|
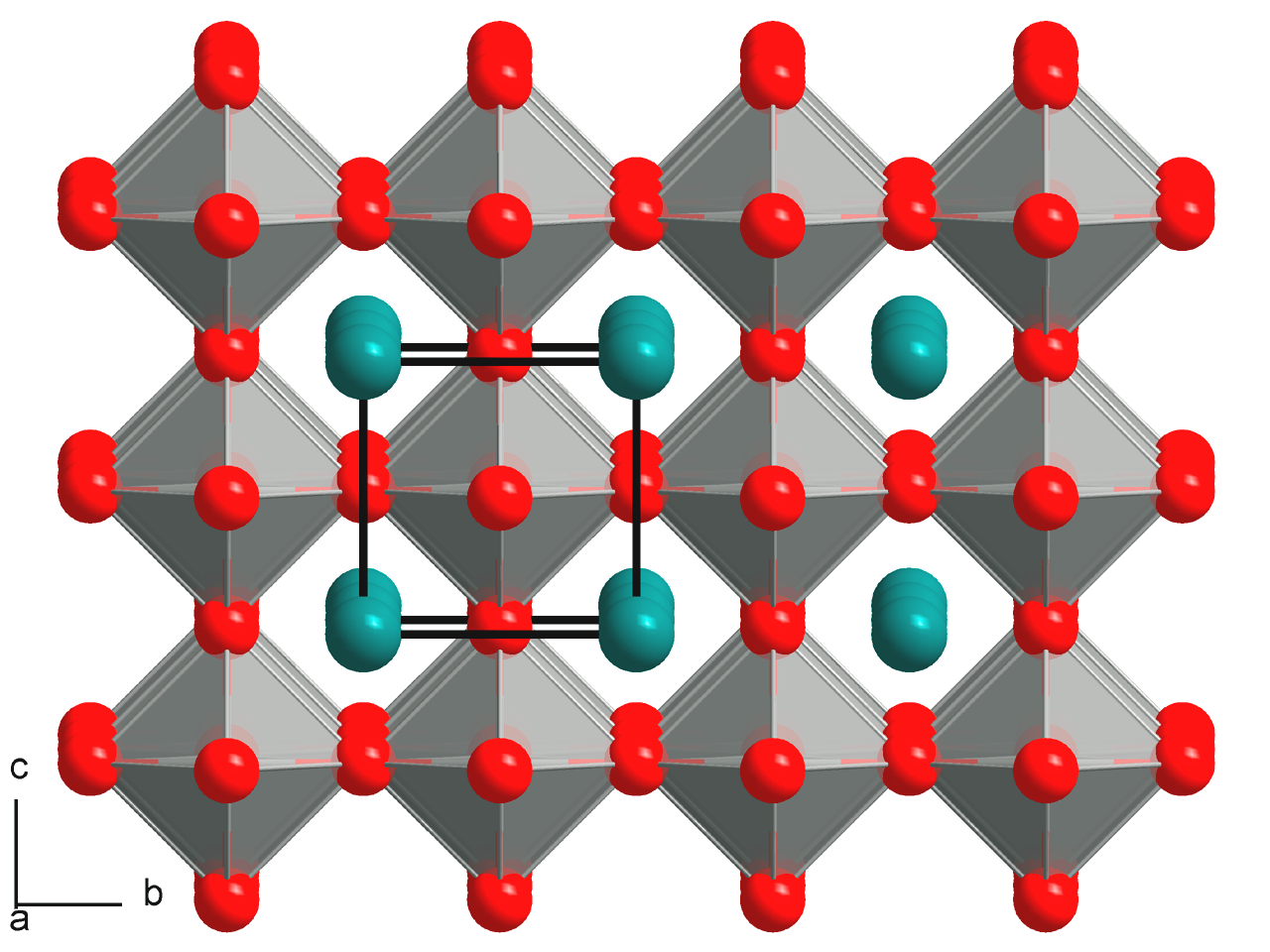
Antiperovskite
Antiperovskites (or inverse perovskites) is a type of crystal structure similar to the perovskite structure that is common in nature. The key difference is that the positions of the cation and anion constituents are reversed in the unit cell structure. In contrast to perovskite, antiperovskite compounds consist of two types of anions coordinated with one type of cation. Antiperovskite compounds are an important class of materials because they exhibit interesting and useful physical properties not found in perovskite materials, including as electrolytes in solid-state batteries.Xia W, Zhao Y, Zhao F, et al. Antiperovskite Electrolytes for Solid-State Batteries. Chem Rev. 2022;122(3):3763-3819. Structure The crystal lattice of an antiperovskite structure is the same as that of the perovskite structure, but the anion and cation positions are switched. The typical perovskite structure is represented by the general formula ABX3, where A and B are cations and X is an anion. When t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite Structure
A perovskite is any material with a crystal structure following the formula ABX3, which was first discovered as the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). 'A' and 'B' are two positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite forms may exist where either/both the A and B sites have a configuration of A1x-1A2x and/or B1y-1B2y and the X may deviate from the ideal coordination configuration as ions within the A and B sites undergo changes in thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctite
Arctite ( Na2 Ca4( P O4)3 F) is a colourless mineral found in the Kola Peninsula northern Russia. Its IMA symbol is Arc. It has a Mohs hardness of 5 and has a specific gravity of 3.13. Arctite is transparent with a vitreous lustre. Arctite has a perfect cleavage and a trigonal crystal system. It is also a naturally occurring antiperovskite. Common associates of arctite include aegirine Aegirine is a member of the clino pyroxene group of inosilicate minerals. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula Na Fe Si2 O6 in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augit ..., natisite, lomonosovite, umbite and thenardite. References Webmineral data Phosphate minerals Trigonal minerals Minerals in space group 166 {{phosphate-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kogarkoite
Kogarkoite is a sodium sulfate fluoride mineral with formula Na3(SO4)F. It has a pale blue color, a specific gravity of about 2.67 and a hardness of 3.5. The crystal is monoclinic and is a type of naturally occurring antiperovskite. Kogarkoite is named after the Russian petrologist Lia Nikolaevna Kogarko (born 1936) who discovered the mineral. Discovery and occurrence Kogarkoite was first described in 1973 for an occurrence on Alluaiv Mountain, Lovozero Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia. On Alluaiv it occurs in pegmatitic veins in nepheline syenite. It occurs with sodalite in syenite xenoliths in an alkali intrusive complex at Mont Saint-Hilaire, Canada. In Hortense Hot Spring, Chaffee County, Colorado, it occurs as a sublimate. It occurs at Lake Natron near Ol Doinyo Lengai, Tanzania and Suswa Volcano, Lake Magadi, Kenya. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition follows name. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Stability
In chemistry, chemical stability is the thermodynamic stability of a chemical system. Thermodynamic stability occurs when a system is in its lowest energy state, or in chemical equilibrium with its environment. This may be a dynamic equilibrium in which individual atoms or molecules change form, but their overall number in a particular form is conserved. This type of chemical thermodynamic equilibrium will persist indefinitely unless the system is changed. Chemical systems might undergo changes in the phase of matter or a set of chemical reactions. State A is said to be more thermodynamically stable than state B if the Gibbs free energy of the change from A to B is positive. Versus reactivity Thermodynamic stability applies to a particular system. The reactivity of a chemical substance is a description of how it might react across a variety of potential chemical systems and, for a given system, how fast such a reaction could proceed. Chemical substances or states can pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR. The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on spin orientation. The main application of GMR is in magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ion Conductor
In materials science, fast ion conductors are solid conductors with highly mobile ions. These materials are important in the area of solid state ionics, and are also known as solid electrolytes and superionic conductors. These materials are useful in batteries and various sensors. Fast ion conductors are used primarily in solid oxide fuel cells. As solid electrolytes they allow the movement of ions without the need for a liquid or soft membrane separating the electrodes. The phenomenon relies on the hopping of ions through an otherwise rigid crystal structure. Mechanism Fast ion conductors are intermediate in nature between crystalline solids which possess a regular structure with immobile ions, and liquid electrolytes which have no regular structure and fully mobile ions. Solid electrolytes find use in all solid-state supercapacitors, batteries, and fuel cells, and in various kinds of chemical sensors. Classification In solid electrolytes (glasses or crystals), the ionic condu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came more than a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the balanced equation is: : Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. This particular chemical equation is an example of complete combustion. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldschmidt Tolerance Factor
Goldschmidt's tolerance factor (from the German word ''Toleranzfaktor'') is an indicator for the stability and distortion of crystal structures. It was originally only used to describe the perovskite ABO3 structure, but now tolerance factors are also used for ilmenite. Alternatively the tolerance factor can be used to calculate the compatibility of an ion with a crystal structure. The first description of the tolerance factor for perovskite was made by Victor Moritz Goldschmidt in 1926. Mathematical expression The Goldschmidt tolerance factor (t) is a dimensionless number that is calculated from the ratio of the ionic radii: In an ideal cubic perovskite structure, the lattice parameter (i.e., length) of the unit cell (a) can be calculated using the following equation: Perovskite structure The perovskite structure has the following tolerance factors (t): See also * Goldschmidt classification * Victor Goldschmidt Victor Moritz Goldschmidt (27 January 1888 in Z� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |