|
Apalachicola People
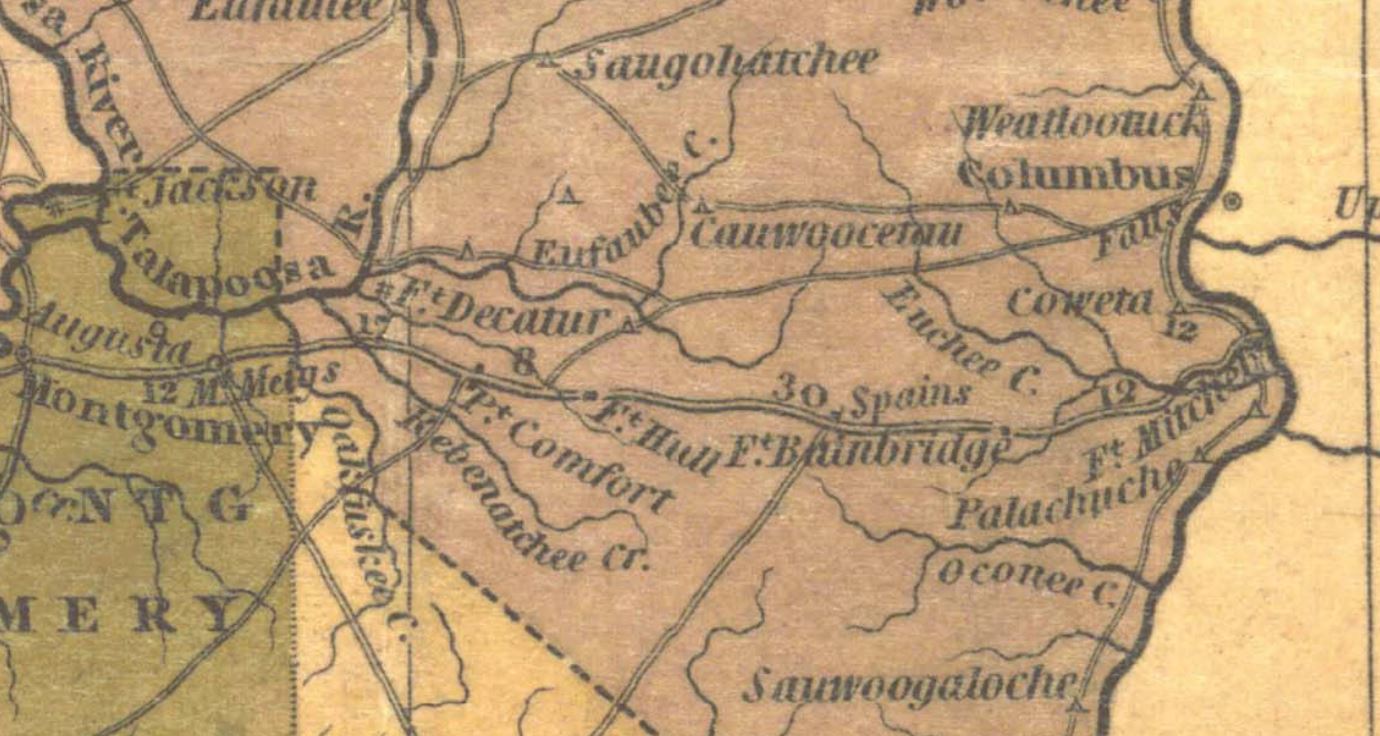
Apalachicola (sometimes Palachacola) was the name of a Native American town and chiefdom, and of the people living in it, and of a group of towns associated with it, located along the lower part of the Chattahoochee River in present-day Alabama and Georgia. The Spanish called the association of towns the Apalachicola Province. It is believed that before the 17th century, the residents of all the Apalachicola towns spoke the Hitchiti language, although other towns whose people spoke Muscogee relocated among the Apalachicolas along the Chattahoochee River in the middle- to later- 17th century. All of the Apalachicola towns moved to central Georgia at the end of the 17th century, where the English called them "Ochese Creek Indians". They moved back to the Chattahoochee River after 1715, with the English then calling them "Lower Creeks" ("Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy"), while the Spanish called them "Ochese". Origins In the first half of the 17th century, a number of tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitchiti
The Hitchiti ( ) were a historic indigenous tribe in the Southeast United States. They formerly resided chiefly in a town of the same name on the east bank of the Chattahoochee River, four miles below Chiaha, in western present-day Georgia. The natives possessed a narrow strip of good land bordering on the river. The Hitchiti had a reputation of being honest and industrious. Their autonym was possibly ''Atcik-hata'', while the Coushatta knew them as the ''At-pasha-shliha'', "mean people". Under pressure from European Americans, the Hitchiti moved into Florida. While some survived there, others signed a treaty for their land in exchange for lands in Indian Territory, and were forced west. English "Hitchiti" was Spanish "Achito". Location The Hitchiti are often associated with an area in present-day Chattahoochee County. But at an earlier period, they occupied land on the lower course of the Ocmulgee River. Early English maps show their town on the site where present-day Macon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex History of Spain, history, including a number of different languages, both indigenous and local linguistic descendants of the Roman Empire, Roman-imposed Latin language, of which Spanish language, Spanish is the largest and the only one that is official throughout the whole country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque language, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan language, Catalan and Galician language, Galician. Many populations outside Spain have ancestors who Spanish diaspora, emigrated from Spain and share elements of a Hispanic culture. The most notable of these comprise Hispanic America in the Western Hemisp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coweta (tribal Town)
Coweta was a tribal town and one of the four mother towns of the Muscogee ConfederacyIsham, Theodore and Blue Clark"Creek (Mvskoke)." ''Oklahoma Historical Society's Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture.'' Retrieved 20 Aug 2012. in what is now the Southeast United States, along with Kasihta (Cusseta), Abihka, and Tuckabutche.Walker, Willard B.; ''Creek Confederacy Before Removal''; Sturtevant, William C. (general editor) and Fogelson, Raymond D. (volume editor); ''Handbook of North American Indians: Southeast'': Volume 14; Washington DC; Smithsonian Institution; 2004; . Coweta was located on the Chattahoochee River in what the Spanish called Apalachicola Province now in the modern state of Alabama. It was a central trading city of the Lower Towns of the Mucogee Confederacy. Members of the tribal town were also known as ''Caouitas'' or ''Caoüita''. . 391/sup> The Cherokee language name for all the Lower Creek is ''Anikhawitha.'' . 391/sup> Notable members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savannah River
The Savannah River is a major river in the southeastern United States, forming most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia. Two tributaries of the Savannah, the Tugaloo River and the Chattooga River, form the northernmost part of the border. The Savannah River drainage basin extends into the southeastern side of the Appalachian Mountains just inside North Carolina, bounded by the Eastern Continental Divide. The river is around long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 26, 2011 The Savannah was formed by the confluence of the Tugaloo River and the Seneca River. Today this confluence is submerged beneath Lake Hartwell. The Tallulah Gorge is located on the Tallulah River, a tributary of the Tugaloo River that forms the northwest branch of the Savannah River. Two major cities are located along the Savannah River: Savannah and Augusta, Georgia. They were nuclei of early Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Woodward (colonist)
Henry Woodward (c. 1646 – c. 1690), was a Barbados-born merchant and colonist who was one of the first white settlers in the Carolinas. He established relationships with many Native American Indians in the American southeast. He initiated trade, primarily in deerskins and slaves, with many Indian towns and tribes. Early life Not much is known about Henry Woodward's early life. He is thought to have been born in Barbados. His father was William Woodward and his mother was Esther Martin. In 1666, Henry Woodward accompanied Captain Robert Sandford's exploration of the South Carolina coast. Woodward volunteered to remain in the Port Royal Sound vicinity and live among the Cusabo Indians, to establish relations and learn their language. For this he was granted, temporarily, "formall possession of the whole Country to hold as Tennant att Will" by the Lords Proprietors.''Henry Woodward.'' Dictionary of American Biography Base Set. American Council of Learned Societies, 1928-1936. Repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and the Spanish Empire during Spanish colonization of the Americas. While its boundaries were never clearly or formally defined, the territory was initially much larger than the present-day state of Florida, extending over much of what is now the southeastern United States, including all of present-day Florida plus portions of Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Louisiana. Spain's claim to this vast area was based on several wide-ranging expeditions mounted during the 16th century. A number of missions, settlements, and small forts existed in the 16th and to a lesser extent in the 17th century; they were eventually abandoned due to pressure from the expanding English and French colonial settlements, the collap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuchi
The Yuchi people, also spelled Euchee and Uchee, are a Native American tribe based in Oklahoma. In the 16th century, Yuchi people lived in the eastern Tennessee River valley in Tennessee. In the late 17th century, they moved south to Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina, settling near the Muscogee Creek people.Jackson 416 Some also migrated to the panhandle of Florida. After suffering many fatalities from epidemic disease and warfare in the 18th century, several surviving Yuchi bands were removed to Indian Territory in the 1830s, together with their allies the Muscogee Creek. Today, the Yuchi live primarily in the northeastern Oklahoma area, where many are enrolled citizens of the federally recognized Muscogee (Creek) Nation. They maintain a distinct cultural identity, and some speak the Yuchi language, a linguistic isolate. Name The term ''Yuchi'' translated to "over there sit/live" or "situated yonder." Their autonym, or name for themselves, Tsoyaha or Coyaha, means "Childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
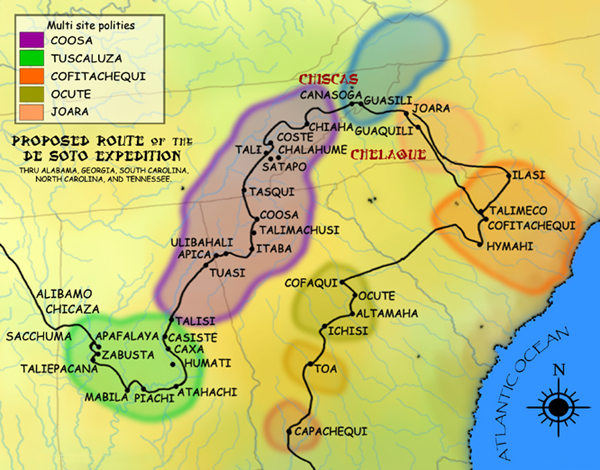
Chisca
The Chisca were a tribe of Native Americans living in present-day eastern Tennessee and southwestern Virginia in the 16th century, and in present day Alabama, Georgia, and Florida in the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries, by which time they were known as Yuchi. The Hernando de Soto expedition heard of, and may have had brief contact with, the Chisca in 1540. The Juan Pardo expeditions of 1566 and 1568 encountered the Chisca, and engaged in battles with them. By early in the 17th century, Chisca people were present in several parts of Spanish Florida, engaged at various times and places in alternately friendly or hostile relations with the Spanish and the peoples of the Spanish mission system. After the capture of a fortified Chisca town by the Spanish and Apalachee in 1677, some Chisca took refuge in northern Tennessee, where they were absorbed into the Shawnee, and in Muscogee towns in Alabama. Around the turn of the 18th century some Chisca, by then generally called Yuchi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachee People
The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River,Bobby G. McEwan, "Apalachee and Neighboring Groups," 669. at the head of Apalachee Bay, an area known as the Apalachee Province. They spoke a Muskogean language called Apalachee, which is now extinct. The Apalachee occupied the site of Velda Mound starting about 1450 CE, they but had mostly abandoned it when Spanish started settlements in the 17th century. They first encountered Spanish explorers in 1528, when the Narváez expedition arrived. Their tribal enemies, European diseases, and European encroachment severely reduced their population. Warfare from 1701 to 1704 devastated the Apalachee, and they abandoned their homelands by 1704, fleeing north to the Carolinas, Georgia, and Alabama. Language The Apalachee language was a Muskogean la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koasati Language
Koasati (also Coushatta) is a Native American languages, Native American language of Muskogean languages, Muskogean origin. The language is spoken by the Coushatta people, most of whom live in Allen Parish north of the town of Elton, Louisiana, though a smaller number share a Indian reservation, reservation near Livingston, Texas, with the Alabama (people), Alabama people. In 1991, Linguistics, linguist Geoffrey Kimball estimated the number of speakers of the language at around 400 people, of whom approximately 350 live in Louisiana. The exact number of current speakers is unclear, but Coushatta Tribe officials claim that most tribe members over 20 speak Koasati.April 9, 2009. Comments Pertaining to the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 Broadband Initiatives. www.ntia.doc.gov/broadbandgrants/comments/7B49.pdf In 2007, the Coushatta Tribe of Louisiana, in collaboration with McNeese State University and the College of William and Mary, began the Koasati (Coushatta) Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallapoosas
The Tallapoosas were a division of the Upper Creeks in the Muscogee Confederacy. Prior to Removal to Indian Territory, Tallapoosa lived along the Tallapoosa River in Alabama. They are also called the Cadapouches or Canapouches, which was mistakenly considered a synonym for the Catawba of the Carolina. 16th century Spanish explorers described towns along the Tallapoosa as being surrounded by protective wooden palisades. In later years, the palisades were no longer built. They made ceramics using grit as a temper. 17th century Over 30 towns along the Tallapoosa, Coosa, and Chattahoochee Rivers allied to form the Muscogee Confederacy. The Tallapoosa were among these Upper Creeks, who were more culturally and politically conservative than the Lower Creek towns. 18th century The Tallapoosas fought in the siege of Pensacola. Although these warriors proved their effectiveness in combining native tactics and European arms, the English failed to compensate them adequately and seriousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coosa Chiefdom
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon and Murray counties in Georgia, in the United States."Late Prehistoric/Early Historic Chiefdoms (ca. A.D. 1300-1850)" ''''. Retrieved July 22, 2010. It was inhabited from about 1400 until about 1600, and dominated several smaller chiefdoms. The total population of Coosa's area of influence, reaching into present-day Tennessee and Alabama, has been estimated at 50,000. |