|
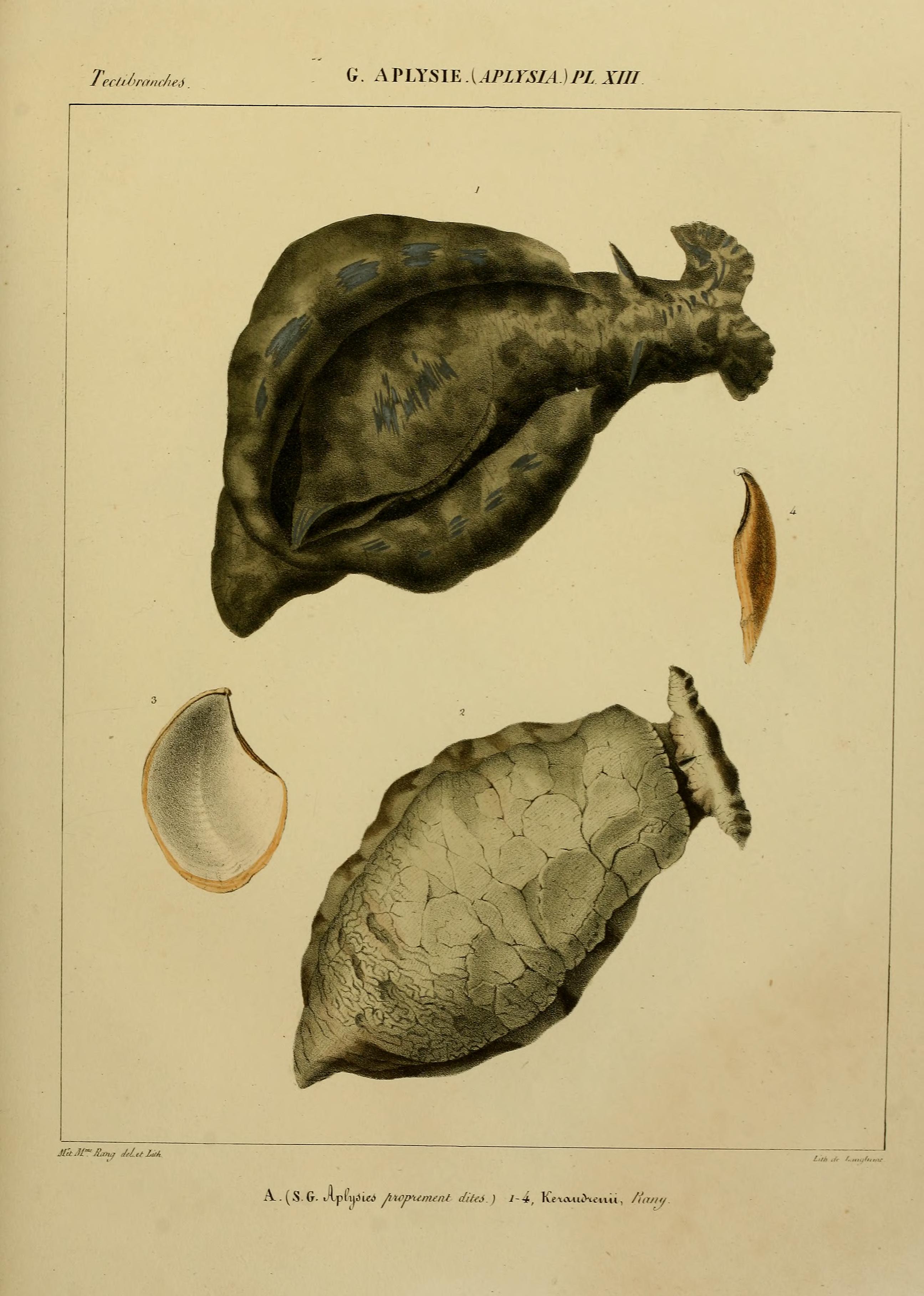
Aplysia Dactylomela
''Aplysia dactylomela'', the spotted sea hare, is a species of large sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod in the family Aplysiidae, the sea hares. Distribution and taxonomy As traditionally defined, this species of sea hare was cosmopolitan, being found in almost all tropical and warm temperate seas,Alexander, and Valdés (2013). ''The ring doesn’t mean a thing: Molecular data suggests a new taxonomy for two Pacific species of sea hares (Mollusca, Opisthobranchia, Aplysiidae).'' Pacific Science 67: 283–294. including the Mediterranean Sea where first seen in 2002 and likely self-established due to increasing temperatures.Valdés, Alexander, Crocetta, Yokeş, Giacobbe, Poursanidis, Zenetos, Cervera, Caballer, Galil, and Schembri (2013). ''The origin and dispersal pathway of the spotted sea hare Aplysia dactylomela (Mollusca: Opisthobranchia) in the Mediterranean Sea.'' Aquatic Invasions 8(4): 427–436. Based on genetic evidence, the population from the Indo-Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sander Rang
Sander Rang or Paul Charles Leonard Alexander Rang (1793, Utrecht -1844, Mayotte) was a French conchologist and interpreter of Arabic texts. He was, in 1816, one of the survivors of the sinking of the frigate ''Medusa'', on which he was an ensign. He spent a good part of his life in La Rochelle, where he published his early zoological observations, in particular in the bulletins of the Society of Natural Sciences of Charente-Maritimes.In 1841 Rang was one of the founding members of the Société des Amis des Arts now the Musée des Beaux-Arts de La Rochelle.He specialised in marine fauna notably in sea hares, cephalopods and other molluscs and on the heterogenous group known as zoophytes. Sander Rang described many new mollusc species including the sea hares ''Aplysia dactylomela'', '' Dolabrifera dolabrifera'', the cuttlefish ''Sepia hierredda'' and the land snails ''Striosubulina striatella'', '' Pleurodonte desidens '' and ''Opeas hannense''. Biography Sander Rang was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the northern coast of South America. The Gulf of Mexico lies to the northwest. The entire area of the Caribbean Sea, the numerous islands of the West Indies, and adjacent coasts are collectively known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, Gulf of Venezuela, Gulf of Darién, Golfo de los Mosquitos, Gulf of Paria and Gulf of Honduras. The Caribbean Sea has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia
''Aplysia'' () is a genus of medium-sized to extremely large sea slugs, specifically sea hares, which are one clade of large sea slugs, marine gastropod mollusks. These benthic herbivorous creatures can become rather large compared with most other mollusks. They graze in tidal and subtidal zones of tropical waters, mostly in the Indo-Pacific Ocean (23 species); but they can also be found in the Atlantic Ocean (12 species), with a few species occurring in the Mediterranean. ''Aplysia'' species, when threatened, frequently release clouds of ink, it is believed in order to blind the attacker (though they are in fact considered edible by relatively few species). Following the lead of Eric R. Kandel, the genus has been studied as a model organism by neurobiologists, because its gill and siphon withdrawal reflex, as studied in ''Aplysia californica'', is mediated by electrical synapses, which allow several neurons to fire synchronously. This quick neural response is necessary f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Diversity Web
Animal Diversity Web (ADW) is an online database that collects the natural history, classification, species characteristics, conservation biology, and distribution information on thousands of species of animals. The website includes thousands of photographs, hundreds of sound clips, and a virtual museum. Overview The ADW acts as an online encyclopedia, with each individual species account displaying basic information specific to that species. The website used a local, relational database written by staff and student contributors from the University of Michigan. Each species account includes geographic range, habitat, physical description, development, ecosystem roles, reproduction, life span, communication and perception, behavior, food habits, predation, and conservation status. The organization of the site reinforces past biology knowledge by providing sharp images and showing common phyla on the home page. The Animal Diversity Web has resources other than its databa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919) and is derived from the word toxic. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. Toxins vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Toxins are largely secondary metabolites, which are organic compounds that are not directly involved in an organism's growth, development, or reproduction, instead often aiding it in matters of defense. Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; plural: parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed lateral outgrowths that bear the chaetae. In several groups of sea snails and sea slugs, 'parapodium' refers to lateral fleshy protrusions. __TOC__ Annelid parapodia Most species of polychaete annelids have paired, fleshy parapodia which are segmentally arranged along the body axis. Parapodia vary greatly in size and form, reflecting a variety of functions, such as gas exchange, anchorage, protection and locomotion. General description Parapodia in polychaetes can be uniramous (consisting of one lobe or ramus) but are usually biramous (two lobes or rami). In the latter case, the dorsal lobes are called notopodia and the ventral lobes neuropodia. Both neuropodia and notopodia may possess a bundle of chaetae (neurochaetae and notochaet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" etymology of "electron"">Electron#Etymology">etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , '' -logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring. Definition and scope Classical electrophysiological techniques Principle and mechanisms Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that pertains broadly to the flow of ions (ion current) in biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Ganglion
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at front and to the sides, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Grass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the order Alismatales (in the clade of monocotyledons). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago. The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows" resembling grassland; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grasses of the family Poaceae. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollinator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant cloak or cape, see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for example, the siphon. Mantle cavity The ''mantle cavity'' is a central fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |