least populous region in the Philippines, with a population less than that of the city of Manila. The region comprises six provinces: Abra, Apayao, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga and Mountain Province. The regional center is the highly urbanized city of Baguio. The region was officially created on July 15, 1987, and covers most of the Cordillera Central (Luzon), Cordillera Mountain Range of Luzon and is home to numerous ethnic peoples. The Nueva Vizcaya province has a majority of Igorot people, Igorot population, but w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mankayan, Benguet
Mankayan, officially the Municipality of Mankayan ( ilo, Ili ti Mankayan; tl, Bayan ng Mankayan), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Benguet, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 37,233 people. The municipality is known as a mining town, being the location of several mines, including the Lepanto Consolidated Mining Company. Etymology The name "Mankayan" is derived from ''Nancayan'', the Hispanic term of the native name of the place, ''Nangkayang'' (which means "high up in the mountain"). History Pre-colonial period Nangkayang was once a heavily forested area. The natives of the surrounding settlements of ''Panat'' and ''Bag-ongan'' mined gold through the ''labon'' system, after its reported discovery in a river. Copper was later discovered by the end of the 16th century in ''Kamangga-an'' (location of present-day Lepanto). Spanish period By the 1800s, the Spanish colonial government sent expeditions to survey the mines. On February 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrace (agriculture)
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore called terracing. Graduated terrace steps are commonly used to farm on hilly or mountainous terrain. Terraced fields decrease both erosion and surface runoff, and may be used to support growing crops that require irrigation, such as rice. The Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras have been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of the significance of this technique. Uses Terraced paddy fields are used widely in rice, wheat and barley farming in east, south, southwest, and southeast Asia, as well as the Mediterranean Basin, Africa, and South America. Drier-climate terrace farming is common throughout the Mediterranean Basin, where they are used for vineyards, olive trees, cork oak, and other crops. Ancient history Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carabao
The carabao ( es, Carabao; tgl, Kalabaw; ceb, Kabaw; ilo, Nuang) is a domestic swamp-type water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis'') native to the Philippines. Carabaos were introduced to Guam from the Spanish Philippines in the 17th century. They have acquired great cultural significance to the Chamorro people and are considered the unofficial national animal of Guam. In Malaysia, carabaos (known as kerbau in Malay) are the official animal of the state of Negeri Sembilan. Etymology The Spanish word is derived from Visayan (likely Waray) . Cognates include Cebuano , Javanese , Malay , and Indonesian Dutch . The female is called (in Spanish) a . The word's resemblance to ''caribou'' is coincidental, and they do not share a common etymology — an example of a false cognate. Carabaos are also known in Tagalog as (derived from Spanish). Before the Spanish era, carabaos were more widely known as ''nuang'' among the Ilocanos of Northern Luzon, and ''anowang'' and ''damulag'' among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan, is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the closed-canopy old-growth tropical forests of Southeast Asia, though they can also be found in other parts of tropical Asia and Africa. Most rattan palms are ecologically considered lianas due to their climbing habits, unlike other palm species. A few species also have tree-like or shrub-like habits. Around 20% of rattan palm species are economically important and are traditionally used in Southeast Asia in producing wickerwork furniture, baskets, canes, woven mats, cordage, and other handicrafts. Rattan canes are one of the world's most valuable non-timber forest products. Some species of rattan also have edible scaly fruit and heart of palm. Despite increasing attempts in the last 30 years at commercial cultivation, almost all rattan products still come from wild-harvested plants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adultery
Adultery (from Latin ''adulterium'') is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal consequences, the concept exists in many cultures and is similar in Christianity, Judaism and Islam. Adultery is viewed by many jurisdictions as offensive to public morals, undermining the marriage relationship. Historically, many cultures considered adultery a very serious crime, some subject to severe punishment, usually for the woman and sometimes for the man, with penalties including capital punishment, mutilation, or torture. Such punishments have gradually fallen into disfavor, especially in Western countries from the 19th century. In countries where adultery is still a criminal offense, punishments range from fines to caning and even capital punishment. Since the 20th century, criminal laws against adultery have become controversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose Flute
The nose flute is a musical instrument often played in Polynesia and the Pacific Rim countries. Other versions are found in Africa. Hawaii In the North Pacific, in the Hawaiian islands the nose flute was a common courting instrument. In Hawaiian, it is variously called ''hano'', "nose flute", by the more specific term ''ʻohe hano ihu'', "bamboo flute ornose," or ''ʻohe hanu ihu'', "bamboo ornose breath". It is made from a single bamboo section. According to ''Arts and Crafts of Hawai`i'' by Te Rangi Hiroa, old flutes in the Bishop Museum collection have a hole at the nose area for the breath, and two or three fingering holes. In the three-finger-hole specimen, one fingering hole is placed near the breath hole. Lengths range from . Oral tradition in various families states that numbers of fingering holes ranged from one to four, and location of the holes varied depending on the musical taste of the player. Though primarily a courting instrument played privately and for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panpipe
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth). Multiple varieties of pan flutes have been popular as folk instruments. The pipes are typically made from bamboo, Arundo donax, giant cane, or local reeds. Other materials include wood, plastic, metal and ivory. Name The pan flute is named after Pan (god), Pan, the List of Greek mythological figures, Greek god of nature and shepherds often depicted with such an instrument. The pan flute has become widely associated with the character Peter Pan created by Sir James Matthew Barrie, whose name was inspired by the god Pan. In Greek mythology, Syrinx (Σύριγξ) was a forest nymph. In her attempt to escape the affection of god Pan (a creature half goat and half man), she was transformed into a water-reed or calamos (cane-reed). Then, Pan cut several reeds, placed them in paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Kinship
Bilateral descent is a system of family lineage in which the relatives on the mother's side and father's side are equally important for emotional ties or for transfer of property or wealth. It is a family arrangement where descent and inheritance are passed equally through both parents. Families who use this system trace descent through both parents simultaneously and recognize multiple ancestors, but unlike with cognatic descent it is not used to form descent groups. While bilateral descent is increasingly the norm in Western culture, traditionally it is only found among relatively few groups in West Africa, India, Australia, Indonesia, Melanesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Polynesia. Anthropologists believe that a tribal structure based on bilateral descent helps members live in extreme environments because it allows individuals to rely on two sets of families dispersed over a wide area. Historically, North Germanic peoples in Scandinavia the Late Iron Age and Early Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Keesing
Felix M. Keesing (January 5, 1902 – April 1961) was a New Zealand-born anthropologist who specialized in the study of the Philippine Islands and the South Pacific. He came to the United States in the 1940s and taught at Stanford University, California, 1942–1961. He and Marie Margaret Martin Keesing, also an anthropologist, were married in July 1928. They had two sons, economist Donald Beaumont Keesing (1933–2004) and Roger Martin Keesing (1935–1993), who also became an anthropologist. Early life and family Felix Keesing was born in Taiping, Perak, in what was then British Malaya, on January 5, 1902. Known to his friends as “Fee,” Keesing graduated from Auckland University College in 1926 with first-class honors in education. He was soon engaged to marry Marie Martin. During their engagement, setting a pattern they would follow throughout their lives, Marie collaborated with him as he rewrote his Master's thesis for the 1928 publication ''The Changing Maori'' (Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

_with_fruits_(7844049166).jpg)



