|
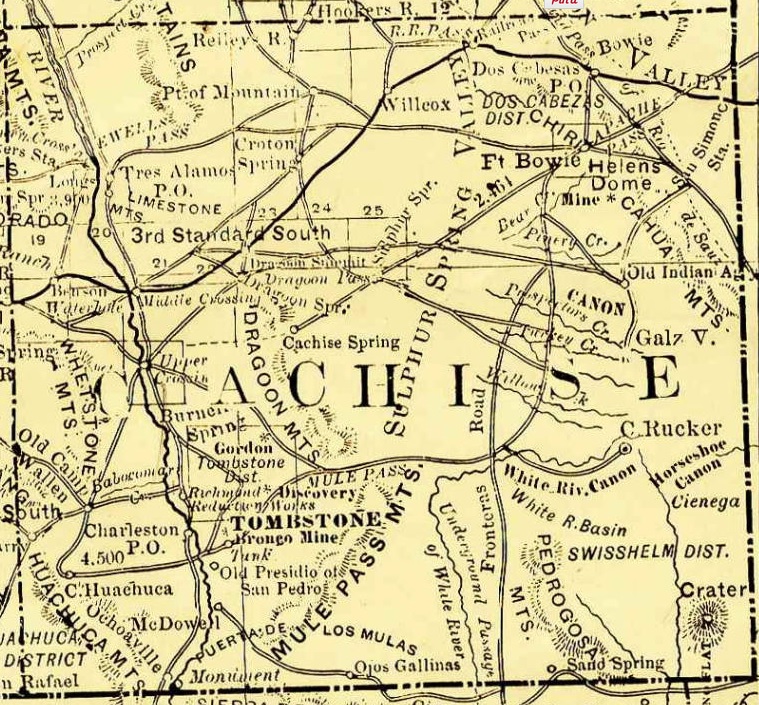
Apache Pass
Apache Pass, also known by its earlier Spanish name Puerto del Dado ("Pass of the Die"), is a historic mountain pass in the U.S. state of Arizona between the Dos Cabezas Mountains and Chiricahua Mountains at an elevation of . It is approximately east-southeast of Willcox, Arizona, in Cochise County. Apache Spring A natural freshwater spring, Apache Spring, emerges from a geological fault line running through the pass. The history of Apache Pass begins with this spring – as the only reliable water source for many miles, the spring served as a critical resupply point for early travelers through the area. Indigenous peoples and westward migrants alike depended on the spring. For the local Apache people, the spring at Apache Pass became a sort of crossroads, with many trails from different directions converging on the site. The great Chiricahua Apache leader Cochise, along with many of his followers, favored the area as a camping spot in winter and spring. There were often hundre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Bowie
Fort Bowie was a 19th-century outpost of the United States Army located in southeastern Arizona near the present day town of Willcox, Arizona. The remaining buildings and site are now protected as Fort Bowie National Historic Site. Fort Bowie was established by the California Volunteers in 1862, after a series of engagements between the California Column and the Chiricahua Apaches. The most violent of these conflicts was the Battle of Apache Pass in July 1862. The fort was named in honor of Colonel George Washington Bowie commander of the 5th Regiment California Volunteer Infantry who first established the fort. The first Fort Bowie resembled a temporary camp rather than a permanent army post. In 1868, a second, more substantial Fort Bowie was built which included adobe barracks, houses, corrals, a trading post, and a hospital. The second Fort Bowie was built on a plateau about to the east of the first site. For more than 30 years Fort Bowie and Apache Pass were the foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Coffee Hays
John Coffee "Jack" Hays (January 28, 1817 – April 21, 1883) was an American military officer. A captain in the Texas Rangers and a military officer of the Republic of Texas, Hays served in several armed conflicts from 1836 to 1848, including against the Comanche Empire in Texas and during the Mexican–American War. Biography John Hays was born at Little Cedar Lick, Wilson County, Tennessee. His father Harmon A. Hays fought in the War of 1812, naming his son for a relative by marriage, Colonel John Coffee. In 1836, at the age of 19, Hays migrated to the Republic of Texas. Sam Houston appointed him as a member of a company of Texas Rangers because he knew the Hays family from his Tennessee years. He met with Houston and delivered a letter of recommendation from then-President Andrew Jackson, his great uncle. Rachel Jackson was Hays' great aunt of the Donelson family, a relative of his mother. In the following years, Hays led the Rangers on a campaign against the Comanche i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Simon, Arizona
San Simon is a census-designated place in Cochise County, Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, it had a population of 165. San Simon is located along Interstate 10, east of Willcox. The community has a ZIP code of 85632. History San Simon was the location of the San Simon Station of the Butterfield Overland Mail on the San Simon River between Apache Pass and Stein's Peak Stations. It was a later relay station established to provide water and change horses on the route. In September 1880, Southern Pacific's rail line construction from the west reached San Simon and started rail service.Ascarza, William (22 November 2015)Mining in Chiricahua Mountains had varied success ''Arizona Daily Star'' Once a junction was made in March 1881 with eastern rails in Deming, New Mexico, the line became the second transcontinental rail route across the United States.(12 March 1881)Completion of the New Trans-Continental Route ''Pacific Rural Press'' San Simon was within P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doubtful Canyon
Doubtful Canyon was the name of two canyons in the Peloncillo Mountains, once considered in the 19th century as one canyon that served as the pass through those mountains. Today the canyon bearing the name Doubtful Canyon, is mostly in Cochise County, Arizona, near the New Mexico border. It descends to the east into the Animas Valley past Steins Peak it is in Hidalgo County, New Mexico. Doubtful Canyon has a tributary, Little Doubtful Canyon that joins it just east of the Arizona New Mexico border. The western canyon is now called West Doubtful Canyon and it descends into the San Simon Valley, in Cochise County, Arizona. History The mountain water sources and the low north south divide that lay between the two Doubtful canyons made it a favored shortcut for early east west travelers to the Southern Emigrant Trail wagon road that ran farther south before turning west. Doubtful Canyon and West Doubtful Canyon formed the pass where the Butterfield Overland Mail passed throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stein's Peak Station
Stein's Peak Station, was one of the original stage stations of the Butterfield Overland Mail. Its ruins are still to be seen in Doubtful Canyon, at an elevation of 4652 feet, northeast of Stein's Peak in Hidalgo County, New Mexico. Stein's Peak Station, was east of Apache Pass Station and west of Soldier's Farewell Stage Station. Later stations were located midway between these stations to provide water and changes of horse teams in the hot, arid climate. These were San Simon Station to the west and Mexican Springs Station Shakespeare is a ghost town in Hidalgo County, New Mexico, United States. It is currently part of a privately owned ranch, sometimes open to tourists. The entire community was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. History ... to the east of Lordsburg, New Mexico. References New Mexico Territory Butterfield Overland Mail in New Mexico Territory Geography of Hidalgo County, New Mexico Stagecoach stations in New Mexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon Springs, Arizona
Dragoon Springs is an historic site in what is now Cochise County, Arizona, at an elevation of . The name comes from a nearby natural spring, Dragoon Spring, to the south in the Dragoon Mountains at (). The name originates from the 3rd U.S. Cavalry Dragoons who battled the Chiricahua, including Cochise, during the Apache Wars. The Dragoons established posts around 1856 after the Gadsden Purchase made the area a U.S. territory. Dragoon Spring was a watering place on the Southern Emigrant Trail in territory which eventually joined the United States in the Gadsden Purchase, becoming part of the New Mexico Territory. Following the purchase, Dragoon Spring was used as a watering place by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line, commonly called the "Jackass Mail", starting in July 1857. After Butterfield started service in September 1858, the Jackass Mail was still operating using Butterfield's improved trail. Dragoon Springs Stage Station was the second of the two stone fortifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco, California
San Francisco (; Spanish for "Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th most populous in the United States, with 815,201 residents as of 2021. It covers a land area of , at the end of the San Francisco Peninsula, making it the second most densely populated large U.S. city after New York City, and the fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs. Among the 91 U.S. cities proper with over 250,000 residents, San Francisco was ranked first by per capita income (at $160,749) and sixth by aggregate income as of 2021. Colloquial nicknames for San Francisco include ''SF'', ''San Fran'', ''The '', ''Frisco'', and ''Baghdad by the Bay''. San Francisco and the surrounding San Francisco Bay Area are a global center of economic activity and the arts and sciences, spurred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Louis, Missouri
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which extends into Illinois, had an estimated population of over 2.8 million, making it the largest metropolitan area in Missouri and the second-largest in Illinois. Before European settlement, the area was a regional center of Native American Mississippian culture. St. Louis was founded on February 14, 1764, by French fur traders Gilbert Antoine de St. Maxent, Pierre Laclède and Auguste Chouteau, who named it for Louis IX of France. In 1764, following France's defeat in the Seven Years' War, the area was ceded to Spain. In 1800, it was retroceded to France, which sold it three years later to the United States as part of the Louisiana Purchase; the city was then the point of embarkation for the Corps of Discovery on the Lewis and Clark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfield Overland Mail
Butterfield Overland Mail (officially the Overland Mail Company)Waterman L. Ormsby, edited by Lyle H. Wright and Josephine M. Bynum, "The Butterfield Overland Mail", The Huntington Library, San Marino, California, 1991. was a stagecoach service in the United States operating from 1858 to 1861. It carried passengers and U.S. Mail from two eastern termini, Memphis, Tennessee, and St. Louis, Missouri, to San Francisco, California. The routes from each eastern terminus met at Fort Smith, Arkansas, and then continued through Indian Territory ( Oklahoma), Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Mexico, and California ending in San Francisco.Goddard Bailey, Special Agent to Hon. A.V. Brown. P.M., Washington, D.C., The Senate of the United States, Second Session, Thirty-Fifth Congress, 1858–'59, Postmaster General, Appendix, "Great Overland Mail", Washington, D. C., October 18, 1858.https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.c109481050;view=1up;seq=745 On March 3, 1857, Congress authorized the U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Emigrant Trail
:''The Southern Emigrant Trail should not be confused with the Applegate Trail, which is part of the Northern Emigrant Trails.'' Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857–1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico
) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English language, English, Spanish language, Spanish (New Mexican Spanish, New Mexican), Navajo language, Navajo, Keres language, Keres, Zuni language, Zuni , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = New Mexico Legislature , Upperhouse = New Mexico Senate, Senate , Lowerhouse = New Mexico House of Representatives, House of Representatives , Judiciary = New Mexico Supreme Court , Senators = * * , Representative = * * * , postal_code = NM , TradAbbreviation = N.M., N.Mex. , area_rank = 5th , area_total_sq_mi = 121,591 , area_total_km2 = 314,915 , area_land_sq_mi = 121,298 , area_land_km2 = 314,161 , area_water_sq_mi = 292 , area_water_km2 = 757 , area_water_percent = 0.24 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burro Cienega
Burro Cienega is a stream that arises at an elevation of 5990 feet, at , in the Big Burro Mountains in Grant County, New Mexico. Its mouth is at 4196 feet at a playa about 5.5 miles southeast of Lordsburg in Hidalgo County, New Mexico. History Ojo Ynez, a spring, and watering place on the old road from Janos, Chihuahua, to the Santa Rita copper mines was located in the valley of the Burro Cienega two miles upstream from where the road crossed the stream just northeast of Soldiers Farewell Hill. It was subsequently a watering place on Cooke's Wagon Road and the route of the San Antonio–San Diego Mail Line, 10 miles southwest of Ojo de Vaca (Cow Spring) and 2 miles northeast of the later Soldier's Farewell Stage Station on the route of the Butterfield Overland Mail. See also *List of rivers of New Mexico A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

