|
Antelope Valley Fair
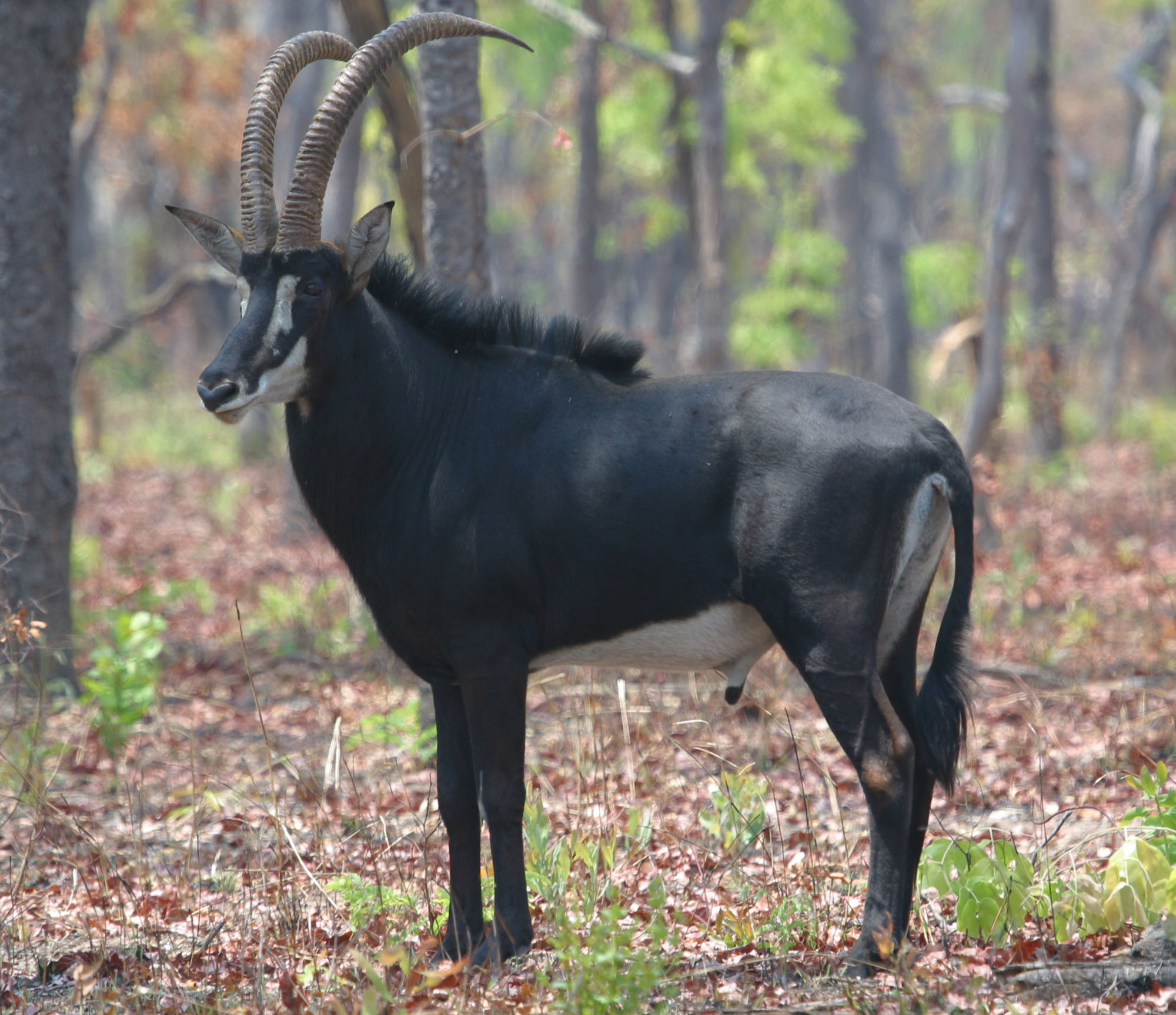
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous (ecology), indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia. Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals belonging to the family (biology), family Bovidae of the order Even-toed ungulate, Artiodactyla. A stricter definition, also known as the "true antelopes," includes only the genus, genera ''gazelle, Gazella'', ''Nanger'', ''Eudorcas'' and ''Antilope''. One North America, North American species, the pronghorn, is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope," but it belongs to a different family from the African and Eurasian antelopes. A group of antelope is called a herd. Unlike deer antlers, which are shed and grown annually, antelope horns grow continuously. Etymology The English word "antelope" first appeared in 1417 and is derived from the Old French ''antelop'', itself derived from Medieval Latin ''ant( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is an antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources. It stands up to high at the shoulder. Males weigh , with an average of . Females are lighter, weighing or on average. Males have long, ringed horns, though females may develop horns as well. The white fur on the chin and around the eyes is in sharp contrast with the black stripes on the face. The coats of males show a two-tone colouration; while the upper parts and outsides of the legs are dark brown to black, the underparts and the insides of the legs are white. Females and juveniles are yellowish fawn to tan. The blackbuck is the sole living member of the genus ''Antilope'' and was scientifically described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized. The blackbuck is active mainly during the day. It forms three type of small groups, female, male, and bachelor h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilope
''Antilope'' is a genus of twisted-horn bovid that contains a single living species, the blackbuck of South Asia South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; .... Two extinct species are also known. Many fossil antelopes were included in this genus, but have since been placed in new genera; for example the species formerly known as ''Antilope planicornis'' is now placed in its own genus, '' Nisidorcas''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1416078 Taxa named by Peter Simon Pallas True antelopes Mammal genera Mammal genera with one living species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudorcas
''Eudorcas'' is a genus of antelope; the species are commonly called gazelles. ''Eudorcas'' was originally considered a subgenus of the genus ''Gazella A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, ''Eudorcas'' and ''Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third f ...'' but has since been elevated to generic status. The five species within the genus ''Eudorcas'' are: Species''Eudorcas'' MSW3 Social structure and behavior  The social str ...
The social str ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanger
{{eventoedungulate-stub ...
''Nanger'' is a genus of antelopes, commonly called gazelles. ''Nanger'' was originally considered a subgenus within the genus ''Gazella'', but has since been elevated to genus status. The three living species within the genus ''Nanger'' are: * ''Nanger vanhoepeni''† References Antilopini Mammal genera Fauna of Sub-Saharan Africa Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . This article also deals with the seven species included in two further genera, ''Eudorcas'' and ''Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third former subgenus, ''Procapra'', includes three living species of Asian gazelles. Gazelles are known as swift animals. Some are able to run at bursts as high as or run at a sustained speed of . Gazelles are found mostly in the deserts, grasslands, and savannas of Africa; but they are also found in southwest and central Asia and the Indian subcontinent. They tend to live in herds, and eat fine, easily digestible plants and leaves. Gazelles are relatively small antelopes, most standing high at the shoulder, and are generally fawn-colored. The gazelle genera are ''Gazella'', ''Eudorcas'', and ''Nanger''. The taxonomy of these genera is confused, and the classification of species and subspecies has been an unsettled issue. Currently, the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even-toed Ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, the family Bovidae consists of 11 (or two) major subfamilies and thirteen major tribes. The family evolved 20 million years ago, in the early Miocene. The bovids show great variation in size and pelage colouration. Excepting some domesticated forms, all male bovids have two or more horns, and in many species, females possess horns, too. The size and shape of the horns vary greatly, but the basic structure is always one or more pairs of simple bony protrusions without branches, often having a spiral, twisted or fluted form, each covered in a permanent sheath of keratin. Most bovids bear 30 to 32 teeth. Most bovids are diurnal. Social activity and feeding usually peak during dawn and dusk. Bovids typically rest before dawn, during midday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastebasket Taxon
Wastebasket taxon (also called a wastebin taxon, dustbin taxon or catch-all taxon) is a term used by some taxonomists to refer to a taxon that has the sole purpose of classifying organisms that do not fit anywhere else. They are typically defined by either their designated members' often superficial similarity to each other, or their ''lack'' of one or more distinct character states or by their ''not'' belonging to one or more other taxa. Wastebasket taxa are by definition either paraphyletic or polyphyletic, and are therefore not considered valid taxa under strict cladistic rules of taxonomy. The name of a wastebasket taxon may in some cases be retained as the designation of an evolutionary grade, however. The term was coined in a 1985 essay by Steven Jay Gould. Examples There are many examples of paraphyletic groups, but true "wastebasket" taxa are those that are known not to, and perhaps not intended to, represent natural groups, but are nevertheless used as convenient groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.jpg)