|
Antwerp Songbook
The Antwerp songbook (Dutch: and on the cover (A ''nice songbook in which you will find several songs'') was published in Antwerp in 1544 by printer Jan Roulans. History The songbook includes lyrics of some 221 'old' and 'new' Dutch songs () to banish sadness and melancholy (), with reference to the tune to which it was sung but without any musical notation. At least five editions of the songbook are known: folios from two probably older editions survived as reinforcement of the cover of other books while the structure of the preserved copy implicates that two earlier editions have existed. Thus, only one edition is preserved in one copy only, collected by '' Duke August von Braunschweig-Wolfenbüttel'' and conserved in the ''Herzog August Bibliothek'' (the library also known as ''Bibliotheca Augusta'') in Wolfenbüttel. One copy likely survived because two years after publication, this songbook was listed in the ''Index Librorum Prohibitorum'', the index of forbidden literatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,Statistics Belgium; ''Loop van de bevolking per gemeente'' (Excel file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, . Retrieved 1 November 2017. it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of around 1,200,000 people, it is the second-largest metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
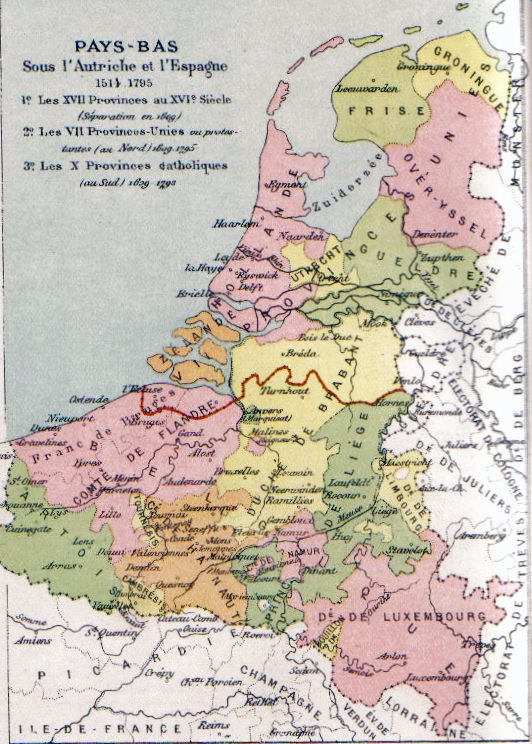
Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the Austrian Habsburgs (Austrian Netherlands, 1714–1794) until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815). The region also included a number of smaller states that were never ruled by Spain or Austria: the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, the Imperial Abbey of Stavelot-Malmedy, the County of Bouillon, the County of Horne and the Princely Abbey of Thorn. The Southern Netherlands comprised most of modern-day Belgium and Luxembourg, small parts of the modern Netherlands and Germany (the Upper Guelders region, as well as the Bitburg area in Germany, then part of Luxembourg), in addition to (until 1678) most of the present Nord-Pas-de-Calais region, and Longwy area in northern France. The (southern) Upper Guelders region consisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Folk Songs
Belgian may refer to: * Something of, or related to, Belgium * Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent * Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German *Ancient Belgian language, an extinct language formerly spoken in Gallia Belgica *Belgian Dutch or Flemish, a variant of Dutch *Belgian French, a variant of French *Belgian horse (other), various breeds of horse *Belgian waffle, in culinary contexts * SS ''Belgian'', a cargo ship in service with F Leyland & Co Ltd from 1919 to 1934 *''The Belgian'', a 1917 American silent film See also * *Belgica (other) Gallia Belgica was a province of the Roman Empire in present-day Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. Belgica may also refer to: Places * Belgica Glacier, Antarctica * Belgica Guyot, an undersea tablemount off Antarctica * Belgica Mountain ... * Belgic (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch-language Belgian Songs
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language spoken countryw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgian Music
The music of Belgium is a cultural mix where Flemings, Flemish Dutch language, Dutch-speaking and Walloons, Walloon French language, French-speaking traditions mix with those of German minorities and of immigrant communities from Democratic Republic of the Congo or other distant countries. Early and classical music Many of the major 15th- and 16th-century composers of the Franco-Flemish School—a current of vocal polyphony that played a central role in European art music of the time—were born and bred in the portion of the Low Countries that is situated in present-day Belgium, often in County of Hainaut, Hainaut. The late medieval composer and music theorist Johannes Ciconia (c. 1370–1412) had been born in Liège, but like many later Flemish polyphonists he spent much of his life working in Renaissance Italy. While it remains unclear why Flemish people, Flemish and other Netherlandish musicians exerted such a strong influence on Renaissance music throughout Europe (with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Literature
Dutch language literature () comprises all writings of literary merit written through the ages in the Dutch language, a language which currently has around 23 million native speakers. Dutch-language literature is the product of the Netherlands, Belgium, Suriname, the Netherlands Antilles and of formerly Dutch-speaking regions, such as French Flanders, South Africa, and Indonesia. The Dutch East Indies, as Indonesia was called under Dutch colonization, spawned a separate subsection in Dutch-language literature. Conversely, Dutch-language literature sometimes was and is produced by people originally from abroad who came to live in Dutch-speaking regions, such as Anne Frank and Kader Abdolah. In its earliest stages, Dutch-language literature is defined as those pieces of literary merit written in one of the Dutch dialects of the Low Countries. Before the 17th century, there was no unified standard language; the dialects that are considered Dutch evolved from Old Frankish. A separate A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Dutch Literature
Middle Dutch literature (1150–1500) is the Dutch literature produced in the Low Countries from the 12th century to the 16th century. It is preceded by only a few fragmentary texts existing in Old Dutch, and it was succeeded by Dutch Renaissance and Golden Age literature. Early stages In the first stages of Dutch literature, poetry was the predominant form of literary expression. In the Low Countries as in the rest of Europe, courtly romance and poetry were popular genres during the Middle Ages. The chivalric epic was a popular genre as well, often featuring King Arthur or Charlemagne (''Karel'') as protagonist (with notable example of '' Karel ende Elegast'', Dutch for "Charlemagne and the elf-spirit/elf-guest"). The first Dutch language writer known by name is the 12th-century County of Loon poet Henric van Veldeke, an early contemporary of Walther von der Vogelweide. Van Veldeke wrote courtly love poetry, a hagiography of Saint Servatius and an epic retelling of the ''Aene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Town
A port is a maritime law, maritime facility comprising one or more Wharf, wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge Affreightment, cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Port of Hamburg, Hamburg, Port of Manchester, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as port of entry, ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the World's busiest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camerata Trajectina
Camerata Trajectina is a Dutch early music ensemble (in English, the word, " camerata," generally means a choir or small chamber orchestra). The ensemble was founded in Utrecht (hence Latin ''trajectina''; of Utrecht) in 1974 by Jos van Veldhoven and Jan Nuchelmans. Following the departure of Veldhoven in 1976 to lead the Utrechts Barok Consort, leadership of the ensemble passed to the current director, the musicologist Louis Peter Grijp (b. 1954). The ensemble has specialised in recovering and sometimes reconstructing Dutch vocal music from the Dutch Golden Age, and much of its discography are of Dutch-language songs which have not been recorded. The ensemble has particularly concentrated on domestic, middle-class, and Dutch-language church music which—unlike the Latin language church music of the Spanish Netherlands—is little known and little researched. The lyrics of the recovered songs often illustrate cultural history, as in the case of the ensemble's two recordings of Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Heinrich Hoffmann Von Fallersleben
August Heinrich Hoffmann (, calling himself von Fallersleben, after his hometown; 2 April 179819 January 1874) was a German poet. He is best known for writing "Das Lied der Deutschen", whose third stanza is now the national anthem of Germany, and a number of popular children's songs, considered part of the Young Germany movement. Biography Hoffmann was born in Fallersleben in Lower Saxony, then in the duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. The son of a merchant and mayor of his native city, he was educated at the classical schools of Helmstedt and Braunschweig, and afterwards at the universities of Göttingen and Bonn. His original intention was to study theology, but he soon devoted himself entirely to literature. In 1823 he was appointed custodian of the university library at Breslau, a post which he held till 1838. He was also made extraordinary professor of the German language and literature at that university in 1830, and ordinary professor in 1835. Hoffmann was deprived of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Brabant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |