|
Anthocarp
An accessory fruit is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the floral ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel.Esau, K. 1977. ''Anatomy of seed plants''. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Accessory fruits are usually indehiscent. Terminology Alternative terms for accessory fruit are false fruit, spurious fruit, pseudofruit, or pseudocarp. These are older terms for accessory fruit that have been criticized as "inapt", and are not used by some botanists today. Examples The following are examples of accessory fruits listed by the plant organ from which the accessory tissue is derived: * Hypanthium-derived: pomes (e.g. apple and pear) * Perianth-derived: ''anthocarps'' of the Nyctaginaceae * Receptacle-derived: fig, mulberry, pineapple, and strawberry * Calyx-derived: '' Gaultheria procumbens'' and ''Syzygium jambos'' Fruit with fleshy seeds, such as pomegranate or mamoncillo, are not considered to be accessory fruits. Research Cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is consumed in large quantities, either fresh or in such prepared foods as jam, juice, pies, ice cream, milkshakes, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavorings and aromas are also widely used in products such as candy, soap, lip gloss, perfume, and many others. The garden strawberry was first bred in Brittany, France, in the 1750s via a cross of ''Fragaria virginiana'' from eastern North America and ''Fragaria chiloensis'', which was brought from Chile by Amédée-François Frézier in 1714. Cultivars of ''Fragaria'' × ''ananassa'' have replaced, in commercial production, the woodland strawberry ('' Fragaria vesca''), which was the first straw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Fruit
The term compound fruit is not used in technical botanical writing, but is sometimes used when it is not clear which of several fruit types is involved. A compound fruit is "composed of two or more similar parts". A compound fruit may be: * An aggregate fruit, in which one flower contains several separate ovaries, which merge during development. * A multiple fruit, in which several flowers, each with an ovary, develop into small fruits that are clustered or fused together into a larger fruit. * A simple fruit formed from a compound ovary. Image:Frambozenkever.jpg, A raspberry is an aggregate fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle larva) Image:Pineapple and cross section.jpg, A pineapple is a multiple fruit Image:Kumato 02.jpg, A tomato is a simple fruit derived from a compound ovary Grape A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Fruit
A raspberry fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle larva) is an aggregate fruit, an aggregate of drupe">raspberry_beetle.html" ;"title="raspberry fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle">raspberry fruit (shown with a raspberry beetle larva) is an aggregate fruit, an aggregate of drupelets image:Aquilegia vulgaris 004.JPG, The fruit of an ''Aquilegia'' flower is one fruit that forms from several ovaries of one flower, and it is an aggregate of follicles. However, because the follicles are not fused to one another, it is not considered an aggregate fruit An aggregate fruit or etaerio () is a fruit that develops from the merger of several ovaries that were separated in a single flower. In contrast, a ''simple fruit'' develops from one ovary, and a '' multiple fruit'' develops from multiple flowers. In languages other than English, the meanings of "aggregate" and "multiple" fruit are reversed, so that "aggregate" fruits merge several flowers. The differences in meaning are due to a reversal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triterpenoids
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids. Structures Triterpenes exist in a great variety of structures. Nearly 200 different skeletons have been identified. These skeletons may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. In general pentacyclic structures (5 rings) tend to dominate. Squalene is biosynthesized through the head-to-head condensation of two farnesyl pyrophosphate units. This coupling converts a pair of C15 components into a C30 product. Squalene serves as precursor for the formation of many triterpenoids, including bacterial hopanoids and eukaryotic sterols. Triterpenoids By definition triterpenoids are triterpenes that possess heteroatoms, usually oxygen. The terms ''triterpene'' and ''triterpenoid'' ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
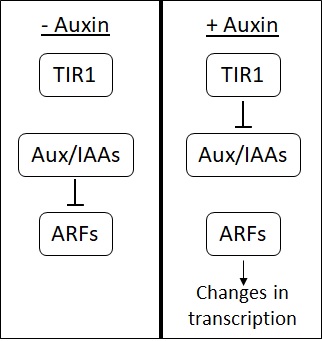
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibberellic Acid
Gibberellic acid (also called gibberellin A3, GA, and GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Its chemical formula is C19H22O6. When purified, it is a white to pale-yellow solid. Plants in their normal state produce large amounts of GA3. It is possible to produce the hormone industrially using microorganisms.Camara, M. C. et al (2015) General Aspects and Applications of Gibberelins and Gibberellic Acid in Plants. In: Hardy, J.. (Org.). Gibberellins and Gibberellic Acid: Biosynthesis, Regulation and Physiological Effects. 1ed.Hauppauge: Nova Science Publishers, 2015, v., p. 1-21. Gibberellic acid is a simple gibberellin, a pentacyclic diterpene acid promoting growth and elongation of cells. It affects decomposition of plants and helps plants grow if used in small amounts, but eventually plants develop tolerance to it. GA stimulates the cells of germinating seeds to produce mRNA molecules that code for hydrolytic enzymes. Gibberellic acid is a very potent hormone whose natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melicoccus Bijugatus
''Melicoccus bijugatus'' is a fruit-bearing tree in the soapberry family Sapindaceae, native or naturalized across the New World tropics including South and Central America, and parts of the Caribbean. Its stone-bearing fruits are edible. It is also called Bajan ackee, genip, guinep, genipe, ginepa, kenèp, quenepa, quenepe, quenette, chenet, skinup, talpa jocote, mamón, limoncillo, canepa, skinip, kenepa, kinnip, huaya, or mamoncillo. Taxonomy The genus ''Melicoccus'' was first described by Patrick Browne, an Irish physician and botanist, in 1756. This description was based on ''M. bijugatus'' trees which were cultivated in Puerto Rico. In 1760, Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin described the first species in Browne's genus, which he named ''M. bijugatus''. In 1762 Linnaeus used a spelling variation of the name ''Melicocca bijuga''. Over the next two centuries, Linnaeus' spelling variation was used in almost all publications. A proposal was made in 1994 to conserve ''Melicocca'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall. The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean region. It was introduced into Spanish America in the late 16th century and into California by New Spain, Spanish settlers in 1769. The fruit is typically in season in the Southern Hemisphere from March to May, and in the Northern Hemisphere from September to February. As intact sarcotestas or juice, pomegranates are used in baking, cooking, juice blends, meal garnish (food), garnishes, smoothies, and alcoholic beverages, such as cocktails and wine. Pomegranates are widely cultivated throughout the Middle East and Caucasus region, North Africa, north and tropical Africa, Iran, Armenia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the drier parts of Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean Basin. Etymology The name pomegranate derives from medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syzygium Jambos
''Syzygium jambos'' is a species of rose apple originating in Southeast Asia and occurring widely elsewhere, having been introduced as an ornamental and fruit tree.Janick, Jules. Paull, Robert E. The Encyclopedia of Fruit & Nuts. Publisher: CABI 2008. Description ''Syzygium jambos'' is a large shrub or small-to-medium-sized tree, typically high, with a tendency to low branching. Its leaves and twigs are glabrous and the bark, though dark brown, is fairly smooth too, with little relief or texture. The leaves are lanceolate, broad, long, pointed, base cuneate with hardly any petiole, lively red when growing, but dark, glossy green on attaining full size. The flowers are in small terminal clusters, white or greenish white, the long, numerous stamens giving them a diameter of . In temperate regions the tree is summer-flowering. The fruit is shaped like some kinds of guava; in fact, the fruit is so like the guava in appearance that people unfamiliar with it may mistake i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaultheria Procumbens
''Gaultheria procumbens'', also called the eastern teaberry, the checkerberry, the boxberry, or the American wintergreen, is a species of ''Gaultheria'' native to northeastern North America from Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland west to southeastern Manitoba, and south to Alabama. It is a member of the Ericaceae (heath family). Growth and habitat ''G. procumbens'' is a small, low-growing shrub, typically reaching tall. The leaves are evergreen, elliptic to ovate, long and broad, with a distinct oil of wintergreen scent. The flowers are pendulous, with a white, sometimes pink-tinged, bell-shaped corolla (botany), corolla with five teeth at the tip long, and above it a white calyx (botany), calyx. They are borne in leaf axils, usually one to three per stem. The anthers are forked somewhat like a snake's tongue, with two awn (botany), awns at the tip. The fruit is red and across. It is an epigynous berry, with the majority of the flesh of the fruit being composed of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)