|
Antheridiophone
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchantia Polymorpha
''Marchantia polymorpha'' is a species of large thalloid liverwort in the class Marchantiopsida. ''M. polymorpha'' is highly variable in appearance and contains several subspecies. This species is dioicous, having separate male and female plants. ''M. polymorpha'' has a wide distribution and is found worldwide.Matthews, Robin F. 1993. Marchantia polymorpha. In: Fire Effects Information System, nline U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/bryophyte/marpol/all.html 017, December 8 Common names include common liverwort or umbrella liverwort. Distribution ''Marchantia polymorpha'' subsp. ''ruderalis'' has a circumpolar boreo-arctic cosmopolitan distribution, found worldwide on all continents except Antarctica. Habitat ''Marchantia polymorpha'' grows on shaded moist soil and rocks in damp habitats such as the banks of streams and pools, bogs, fen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnum Cupressiforme
''Hypnum cupressiforme'', the cypress-leaved plaitmoss or hypnum moss, is a common and widespread species of moss belonging to the genus ''Hypnum''. It is found in all continents except Antarctica and occurs in a wide variety of habitats and climatic zones. It typically grows on tree trunks, logs, walls, rocks and other surfaces. It prefers acidic environments and is fairly tolerant of pollution. It was formerly used as a filling for pillows and mattresses; the association with sleep is the origin of the genus name ''Hypnum'' (from Greek ''Hypnos''). It is a small to medium-sized moss about 2–10 cm long. It is pleurocarpous, having prostrate, creeping stems which form smooth, dense mats. The stems are branched and covered in overlapping leaves giving the impression of a cypress tree. The stem leaves are long and thin measuring 1.0-2.1 mm by 0.3-0.6 mm. They are concave and sickle-shaped, tapering towards the tip. The branch leaves are smaller and narrower than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chara (alga)
''Chara'' is a genus of charophyte green algae in the family Characeae. They are multicellular and superficially resemble land plants because of stem-like and leaf-like structures. They are found in freshwater, particularly in limestone areas throughout the northern temperate zone, where they grow submerged, attached to the muddy bottom. They prefer less oxygenated and hard water and are not found in waters where mosquito larvae are present. They are covered with calcium carbonate deposits and are commonly known as stoneworts. Cyanobacteria have been found growing as epiphytes on the surfaces of ''Chara'', where they may be involved in fixing nitrogen, which is important to plant nutrition. Structure The branching system of ''Chara'' species is complex with branches derived from apical cells which cut off segments at the base to form nodal and internodal cells alternately.Round, F.E. 1965.''The Biology of the algae.'' Ernest Arnold. The main axes bear whorls of branches in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oogonium
An oogonium (plural oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes. In the mammalian fetus Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells. In humans they start to develop between weeks 4 and 8 and are present in the fetus between weeks 5 and 30. Structure Normal oogonia in human ovaries are spherical or ovoid in shape and are found amongst neighboring somatic cells and oocytes at different phases of development. Oogonia can be distinguished from neighboring somatic cells, under an electron microscope, by observing their nuclei. Oogonial nuclei contain randomly dispersed fibrillar and granular material whereas the somatic cells have a more condensed nucleus that creates a darker outline under the microscope. Oogonial nuclei also contain dense prominent nucleoli. The chromosomal material in the nucleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
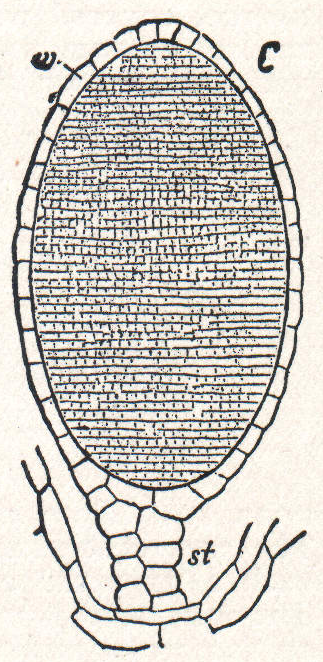
Gametophore
Gametophores are prominent structures in seedless plants on which the reproductive organs are borne. The word gametophore and ‘-phore’ (Greek Φορά, "to be carried"). In mosses, liverworts and ferns (Archegoniata), the gametophores support gametangia (sex organs, female archegonia and male antheridia). If both archegonia and antheridia occur on the same plant, it is called monoecious. If there are separate female and male plants they are called dioecous. In Bryopsida the leafy moss plant (q. v. "Thallus") is the haploid gametophyte. It grows from its juvenile form, the protonema, under the influence of phytohormones (mainly cytokinins). Whereas the filamentous protonema grows by apical cell division, the gametophyte grows by division of three-faced apical cells. See also Rhizoid Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division (mitosis), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces Haploidisation, haploid gametes for sexual reproduction (meiosis), reducing the number of chromosomes from two of each type in the diploid parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells. In cell biology, mitosis (Help:IPA/English, /maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte. Spermatids are connected by cytoplasmic material and have superfluous cytoplasmic material around their nuclei. When formed, ''early round spermatids'' must undergo further maturational events to develop into spermatozoa, a process termed spermiogenesis (also termed ''spermeteliosis''). The spermatids begin to grow a living thread, develop a thickened mid-piece where the mitochondria become localised, and form an acrosome. Spermatid DNA also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive. In 2016 scientists at Nanjing Medical University clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" derives from the French word "tissu", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is studied in both plant anatomy and physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the histological stain, and the optical microscope. Developments in electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, and the use of frozen tissue-sections have enhanced the detail that can be observed in tissues. With these tools, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridia within the androecium. Flowers that bear a gynoecium but no stamens are called ''pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


