|
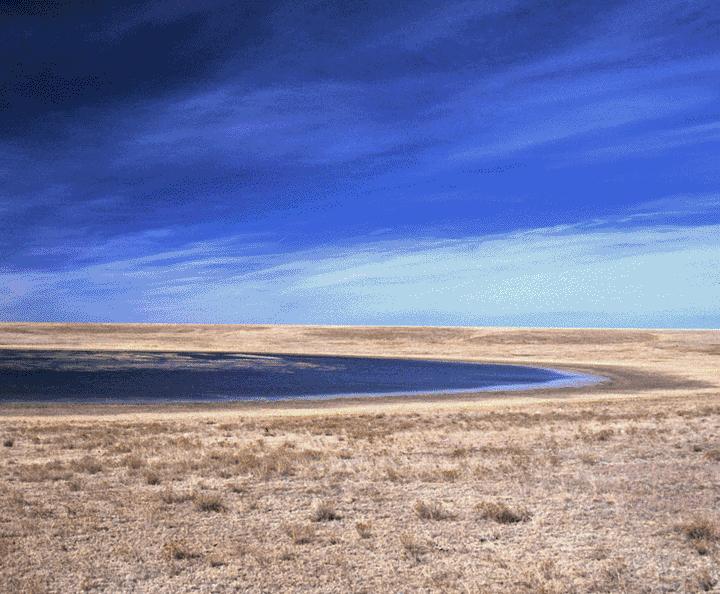
Antelope Lake (Saskatchewan)
Antelope Lake is an endorheic lake in the south-west corner of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The lake is in the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states, and within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion of Canada. The primary inflow for the lake is Bridge Creek, which originates to the south in the Cypress Hills at an elevation of over above sea level. The lake is about north of Gull Lake and the Trans-Canada Highway, just off Highway 37. There are no communities along the lake's shore—only a regional park. About south-east of the lake along the Trans-Canada Highway is a nature reserve called Webb National Wildlife Area. Antelope Lake Regional Park Antelope Lake Regional Park () is located on the western shore of Antelope Lake. The park was founded on 17 October 1972 when the Regional Park Board bought the land from Mr and Mrs Earl Hemsworth. The park is bordered by hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gull Lake, Saskatchewan
Gull Lake is a town in Saskatchewan, Canada, situated on the junction of the Trans-Canada Highway and Highway 37, west of Swift Current. History The history of the Gull Lake community dates back to 1906, when a development company Conrad and Price acquired and surveyed the town site and subdivided it into blocks. Unlike most other towns located along the Canadian Pacific Railway main line, Gull Lake was not planned and established by the railroad. In fact, there was some animosity from the railroad towards this town that bucked their plan. The origin of the name Gull Lake comes from the Cree word for the area, ''Kiaskus'' (''kiyaskos'') which means "little gull". From 1906 to 1909 there was no municipal government or authority other than Conrad and Price: the company had full jurisdiction over civic affairs. In 1909 the citizens of Gull Lake had their community incorporated as a village.Town of Gull Lake History Committee. (1989). Gull Lake memories: a history of the town of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourism In Saskatchewan
There are numerous heritages and cultural attractions in the province of Saskatchewan. Museums, dinosaur digs, aboriginal cultural and heritage sites, art galleries, professional sport venues, spas, handcraft, antique and tea shops, agricultural tours, theatre and archaeological sites comprise over 600 varied Saskatchewan institutions. There are two national parks located in the province of Saskatchewan: Grasslands National Park, Prince Albert National Park. There are also four National Historic Sites operated by Parks Canada in Saskatchewan including Fort Walsh National Historic Site, Batoche National Historic Site, Fort Battleford National Historic Site and Motherwell Homestead National Historic Site. There are 37 provincial parks, provincial recreation areas, natural areas and a Heritage rangeland are also protected on a provincial level. Saskatchewan also has two major cities, Regina and Saskatoon. Regina is home to the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) Academy at Depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes Of Saskatchewan ...
This is a list of lakes of Saskatchewan, a province of Canada. The largest and most notable lakes are listed at the start, followed by an alphabetical listing of other lakes of the province. Larger lake statistics "The total area of a lake includes the area of islands. Lakes lying across provincial boundaries are listed in the province with the greater lake area." A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y Z See also *List of lakes of Canada *List of rivers of Saskatchewan *Geography of Saskatchewan *List of dams and reservoirs in Canada References {{Authority control * Lakes Saskatchewan Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
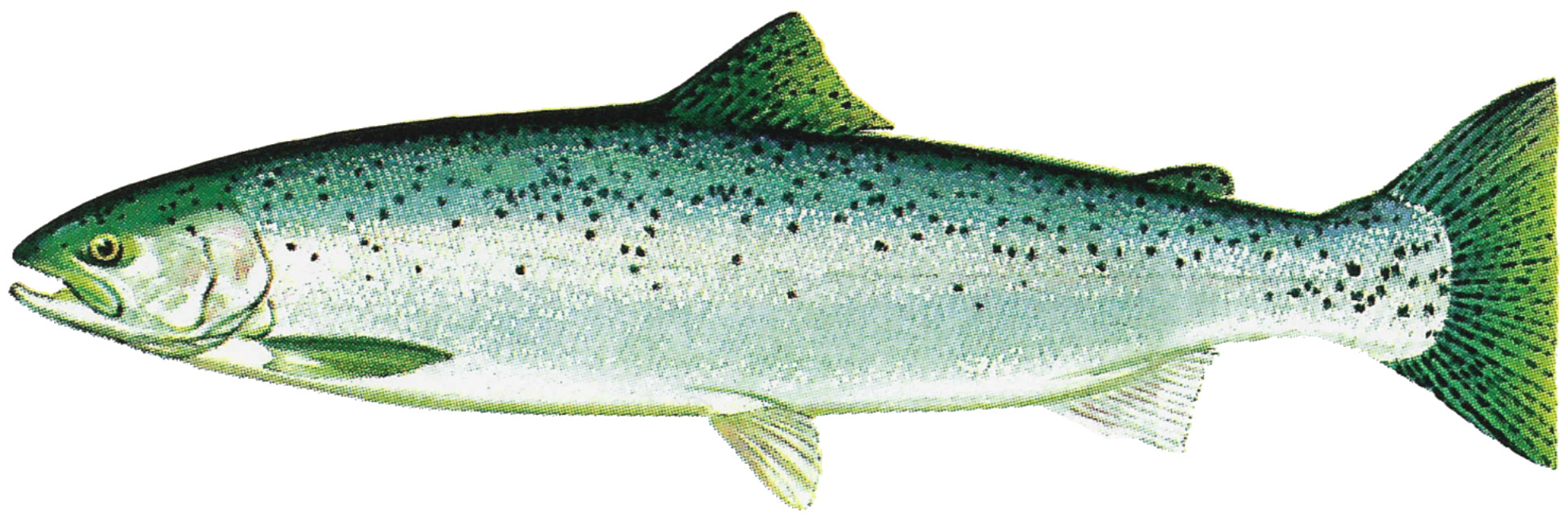
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Wildlife Area
A National Wildlife Area is a conservation designation for a geographical region in Canada that restricts most human activities on that region. However, land use permits may be issued "for activities that are compatible with conservation". Such areas are established and managed by the Canadian Wildlife Service, a division of Environment and Climate Change Canada. They may consist of land and water features, as well as coastal areas extending up to from shore. The largest national wildlife area is the Scott Islands Marine National Wildlife Area in British Columbia, which covers an area of . Protections Each National Wildlife Area involves a management plan which specifies activities which are generally allowed within the protected area, as well as activities requiring permits. Under the Wildlife Area Regulations, traditional, personal and recreational activities such as hunting, fishing, or canoeing are allowed, whereas resource extraction or livestock grazing would be permit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Protected Areas Of Saskatchewan
This is a list of protected areas of Saskatchewan. National parks Provincial parks The Government of Canada, federal government transferred control of natural resources to the Western Canada, western provinces in 1930 with the Natural Resources Acts. At that time, the Saskatchewan government set up its own Department of Natural Resources. In an attempt to get people working and to encourage tourism during the Great Depression, several projects were set up by the government, including setting up a provincial park system in 1931. The founding parks include Cypress Hills, Duck Mountain, Good Spirit Lake, Moose Mountain, Katepwa Point, and Little Manitou Lake#Manitou and District Regional Park, Little Manitou. Greenwater Lake was added in 1932. Two more parks were added by the end of the 1930s and Little Manitou ceased to be a provincial park in 1956 and in 1962, it became a regional park. The list of parks, and their types, come from The Parks Act. Regional park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Highway 37
Highway 37 is a highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It runs from Montana Secondary Highway 241 at the US border near Port of Climax to Highway 32 at Cabri. Highway 37 is about long. This north-south route connects with the horseshoe tourism route at Shaunavon. Going west on the Red Coat Trail Highway 13 leads to Eastend, known for its dinosaur museum. Further west and north is Maple Creek, a cowboy town of the current era. Highway 37 passes near the communities of Climax, Shaunavon, and Gull Lake, as well as Port of Climax and Cabri. Highway 37 connects with Highways 18, 722, 13, 631, 1, 322, and 738 __NOTOC__ Year 738 ( DCCXXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 738 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini cale .... History Saskatchewan Highways and Transportation (SHT), now the Ministry of Highways and Infrastructure und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Highway 1
Highway 1 is the Saskatchewan section of the Trans-Canada Highway mainland route. The total distance of the Trans-Canada Highway in Saskatchewan is . The highway traverses Saskatchewan from the western border with Alberta, from Highway 1, to the Manitoba border where it continues as PTH 1. The Trans-Canada Highway Act was passed on December 10, 1949. The Saskatchewan segment was completed August 21, 1957, and completely twinned on November 6, 2008. The speed limit along the majority of the route is 110 kilometres per hour (70 mph) with urban area thoroughfares slowing to a speed of 80–100 kilometres per hour (50–62 mph). Portions of the highway—the section through Swift Current, an section east of Moose Jaw, and a section between the West Regina Bypass and Balgonie—are controlled-access. Highway 1 serves as a major east-west transport route for commercial traffic. It is the main link between southern Saskatchewan's largest cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypress Hills (Canada)
The Cypress Hills are a geographical region of hills in southwestern Saskatchewan and southeastern Alberta, Canada. The hills are part of the Missouri Coteau upland. The highest point in the Cypress Hills is at Head of the Mountain in Alberta at . The highest point in Saskatchewan is , in a farmer's field in the Cypress Hills, at . Name The Cypress Hills have been known by a wide number of Indigenous and European names throughout their history. An 1882 Blackfoot–English dictionary written by C. M. Lanning provided the Blackfoot language name , which translates as "striped earth" or "earth over earth". The Cree language name, in use at the same time, is , (spelled in a variety of anglicized forms including "Mun-a-tuh-gow"), sometimes said to mean "beautiful upland" but more accurately referring to "an area to be respected, protected, taken care of and/or taken care with". The Assiniboine language name is . The Gros Ventre language name is ' "pine trees". Early Métis hunters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Lake
An endorheic lake (also called a sink lake or terminal lake) is a collection of water within an endorheic basin, or sink, with no evident outlet. Endorheic lakes are generally saline as a result of being unable to get rid of solutes left in the lake by evaporation. These lakes can be used as indicators of anthropogenic change, such as irrigation or climate change, in the areas surrounding them. Lakes with subsurface drainage are considered cryptorheic. Components of endorheic lakes The two main ways that endorheic lakes accumulate water are through river flow into the lake (discharge) and precipitation falling into the lake. The collected water of the lake, instead of discharging, can only be lost due to either evapotranspiration or percolation (water sinking underground, e.g., to become groundwater in an aquifer). Because of this lack of an outlet, endorheic lakes are mostly salt water rather than fresh water. The salinity in the lake gradually builds up through years as wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains Ecoregion
The ecology of the Great Plains is diverse, largely owing to their great size. Differences in rainfall, elevation, and latitude create a variety of habitats including short grass, mixed grass, and tall-grass prairies, and riparian ecosystems. The Great Plains extend from Mexico in the south through the central United States to central Canada. Many sub-regions exist within the area. The region is home to many animals, including American bison, pronghorn, mule, and white tailed deer, and birds such as ducks, hawks, and sparrows, along with many invertebrate species. Settlement of "America's breadbasket" led to ecological destruction. Widespread agriculture led to the near-complete extermination of the American bison in the late 1800s and the reduction of the tallgrass prairie to less than 1% of its former extent. The plains are now largely agricultural, with large ranches and farms. However, restoration efforts in some areas, like American Prairie in Montana, are leading to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |