|
Antennopoda
The Antennopoda (or Arthropoda) are a proposed clade consisting of the Euarthropoda and the Onychophora, as sister of the Tardigrade, Tardigrada, together forming the Panarthropoda. ''Stanleycaris'' appears to be a basal Euarthropod. Antennopoda was defined by De Haro, where Tartigrada was not included in his tree. In a subsequent article of him, his use of Antennopoda was inconsistent with the current usage. Especially the position of the Tartigrada is disputed. References {{Reflist Panarthropoda Protostome unranked clades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panarthropoda
Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada (water bears) and Onychophora (velvet worms). Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well. Common characteristics of the Panarthropoda include a segmented body, paired ladder-like, ventral nervous system, and the presence of paired appendages correlated with body segments. Taxonomy Not all studies support the monophyly of Panarthropoda, but most do, including neuroanatomical, phylogenomic and palaeontological studies. At least a close relationship between onychophorans and arthropods is widely agreed upon, but the position of tardigrades is more controversial. Some phylogenomic studies have f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrade
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär ("little water bear"). In 1777, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada (), which means "slow steppers". They have been found in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other known forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,300 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa consisting of animals th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrada
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär ("little water bear"). In 1777, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada (), which means "slow steppers". They have been found in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other known forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,300 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa consisting of animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euarthropoda
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. Their nervous system is "ladder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onychophora
Onychophora (from grc, ονυχής, , "claws"; and , , "to carry"), commonly known as velvet worms (due to their velvety texture and somewhat wormlike appearance) or more ambiguously as peripatus (after the first described genus, '' Peripatus''), is a phylum of elongate, soft-bodied, many-legged panarthropods. In appearance they have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars, and slugs. They prey upon other invertebrates, which they catch by ejecting an adhesive slime. Approximately 200 species of velvet worms have been described, although the true number of species is likely greater. The two extant families of velvet worms are Peripatidae and Peripatopsidae. They show a peculiar distribution, with the peripatids being predominantly equatorial and tropical, while the peripatopsids are all found south of the equator. It is the only phylum within Animalia that is wholly endemic to terrestrial environments, at least among extant members. Velvet worms are generally c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
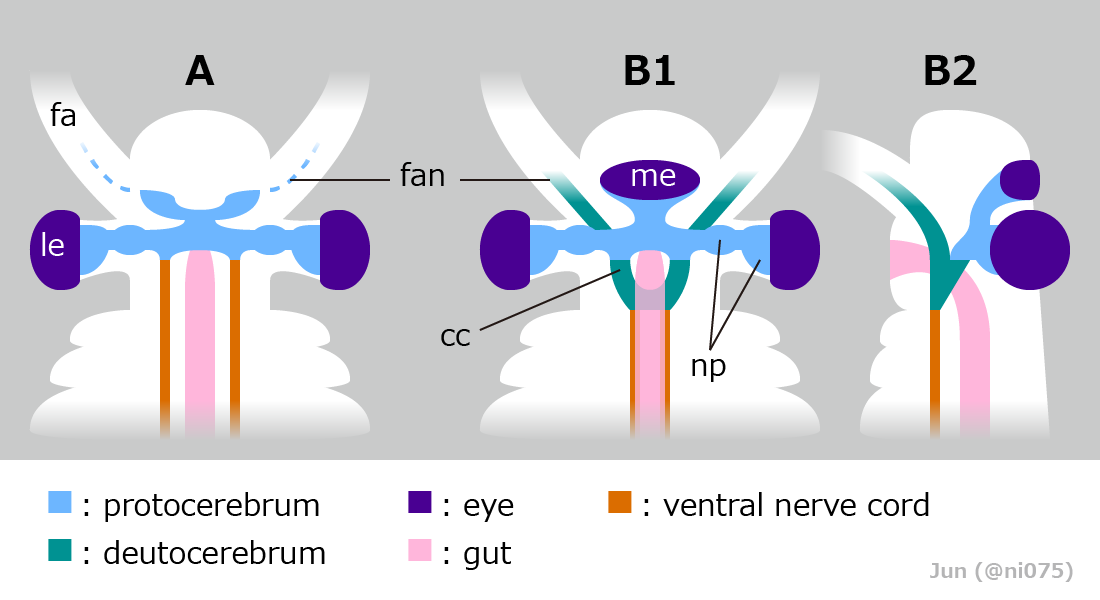
Stanleycaris
''Stanleycaris'' is an extinct, monotypic genus of hurdiid radiodont from the middle Cambrian (Miaolingian). The type species is ''Stanleycaris hirpex''. ''Stanleycaris'' was described from the Stephen Formation near the Stanley Glacier and Burgess Shale locality of Canada, as well as Wheeler Formation of United States. The genus was characterized by the rake-like frontal appendages with robust inner spines. ''Stanleycaris'' was originally described only from frontal appendages and oral cone. However, in 2022, 268 specimens of ''Stanleycaris'', many of which were complete, were studied, making ''Stanleycaris'' a well documented radiodont. ''Stanleycaris'' had three eyes, a bizarre configuration previously unknown among other radiodont genera; yet this head anatomy supports early differentiation among arthropod head and trunk segmentation. The original description of the taxon appeared in an online supplement to the article published by Jean-Bernard Caron, Robert R. Gaines, M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanleycaris Hirpex
''Stanleycaris'' is an extinct, monotypic genus of hurdiid radiodont from the middle Cambrian (Miaolingian). The type species is ''Stanleycaris hirpex''. ''Stanleycaris'' was described from the Stephen Formation near the Stanley Glacier and Burgess Shale locality of Canada, as well as Wheeler Formation of United States. The genus was characterized by the rake-like frontal appendages with robust inner spines. ''Stanleycaris'' was originally described only from frontal appendages and oral cone. However, in 2022, 268 specimens of ''Stanleycaris'', many of which were complete, were studied, making ''Stanleycaris'' a well documented radiodont. ''Stanleycaris'' had three eyes, a bizarre configuration previously unknown among other radiodont genera; yet this head anatomy supports early differentiation among arthropod head and trunk segmentation. The original description of the taxon appeared in an online supplement to the article published by Jean-Bernard Caron, Robert R. Gaines, M. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |