|
Antoine-Alexis Perier De Salvert
Antoine Alexis Perier (16911757), also known as Perier the Younger (french: Perier jeune), Perier the Cadet, and (after 1729) Perier de Salvert, was a French naval officer appointed to the rank of chef d'escadre in 1752, commander of the order of Saint-Louis. Early life Perier de Salvert was the son of Étienne Perier and Marie de Launay. His father was a non-noble shipowner and merchant in Le Havre and a captain of the Port of Dunkirk. (In October 1726, he was ennobled via letters patent of Louis XV together with his father and his brother Étienne in recognition of the family's decades of service to the king). From 1701 to 1702 he sailed as a privateer on a frigate off the English coast, and then on the ''Escadre du Nord'' under Pointis and . In 1705, his father securred him a position as a garde de la Marine, but he continued to serve in a fleet of French corsairs. Career in the French Navy From 1705 he became a ensign on several privateer ships in Duguay-Trouin's squad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Notre-Dame, Versailles
The Church of Notre-Dame, Versailles (french: Église Notre-Dame de Versailles), is a Roman Catholic parish church in Versailles, Yvelines, France, in the Rue de la Paroisse. History The church was built at the command of Louis XIV by Jules Hardouin-Mansart in the Baroque (French Classicism) (see: 17th-century French art ) architectural style and was consecrated on 30 October 1686. The parish of Notre-Dame included the Palace of Versailles and thus registered the baptisms, marriages and burials of the French royal family. In 1791 it was declared a cathedral but converted to a Temple of Reason in 1793. After the Revolution the bishop of Versailles chose the Church of Saint-Louis as his seat instead (the present Versailles Cathedral). Between 1858 and 1873, a new chapel was added by the architect Le Poittevin, who also built the market-halls of the ''Marché Notre-Dame''. The church contains sculptures by Pierre Mazzeline and Noël Jouvenet. The church has been classed as a ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensign (rank)
Ensign (; Late Middle English, from Old French (), from Latin (plural)) is a junior rank of a commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries, normally in the infantry or navy. As the junior officer in an infantry regiment was traditionally the carrier of the ensign flag, the rank acquired the name. This rank has generally been replaced in army ranks by second lieutenant. Ensigns were generally the lowest-ranking commissioned officer, except where the rank of subaltern existed. In contrast, the Arab rank of ensign, لواء, ''liwa''', derives from the command of units with an ensign, not the carrier of such a unit's ensign, and is today the equivalent of a major general. In Thomas Venn's 1672 ''Military and Maritime Discipline in Three Books'', the duties of ensigns are to include not only carrying the color but assisting the captain and lieutenant of a company and in their absence, have their authority. "Ensign" is ''enseigne'' in French, and ''chorąży'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
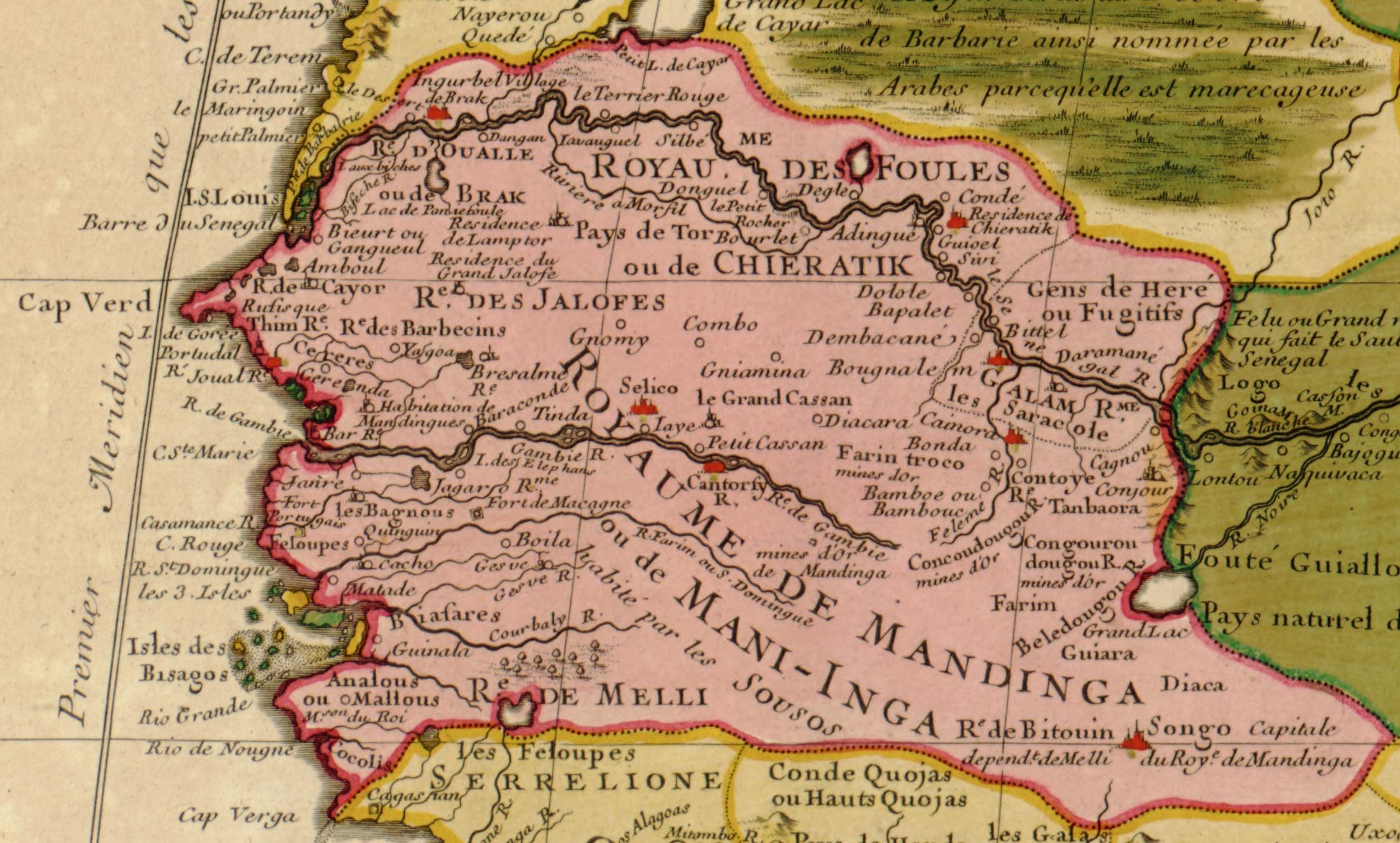
Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publications. p. 11. . and is surrounded by Senegal, except for its western coast on the Atlantic Ocean. The Gambia is situated on both sides of the lower reaches of the Gambia River, the nation's namesake, which flows through the centre of the Gambia and empties into the Atlantic Ocean, thus the long shape of the country. It has an area of with a population of 1,857,181 as of the April 2013 census. Banjul is the Gambian capital and the country's largest metropolitan area, while the largest cities are Serekunda and Brikama. The Portuguese in 1455 entered the Gambian region, the first Europeans to do so, but never established important trade there. In 1765, the Gambia was made a part of the British Empire by establishment of the Gambia. In 1965, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunta Kinteh Island
Kunta Kinteh Island, formerly called James Island and St Andrew's Island, is an island in the Gambia River, from the river mouth and near Juffureh in the Republic of the Gambia. Fort James is located on the island. It is less than 3.2 km (2 miles) from Albreda on the river's northern bank. As an important historical site in the West African slave trade, it is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, together with related sites including a ruined Portuguese chapel and a colonial warehouse in Albreda, the ''Maurel Frères Building'' in Juffureh, and Fort Bullen and Six-Gun Battery, which are located at the mouth of the Gambia River. History The first record of European interaction with the island is in May 1456, when a Portuguese expedition led by Italian explorers Alvise Cadamosto and Antoniotto Usodimare moored off the island. They buried one of their sailors, named Andrew, on the island, giving it its first European name—St Andrew's Island. Diogo Gomes also anchored o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compagnie Du Sénégal
The Compagnie du Sénégal ( French for the "Senegal Company" or, more literally, the "Company of the Senegal") was a 17th-century French chartered company that administered the territories of Saint-Louis and Gorée island as part of French Senegal. First company The company succeeded to some of the territories of the French West India Company in 1672, just prior to its bankruptcy and the revocation of its charter in 1674. Sieur de Richemont served as governor of its territories from 1672 to 1673 and was succeeded by the company's director Jacques Fuméchon, who served until 1682. The company's operations were then taken over by the and . Second company In 1696, the Compagnie royale du Sénégal was established and operated by Jean Bourguignon from March 1696 to April 1697 and then by until May 1702. They traded slaves with the Hausa Kingdoms, Mali, and the Moors in Mauritania. Third company In 1709, a third Compagnie du Sénégal was established. See also * Compagnie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Blackwall (1696)
''Blackwall'' was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the English Royal Navy, launched at Blackwall Yard in 1696. In September 1705, whilst under the command of Captain Samuel Martin ''Blackwall'', along with two smaller vessels, had been ordered to convoy some merchantmen to the Baltic. On 20 October, as ''Blackwall'' and her two consorts HMS ''Sorlings'' and HMS ''Pendennis''Roche, vol.1 p. 345 were convoying the return voyage, they encountered a superior French force. All the English ships were captured, ''Blackwall'' herself being taken by the French ship ''Protée''. Both Captain Martin and the French commander were killed in the action.Ships of the Old Navy, ''Blackwall''. ''Blackwall'' was commissioned into the French Navy under the name ''Blekoualle''; she was recaptured on 15 March 1708 but was not taken back into service in the Royal Navy, the decision being taken to have her broken up instead. However, she was captured again by the French in 1709, this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Francis Edward Stuart
James Francis Edward Stuart (10 June 16881 January 1766), nicknamed the Old Pretender by Whigs, was the son of King James II and VII of England, Scotland and Ireland, and his second wife, Mary of Modena. He was Prince of Wales from July 1688 until, just months after his birth, his Catholic father was deposed and exiled in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. James II's Protestant elder daughter (the prince's half-sister) Mary II and her husband (the prince's cousin) William III became co-monarchs. The Bill of Rights 1689 and Act of Settlement 1701 excluded Catholics such as James from the English and British thrones. James Francis Edward was raised in Continental Europe and known as the Chevalier de St. George. After his father's death in 1701, he claimed the English, Scottish and Irish crowns as James III of England and Ireland and James VIII of Scotland, with the support of his Jacobite followers and Louis XIV of France, a cousin of his father. Fourteen years late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Devonshire (1692)
HMS ''Devonshire'' was an 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 5 April 1692. She was rebuilt at Woolwich Dockyard Woolwich Dockyard (formally H.M. Dockyard, Woolwich, also known as The King's Yard, Woolwich) was an English Royal Navy Dockyard, naval dockyard along the river Thames at Woolwich in north-west Kent, where many ships were built from the early 1 ... in 1704, but was destroyed in action in 1707 during the Battle at The Lizard on 21 October. Notes References *Lavery, Brian (2003) ''The Ship of the Line - Volume 1: The development of the battlefleet 1650-1850''. Conway Maritime Press. . Ships of the line of the Royal Navy 1690s ships Ships built on the River Hamble {{UK-line-ship-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Ruby (1652)
HMS ''Ruby'' was a 40-gun frigate of the Commonwealth of England, built by Peter Pett (shipwright), Peter Pett at Deptford Dockyard, Deptford. She took part in actions during all three of the Anglo-Dutch Wars of 1652–1654, 1665–1667 and 1672–1674. She later served in the West Indies, and in 1683 was sent to the Leeward Islands to protect British settlements against Caribbean pirate raids. In 1687, the English pirate Joseph Bannister was captured by the crew of ''Ruby'' and brought to Port Royal for trial. She was rebuilt in 1687. She was captured by the French in October 1707. Construction and specifications The English ''Ruby'' was ordered by the Rump Parliament in May 1651, to be built at Deptford Dockyard under the guidance of Peter Pett (shipwright), Peter Pett. Her dimensions were gundeck with keel for tonnage with a breadth of and a depth of hold of . Her builder's measure tonnage was calculated as tonsWinfield 7 Winfield 18.Lavery, 1984, vol.1, p160. ''Ruby''s gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Chester (1691)
HMS ''Chester'' was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched 21 March 1691 at Woolwich Dockyard. She was captured by the French at the Battle at The Lizard on 21 October 1707. See also *List of ships captured in the 18th century During times of war where naval engagements were frequent, many battles were fought that often resulted in the capture of the enemy's ships. The ships were often renamed and used in the service of the capturing country's navy. Merchant ships were ... Notes References *Lavery, Brian (2003) ''The Ship of the Line - Volume 1: The development of the battlefleet 1650-1850''. Conway Maritime Press. . Ships of the line of the Royal Navy 1690s ships Captured ships {{UK-line-ship-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Cumberland (1695)
HMS ''Cumberland'' was a three-decker 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 12 November 1695. ''Cumberland'' was captured by the French in the Battle at the Lizard in 1707. She served in the French navy under her old name, and in 1715 was sold to Genoa. The Genoese sold her to Spain in 1717 and she was renamed ''Principe de Asturias''. She was recaptured by the British at the Battle of Cape Passaro in 1718, but did not return to service, and was instead sold to Austria in 1720. She was based at Naples Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ... and was renamed ''San Carlos''. She served until being broken up in 1733, having by then served under five flags. Notes References * *Lavery, Brian (2003) ''The Ship of the Line - V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |