|
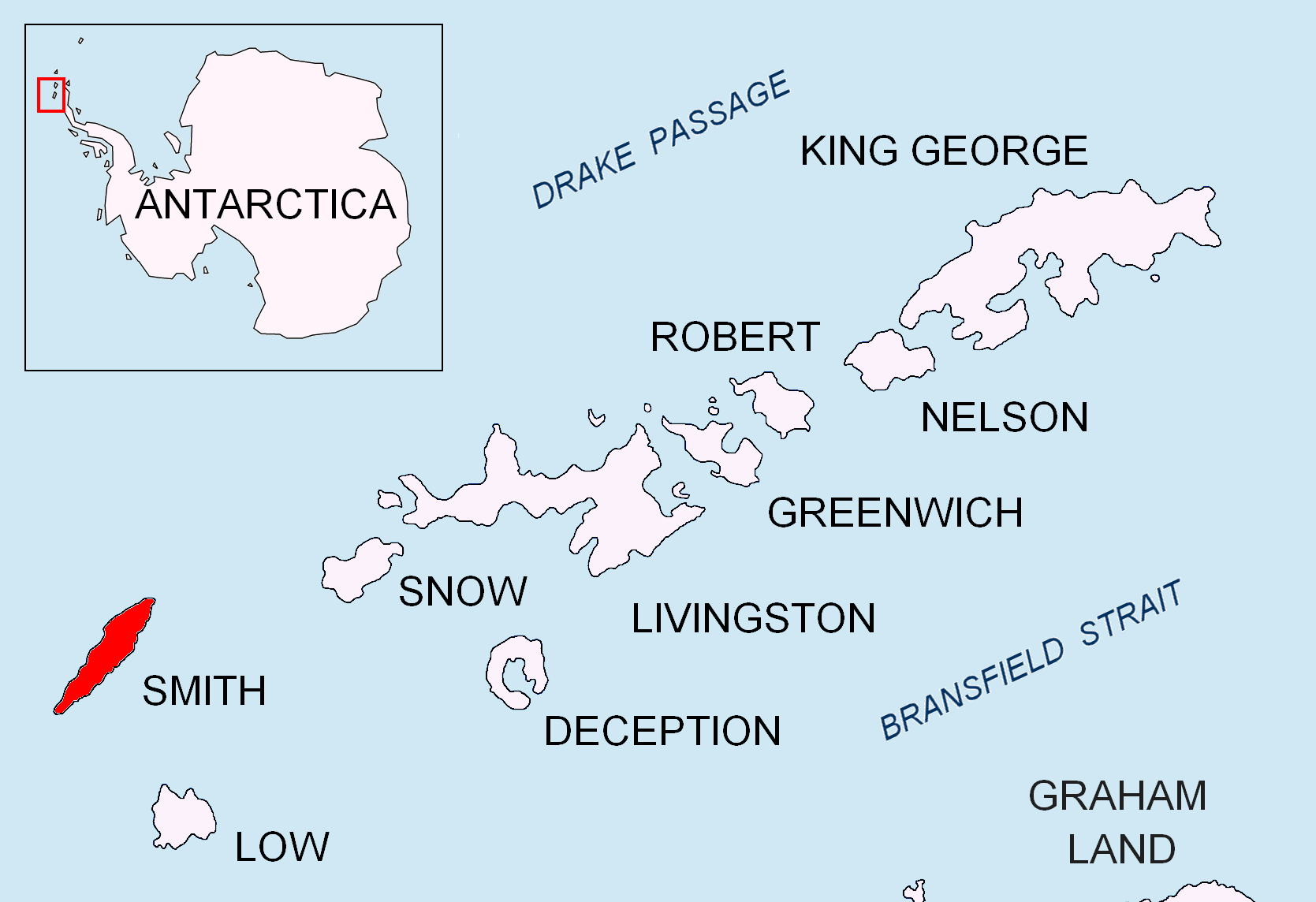
Antim Peak
Antim Peak ( bg, връх Антим, vrah Antim, ; ) is the ice-covered peak rising to 2080 m in Imeon Range on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Situated 2.25 km and 1.3 km northeast of the summit Mount Foster and Evlogi Peak respectively, 5.4 km south-southwest of Mount Pisgah, 16 km southwest of Cape Smith, and 16 km northeast of Cape James. The peak surmounts Chuprene Glacier to the west and northwest, Krivodol Glacier to the northeast and east, and Pashuk Glacier to the southeast. Precipitous and partly ice-free southeast slopes. Confirmed to be a separate peak rather than part of Mount Foster by the team of Greg Landreth that made the first ascent of the latter in 1996. Antim Peak was first ascended by the French mountaineers Mathieu Cortial, Lionel Daudet and Patrick Wagnon on 12 January 2010. Their route called ''Le vol du sérac'' (Flight of the Serac) followed the western spur of the peak.D. Gildea2009–10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountaineering
Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, and bouldering are also considered variants of mountaineering by some. Unlike most sports, mountaineering lacks widely applied formal rules, regulations, and governance; mountaineers adhere to a large variety of techniques and philosophies when climbing mountains. Numerous local alpine clubs support mountaineers by hosting resources and social activities. A federation of alpine clubs, the International Climbing and Mountaineering Federation (UIAA), is the International Olympic Committee-recognized world organization for mountaineering and climbing. The consequences of mountaineering on the natural environment can be seen in terms of individual components of the environment (land relief, soil, vegetation, fauna, and landscape) and location/z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gazett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bulgarian Toponyms In Antarctica
Bulgarian toponyms in Antarctica are approved by the Antarctic Place-names Commission in compliance with its ''Toponymic Guidelines'', and formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution and the established international and Bulgarian practice. Place naming is confined to nameless geographic features situated in the Antarctic Treaty area, the region south of the parallel 60 degrees south latitude. Details of the Bulgarian Antarctic toponyms are published by the websites of the commission and the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Alphabetical lists of the relevant place names: * A * B * C * D * E * F * G * H * I * J * K * L * M * N * O * P * Q * R * S * T * U * V * W * Y * Z See also * Antarctic Place-names Commission * Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica * Bulgarian placename etymology External links Bulgarian Antarctic Gaze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Orthodox Church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarska patriarshiya), is an autocephalous Orthodox jurisdiction. It is the oldest Slavic Orthodox church, with some 6 million members in Bulgaria and between 1.5 and 2 million members in a number of European countries, the Americas, Australia, New Zealand and Asia. It was recognized as autocephalous in 1945 by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. History Early Christianity The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles Paul and Andrew in the 1st century AD, when the first organised Christian communities were formed. By the beginning of the 4th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and the Bulgarian Patriarchate was restored in 1953. The Exarchate (a de facto autocephaly) was unilaterally (without the blessing of the Ecumenical Patriarch) promulgated on , in the Bulgarian church in Constantinople in pursuance of the firman of Sultan Abdülaziz of the Ottoman Empire. The foundation of the Exarchate was the direct result of the struggle of the Bulgarian Orthodox against the domination of the Greek Patriarchate of Constantinople in the 1850s and 1860s. In 1872, the Patriarchate accused the Exarchate that it introduced ''ethno-national'' characteristics in the religious organization of the Orthodox Church, and the secession from the Patriarchate was officially condemned by the Council in Constantinople in September 1872 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antim I
Anthim I (, secular name Atanas Mihaylov Chalakov, ; 1816 – 1 December 1888) was a Bulgarian education figure and clergyman, and a participant in the Bulgarian liberation and church-independence movement. He was the first head of the Bulgarian Exarchate, a post he held from 1872 to 1877. He was also the first Chairman of the National Assembly of Bulgaria, presiding the Constituent Assembly and the 1st Grand National Assembly in 1879. Anthim I was born in Kırk Kilise (Lozengrad) in Eastern Thrace (today Kırklareli, Turkey) and became a monk in the Hilendar monastery on Mount Athos. He studied in the Halki seminary (on the Princes' Islands near Constantinople), in Odessa as well as in Russia. He graduated from the Moscow Theological Academy (in Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra) in 1856. He was ordained hieromonk by Metropolitan of Moscow Philaret Drozdov. He was Archbishop of Preslav (from 1861) and then of Vidin (from 1868). After he unilaterally declared an independent national ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarch
An exarch (; from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'', meaning “leader”) was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical. In the late Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, an ''exarch'' was a governor of a particular territory. From the end of the 3rd century or early 4th, every Roman diocese was governed by a vicarius, who was titled "exarch" in eastern parts of the Empire, where the Greek language and the use of Greek terminology dominated, even though Latin was the language of the imperial administration from the provincial level up until the 440s (Greek translations were sent out with the official Latin text). In Greek texts, the Latin title is spelled βικάριος (). The office of exarch as a governor with extended political and military authority was later created in the Byzantine Empire, with jurisdiction over a particular territory, usually a frontier region at some distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |