|
Aparajitaprccha
The ''Aparajitaprccha'' (''lit.'' "the questions of Aparajit") is a 12th-century Sanskrit text of Bhuvanadeva with major sections on architecture (''Vastu Shastra'') and arts (''Kala''). Predominantly a Hindu text, it largely reflects the north and western Indian traditions. The text also includes chapters on Jain architecture and arts. The text is notable for its sections on temple architecture (''vastu''), sculpture (''shilpa''), painting ('' chitra'') and classical music and dance (''sangita'', ''nritya''). Several incomplete manuscripts of ''Aparajitaprccha'' were discovered in Gujarat in early 20th-century (particularly Baroda), and others later in central and north India. It has at least 239 ''sutras'', each ''sutra'' followed by many verses. This collection is called ''sutrasantana'', and thus extends into over 7500 verses. The first edition and translation of the text was published by Popatbhai Mankad in 1950, while Lal Mani Dubey published another critical study with trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitra (art)
Chitra, also spelled as Citra, is an Indian genre of art that includes painting, sketch and any art form of delineation. The earliest mention of the term ''Chitra'' in the context of painting or picture is found in some of the ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism and Pali texts of Buddhism. Nomenclature ''Chitra'' (IAST: ''Citra'', चित्र) is a Sanskrit word that appears in the Vedic texts such as hymns 1.71.1 and 6.65.2 of the ''Rigveda''. There, and other texts such as ''Vajasaneyi Samhita'', ''Taittiriya Samhita'', ''Satapatha Brahmana'' and ''Tandya Brahmana'', ''Chitra'' means "excellent, clear, bright, colored, anything brightly colored that strikes the eye, brilliantly ornamented, extraordinary that evokes wonder". In the ''Mahabharata'' and the ''Harivamsa'', it means "picture, sktech, dilineation", and is presented as a genre of ''kala'' (arts). Many texts generally dated to the post-4th-century BCE period, use the term ''Chitra'' in the sense of painting, and ''Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
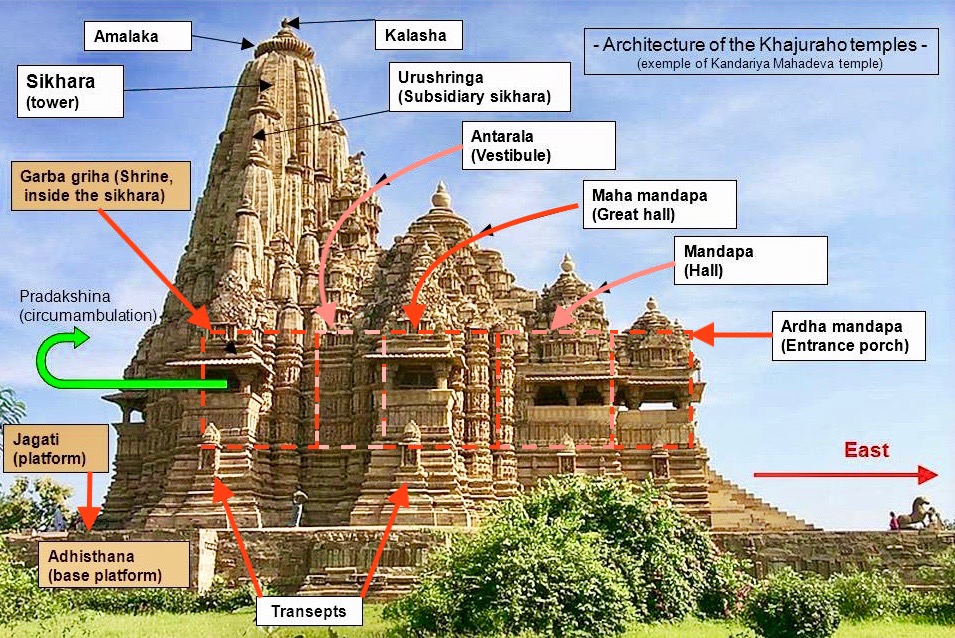
Vastu Shastra
''Vastu shastra'' ( hi, वास्तु शास्त्र, ' – literally "science of architecture") is a traditional Indian system of architecture based on ancient texts that describe principles of design, layout, measurements, ground preparation, space arrangement, and spatial geometry. The designs aim to integrate architecture with nature, the relative functions of various parts of the structure, and ancient beliefs utilising geometric patterns (yantra), symmetry, and directional alignments. Vastu Shastra are the textual part of ''Vastu Vidya'' - the broader knowledge about architecture and design theories from ancient India. Vastu Vidya is a collection of ideas and concepts, with or without the support of layout diagrams, that are not rigid. Rather, these ideas and concepts are models for the organisation of space and form within a building or collection of buildings, based on their functions in relation to each other, their usage and the overall fabric of the Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarangana Sutradhara
''Samarangana Sutradhara'', sometimes referred to as ''Samarāṅgaṇasūtradhāra'', is an 11th-century poetic treatise on classical Indian architecture (Vastu Shastra) written in Sanskrit language attributed to Paramara King Bhoja of Dhar. The title ''Samarāṅgaṇasūtradhāra'' is a compound word that literally means "architect of human dwellings", but can also be decomposed to an alternate meaning as "stage manager for battlefields" – possibly a play of words to recognize its royal author. Three manuscripts of ''Samarangana Sutradhara'' were discovered in early 20th century, while others were found later. They vary somewhat and all survive in an incomplete form. The most complete version is one likely copied and recompiled in the 15th century. This manuscript has 7,430 ''shlokas'' (verses) set in 83 ''adhyayas'' (chapters). A notable aspect of each ''adhyaya'' is that it starts with a verse composed in ''anustubh'' meter (''chanda'' in Hindu texts) and ends with a vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutra
''Sutra'' ( sa, सूत्र, translit=sūtra, translit-std=IAST, translation=string, thread)Monier Williams, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press, Entry fo''sutra'' page 1241 in Indian literary traditions refers to an aphorism or a collection of aphorisms in the form of a manual or, more broadly, a condensed manual or text. Sutras are a genre of ancient and medieval Indian texts found in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. In Hinduism, sutras are a distinct type of literary composition, a compilation of short aphoristic statements.Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pages 54–55 Each sutra is any short rule, like a theorem distilled into few words or syllables, around which teachings of ritual, philosophy, grammar, or any field of knowledge can be woven. The oldest sutras of Hinduism are found in the Brahmana and Aranyaka layers of the Vedas. Every school of Hindu philosophy, Vedic guides for rites of passage, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taranga Temple 2017 ) may refer to:
* Taranga (clothing), worn by Kashmiri women
* Taranga (Jain temple), Jain pilgrimage site in Gujarat, India
* Taranga (magazine), ''Taranga'' (magazine), a weekly Kannada magazine
* Taranga (Māori mythology), the mother of the Māori demigod Māui
* Taranga, Nepal, a village development committee in Nepal
* Hen and Chicken Islands#Taranga (Hen) Island, Taranga (Hen) Island, the largest island of the Hen and Chicken Islands
* Jnan Taranga, the first community radio service in North-East India
* An alternative name for the 1929 film Under the Southern Cross (1929 film), ''Under the Southern Cross''
{{disambig ...
Taranga (a Sanskrit and Pali word meaning wave In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasollasa
The ' also known as ''Abhilashitartha Chintamani'', is an early 12th-century Sanskrit text composed by the Kalyani Chalukya king Someshvara III, who ruled in present-day Karnataka . It is an encyclopedic work covering topics such as polity, governance, ethics, economics, astronomy, astrology, rhetoric, veterinary medicine, horticulture, perfumes, food, architecture, games, painting, poetry, dance and music. The text is a valuable source of socio-cultural information on 11th- and 12th-century India. The encyclopedic treatise is structured as five sub-books with a cumulative total of 100 chapters. It is notable for its extensive discussion of arts, particularly music and dance. It is also notable for including chapters on food recipes and festivals, many of which are a part of modern Indian culture. Another medieval era Sanskrit text with the title ''Mānasollāsa'' also exists, consisting of devotional praise hymns (''stotra''), and it is different from the encyclopedic treatise. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasara
The ''Mānasāra'', also known as ''Manasa'' or ''Manasara Shilpa Shastra'', is an ancient Sanskrit treatise on Indian architecture and design. Organized into 70 ''adhyayas'' (chapters) and 10,000 ''shlokas'' (verses), it is one of many Hindu texts on ''Shilpa Shastra'' – science of arts and crafts – that once existed in 1st-millennium CE. The ''Manasara'' is among the few on Hindu architecture whose complete manuscripts have survived into the modern age. It is a treatise that provides detailed guidelines on the building of Hindu temples, sculptures, houses, gardens, water tanks, laying out of towns and other structures. Title The word ''Manasara'' is a compound of Sanskrit ''māna'' (measurement) and ''sara'' (essence), meaning "essence of measurement" states P.K. Acharya – the scholar who discovered the complete manuscript (70 chapters) and was first to translate it into English in early 20th-century. While the text is now commonly referred as simply ''Manasara'', the San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Texts
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These include the Puranas, Itihasa and Vedas. Scholars hesitate in defining the term "Hindu scriptures" given the diverse nature of Hinduism,Dominic Goodall (1996), Hindu Scriptures, University of California Press, , page ix-xliii but many list the Bhagavad Gita and the Agamas as Hindu scriptures,Klaus Klostermaier (2007), A Survey of Hinduism: Third Edition, State University of New York Press, , pages 46–52, 76–77 and Dominic Goodall includes Bhagavata Purana and Yajnavalkya Smriti in the list of Hindu scriptures as well. History There are two historic classifications of Hindu texts: ''Śruti'' – that which is heard, and ''Smriti'' – that which is remembered. The ''Shruti'' refers to the body of most authoritative, ancient religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Architecture
Hindu architecture is the traditional system of Indian architecture for structures such as temples, monasteries, statues, homes, market places, gardens and town planning as described in Hindu texts. The architectural guidelines survive in Sanskrit manuscripts and in some cases also in other regional languages. These texts include the Vastu shastras, Shilpa Shastras, the ''Brihat Samhita'', architectural portions of the Puranas and the Agamas, and regional texts such as the Manasara among others. By far the most important, characteristic and numerous surviving examples of Hindu architecture are Hindu temples, with an architectural tradition that has left surviving examples in stone, brick, and rock-cut architecture dating back to the Gupta Empire. These architectures had influence of Ancient Persian and Hellenistic architecture. Far fewer secular Hindu architecture have survived into the modern era, such as palaces, homes and cities. Ruins and archaeological studies provide a vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Architectural History
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(13888446659).jpg)