|
Anti-Zionism In The Soviet Union
Soviet anti-Zionism is an Anti Zionist and pro-Arab doctrine promulgated in the Soviet Union during the Cold War. While the Soviet Union initially pursued a pro-Zionist policy after World War II due to its perception that the Jewish state would be socialist and pro-Soviet, its outlook on the Arab–Israeli conflict changed as Israel began to develop a close relationship with the United States and aligned itself with the Western Bloc. Anti-Israel Soviet propaganda intensified after Israel's sweeping victory in the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, and it was officially sponsored by the agitation and propaganda media of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union as well as by the KGB. Among other charges, it alleged that Zionism was a form of racism. The Soviets framed their anti-Zionist propaganda in the guise of a study of modern Zionism, dubbed ''Zionology''. The Soviet anti-Israel policy included the regulated denial of permission for Jews in the Soviet Union to emigrate, primarily t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Zionism
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestine – the biblical Land of Israel – was flawed or unjust in some way.Mor, Shany. "On Three Anti-Zionisms." ''Israel Studies'', vol. 24, no. 2, summer 2019, pp. 206+. Gale In Context: World History. Accessed 2 Nov. 2022. Until World War II, anti-Zionism was widespread among Jews for varying reasons. Orthodox Jews opposed Zionism on religious grounds, as preempting the Messiah, while secular Jews felt uncomfortable with the idea that Jewish peoplehood was a national or ethnic identity. Opposition to Zionism in the Jewish diaspora was surmounted only from the 1930s onward, as conditions for Jews deteriorated radically in Europe and, with the Second World War, the sheer scale of the Holocaust struck home. Thereafter, Jewish anti-Zionist g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
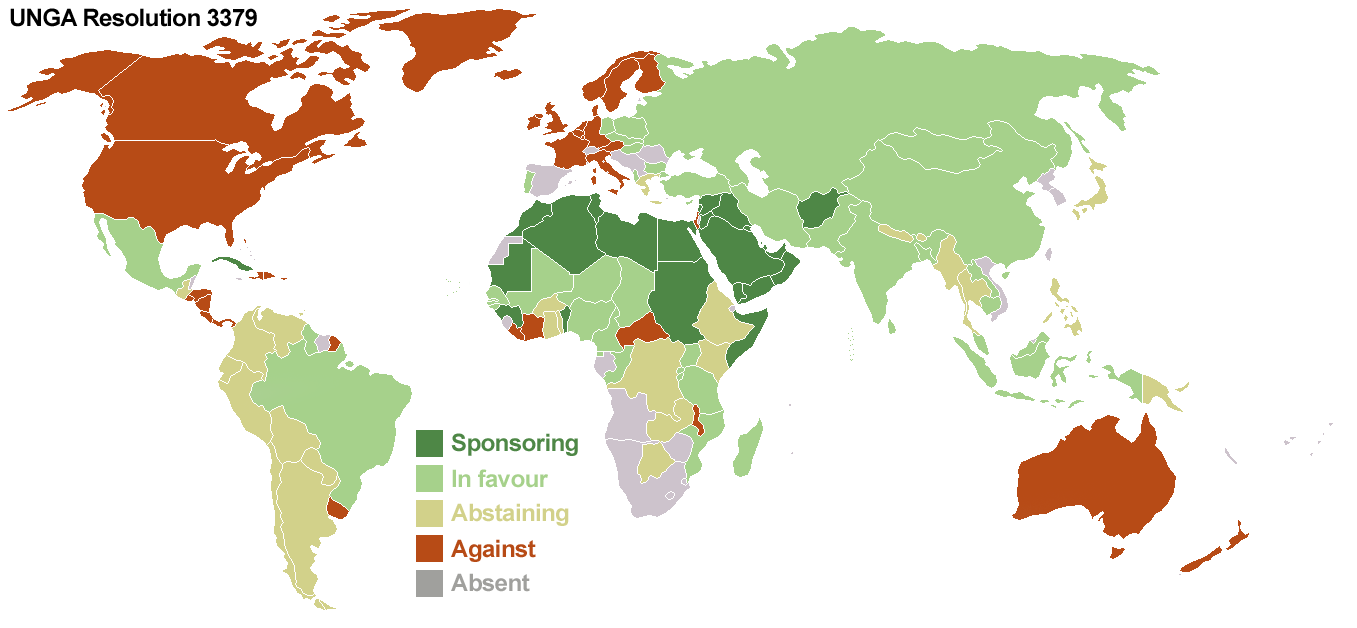
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, adopted on 10 November 1975 by a vote of 72 to 35 (with 32 abstentions), "determine that Zionism is a form of racism and racial discrimination". It was revoked in 1991 with UN General Assembly Resolution 46/86. The vote on Resolution 3379 took place approximately one year after UNGA 3237 granted the PLO Permanent Observer status, following PLO president Yasser Arafat's "olive branch" speech to the General Assembly in November 1974. The resolution was passed with the support of the Soviet bloc, in addition to the Arab- and Muslim-majority countries, many African countries, and a few others. Background In July 1920, at the San Remo conference, a Class "A" League of Nations mandates over Palestine was allocated to the British. The preamble of the mandate document declared: Whereas the Principal Allied Powers have also agreed that the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the declaration originally made on No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally recognized. Examples Between 1805 and 1914, the ruling dynasty of Egypt were subject to the rulers of the Ottoman Empire, but acted as de facto independent rulers who maintained a polite fiction of Ottoman suzerainty. However, starting from around 1882, the rulers had only de jure rule over Egypt, as it had by then become a British puppet state. Thus, by Ottoman law, Egypt was de jure a province of the Ottoman Empire, but de facto was part of the British Empire. In U.S. law, particularly after ''Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954), the difference between de facto segregation (segregation that existed because of the voluntary associations and neighborhoods) and de jure segregation (segregation that existed because of local laws that m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His Majesty's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
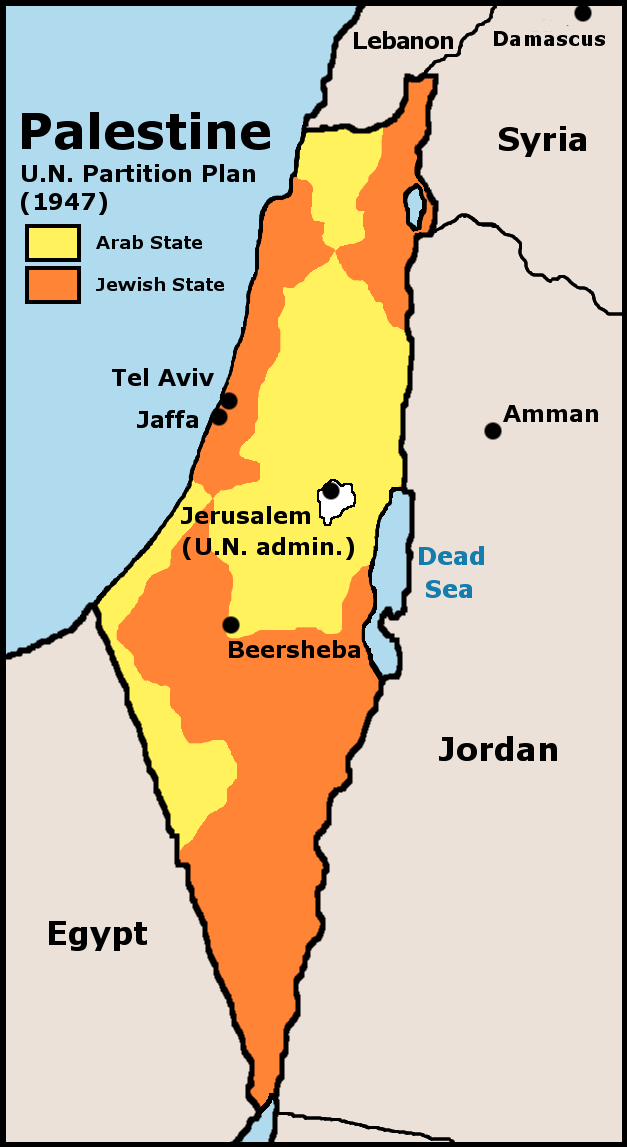
United Nations Partition Plan For Palestine
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II). The resolution recommended the creation of independent Arab and Jewish States and a Special International Regime for the city of Jerusalem. The Partition Plan, a four-part document attached to the resolution, provided for the termination of the Mandate, the progressive withdrawal of British armed forces and the delineation of boundaries between the two States and Jerusalem. Part I of the Plan stipulated that the Mandate would be terminated as soon as possible and the United Kingdom would withdraw no later than 1 August 1948. The new states would come into existence two months after the withdrawal, but no later than 1 October 1948. The Plan sought to address the conflicting objectives and claims of two competing movements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed during the Cold War (1947–1991). These states followed the ideology of Marxism–Leninism, in opposition to the Capitalism, capitalist Western Bloc. The Eastern Bloc was often called the Second World, whereas the term "First World" referred to the Western Bloc and "Third World" referred to the Non-Aligned Movement, non-aligned countries that were mainly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America but notably also included former Tito–Stalin split, pre-1948 Soviet ally SFR Yugoslavia, which was located in Europe. In Western Europe, the term Eastern Bloc generally referred to the USSR and Central and Eastern European countries in the Comecon (East Germany, Polish People's Republic, Poland, Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, Czechoslovakia, Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Johnson (writer)
Paul Bede Johnson (born 2 November 1928) is an English journalist, popular historian, speechwriter, and author. Although associated with the political left in his early career, he is now a conservative popular historian. Johnson was educated at the Jesuit independent school Stonyhurst College, and at Magdalen College, Oxford. He first came to prominence in the 1950s as a journalist writing for and later editing the ''New Statesman'' magazine. A prolific writer, Johnson has written over 40 books and contributed to numerous magazines and newspapers. His sons include the journalist Daniel Johnson, founder of '' Standpoint'' magazine, and the businessman Luke Johnson, former chairman of Channel 4. Early life and career Johnson was born in Manchester. His father, William Aloysius Johnson, was an artist and Principal of the Art School in Burslem, Stoke-on-Trent, Staffordshire. At Stonyhurst College, Johnson received an education grounded in the Jesuit method, which he preferre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the economic, political and social theories and movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can be state/public, community, collective, cooperative, or employee. While no single definition encapsulates the many types of socialism, social ownership is the one common element. Different types of socialism vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, on the structure of management in organizations, and from below or from above approaches, with some socialists favouring a party, state, or technocratic-driven approach. Socialists disagree on whether government, particularly existing government, is the correct vehicle for change. Socialist systems are divided into non-market and market f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism. Born to a poor family in Gori in the Russian Empire (now Georgia), Stalin attended the Tbilisi Spiritual Seminary before joining the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. He edited the party's newspaper, ''Pravda'', and raised funds for Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction via robberies, kidnappings and protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1924 and of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1924. Under his administration, Russia, and later the Soviet Union, became a one-party socialist state governed by the Communist Party. Ideologically a Marxist, his developments to the ideology are called Leninism. Born to an upper-middle-class family in Simbirsk, Lenin embraced revolutionary socialist politics following his brother's 1887 execution. Expelled from Kazan Imperial University for participating in protests against the Russian Empire's Tsarist government, he devoted the following years to a law degree. He moved to Saint Petersburg in 1893 and became a senior Marxist activist. In 1897, he was arrested for sedition and exiled to Shushenskoye in Siberia for three years, where he married ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

