|
Anterolateral Sulcus Of Medulla
The anterolateral sulcus (or ventrolateral sulcus) is a sulcus on the side of the medulla oblongata between the olive and pyramid. The rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by ... (CN XII) emerge from this sulcus. See also * Anterolateral sulcus of spinal cord External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20070927162204/http://www.ib.amwaw.edu.pl/anatomy/atlas/image_02e.htm Medulla oblongata {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (anatomy)
In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus (pl. ''sulci'') is a furrow or fissure (Latin ''fissura'', plural ''fissurae''). It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles (including the heart), as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth. In invertebrate zoology, a sulcus is a fold, groove, or boundary, especially at the edges of sclerites or between segments. In pollen a grain that is grooved by a sulcus is termed sulcate. Examples in anatomy Liver * Ligamentum teres hepatis fissure *Ligamentum venosum fissure *Portal fissure, found in the under-surface of the liver *Transverse fissure of liver, found in the lower surface of the liver *Umbilical fissure, found in front of the liver Lung *Azygos fissure, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivary Body
In anatomy, the olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin ''oliva'' and ''olivae'', singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures in the medulla oblongata, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei. Structure The olivary body is located on the anterior surface of the medulla lateral to the pyramid, from which it is separated by the antero-lateral sulcus and the fibers of the hypoglossal nerve. Behind ( dorsally), it is separated from the postero-lateral sulcus by the ventral spinocerebellar fasciculus. In the depression between the upper end of the olive and the pons lies the vestibulocochlear nerve. In humans, it measures about 1.25 cm. in length, and between its upper end and the pons there is a slight depression to which the roots of the facial nerve are attached. The external arcuate fibers wind across the lower part of the pyramid and olive and enter the inferior peduncle. Olivary nuclei The olive consists of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Pyramids (brainstem)
In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal tract, corticospinal and corticobulbar tract, corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussation, decussate). Structure The ventral portion of the medulla oblongata contains the medullary pyramids. These two ridge-like structures travel along the length of the medulla oblongata and are bordered medially by the anterior median fissure of the medulla oblongata, anterior median fissure. They each have an anterolateral sulcus of medulla, anterolateral sulcus along their lateral borders, where the hypoglossal nerve emerges from. Also at the side of each pyramid there is a pronounced bulge known as an Olivary body, olive. Fibers of the Posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway, posterior column, which transmit somatosensory system, senso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
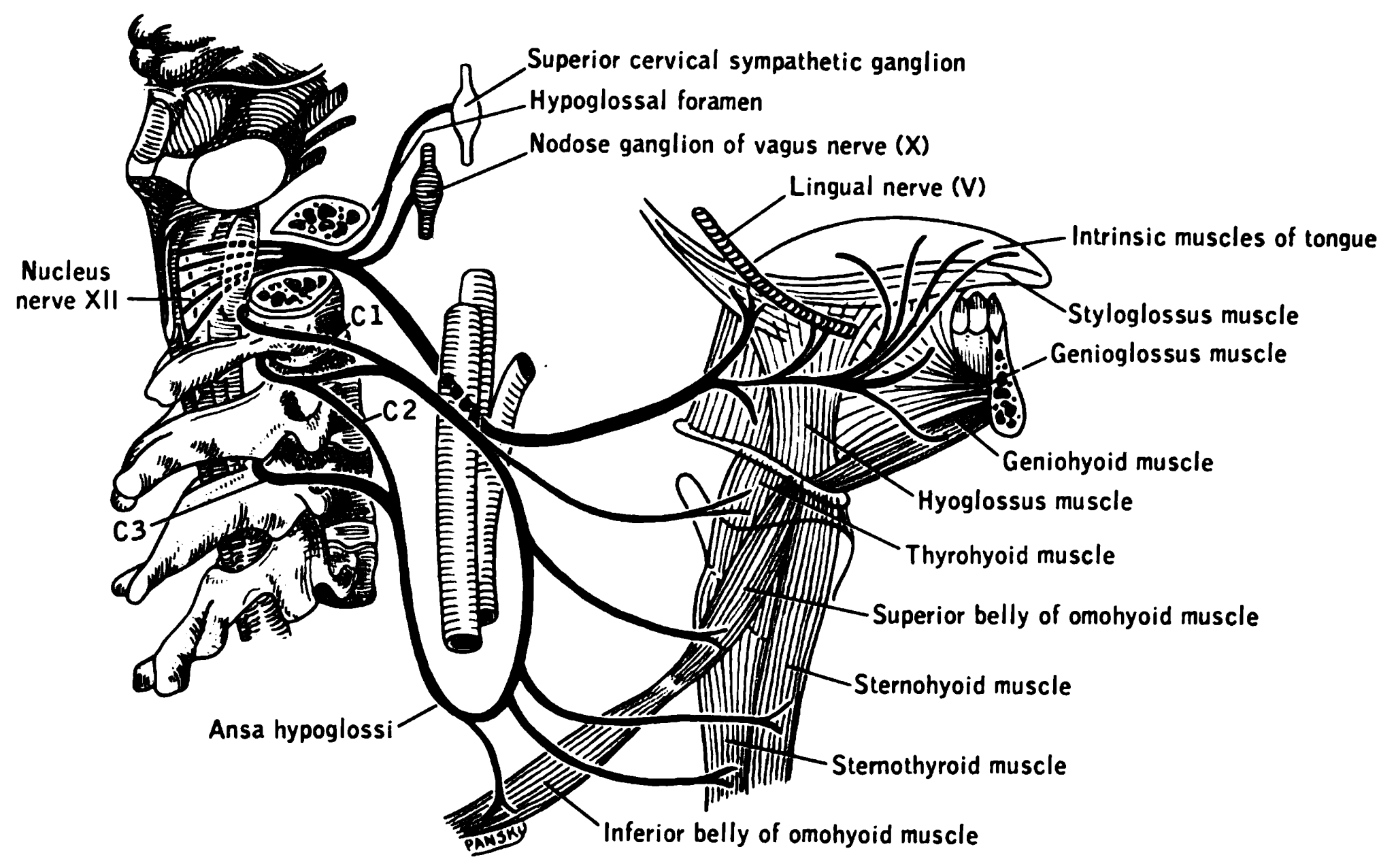
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a solely motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, passes through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve is by Herop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterolateral Sulcus Of Spinal Cord
The Anterolateral sulcus of spinal cord is a landmark on the anterior side of the spinal cord. It denotes the location at which the ventral fibers leave the spinal cord. The anterolateral sulcus is less visible than the posterolateral sulcus. See also * Anterolateral sulcus of medulla The anterolateral sulcus (or ventrolateral sulcus) is a sulcus on the side of the medulla oblongata between the olive and pyramid. The rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial ... References Spinal cord {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |