|
Anterior Commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. In most existing mammals, the great majority of fibers connecting the two hemispheres travel through the corpus callosum, which is over 10 times larger than the anterior commissure, and other routes of communication pass through the hippocampal commissure or, indirectly, via subcortical connections. Nevertheless, the anterior commissure is a significant pathway that can be clearly distinguished in the brains of all mammals. The anterior commissure plays a key role in pain sensation, more specifically sharp, acute pain. It also contains decussating fibers from the olfactory tracts, vital for the sense of smell and chemoreception. The anterior commissure works with the posterior commissure to link the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain and also int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Plane
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wreath'). The coronal plane is so-called because it lies in the direction of Coronal suture. Additional images File:Coronal plane CT scan of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decussating Fibers
Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. . Similarly, the anatomical term chiasma is named after the Greek uppercase 'Χ' (chi). Whereas a decussation refers to a crossing within the central nervous system, various kinds of crossings in the peripheral nervous system are called chiasma. Examples include: * In the brain, where nerve fibers obliquely cross from one lateral side of the brain to the other, that is to say they cross at a level other than their origin. See for examples Decussation of pyramids and sensory decussation. In neuroanatomy, the term ''chiasma'' is reserved for crossing of- or within nerves such as in the optic chiasm. * In botanical leaf taxology, the word ''decussate'' describes an opposite pattern of leaves which has successive pairs at right angles to each other (i.e. rotated 90 degrees along the stem when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve tracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light reflex. Its fibers acquire their medullary sheaths early, but their connections have not been definitively determined. Most of them have their origin in a nucleus, the ''nucleus of the posterior commissure'' (nucleus of Darkschewitsch), which lies in the periaqueductal grey at rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct, in front of the oculomotor nucleus. Some are thought to be derived from the posterior part of the thalamus and from the superior colliculus, whereas others are believed to be continued downward into the medial longitudinal fasciculus. For the pupillary light reflex, the olivary pretectal nucleus In neuroanatomy, the pretectal area, or pretectum, is a midbrain structure composed of seven nuclei and comprises part of the subcortical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosexual Men
Gay men are male homosexuals. Some bisexual men, bisexual and homoromantic men may also dually identify as gay, and a number of young gay men also identify as queer. Historically, gay men have been referred to by a number of different terms, including ''Sexual inversion (sexology), inverts'' and ''uranian (sexology), uranians''. Gay men continue to face significant Discrimination against gay men, discrimination in large parts of the world, particularly in most of LGBT rights in Asia, Asia and LGBT rights in Africa, Africa. In the LGBT rights in the United States, United States, many gay men still face discrimination in their daily lives, though some openly gay men have reached national success and prominence. In Europe, Xavier Bettel currently serves as the prime minister of Luxembourg; Leo Varadkar serves as the Taoiseach and Taoiseach, head of the Government of Ireland (he had previously served as Taoiseach (Prime Minister) from June 2017 to June 2020); and from 2011 to 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain. Introduction In diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), the intensity of each image element (voxel) reflects the best estimate of the rate of water diffusion at that location. Because the mobility of water is driven by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
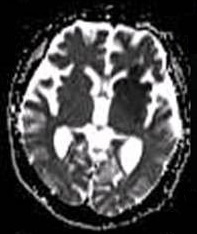
DTI Of The Anterior Commissure
DTI may refer to: Science and technology * Deep trench isolation; See Shallow trench isolation * Dial test indicator * Direct trader input, in the history of electronic data interchange * Diffusion tensor imaging, a structural medical imaging technique * Direct thrombin inhibitor * Diesel turbo injection, a brand name for common rail * Direct tension indicator * Deep tissue injury, see suspected deep tissue injury in List of medical abbreviations: S * Dye transfer inhibitor Organizations * Defence Technology Institute, the Thai defence technology public organisation * Department of Trade and Industry (other), a government department in several countries * Detroit, Toledo and Ironton Railroad * Diversified Technology, Inc. * Directorate of Terrorist Identities, responsible for the Terrorist Identities Datamart Environment Other uses * Debt-to-income ratio In the consumer mortgage industry, debt-to-income ratio (often abbreviated DTI) is the percentage of a consumer's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the neocortex is the largest part of the cerebral cortex (the outer layer of the cerebrum). The neocortex makes up the largest part of the cerebral cortex, with the allocortex making up the rest. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, jaws, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and other body parts, compared to the more common mammalian types. In addition, they lay eggs rather than bearing live young, but, like all mammals, the female monotremes nurse their young with milk. Monotremes have been considered members of Australosphenida, a clade that contains extinct mammals from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Madagascar, South America, and Australia, though this is disputed. The only surviving examples of monotremes are all indigenous to Australia and New Guinea, although there is evidence that they were once more widespread, as ''Monotrematum'' is known from the Paleocene of South America. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and four species of echidnas. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdalae
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures of the cerebrum with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, the central nucleus, and the intercalated cell clusters. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory basal nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neospinothalamic Tract
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal in order to trigger an appropriate defense response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in Chili pepper or Cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers via the spinal cord to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are detected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |