|
Antal Jákli
Antal I. "Tony" Jákli (born 3 October 1958) is a Hungarian-American physicist and professor of Chemical Physics at Kent State University. He is known for his work with bent-core, flexoelectric, and ferroelectric liquid crystals. Education and career Jákli received a Master of Science in 1983 and later a Ph.D. in 1986 in Physics from Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest, Hungary. After postdoctoral fellowships with Alfred Saupe at Kent State University from 1989 to 1992 and at the Max Planck Institute in Halle, Germany, from 1993 to 1995, he became a research fellow at the Research Institute for Solid State Physics in Budapest. He was later awarded a D.Sc. from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences in 2000. He moved to the United States in 1999 to join the Liquid Crystal Institute at Kent State University as a research fellow. He became an assistant professor there in 2004, receiving tenure in 2007 and a promotion to full professorship in 2012. Research His current research in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szombathely
Szombathely (; german: Steinamanger, ; see also other alternative names) is the 10th largest city in Hungary. It is the administrative centre of Vas county in the west of the country, located near the border with Austria. Szombathely lies by the streams ''Perint'' and ''Gyöngyös'' (literally "pearly"), where the Alpokalja (Lower Alps) mountains meet the Little Hungarian Plain. The oldest city in Hungary, it is known as the birthplace of Saint Martin of Tours. Etymology The name ''Szombathely'' is from Hungarian ''szombat'', "Saturday" and ''hely'', "place", referring to its status as a market town, and the medieval markets held on Saturday every week. Once a year during August they hold a carnival to remember the history of "Savaria". The Latin name ''Savaria'' or ''Sabaria'' comes from ''Sibaris'', the Latin name of the river ''Gyöngyös'' (German ''Güns''). The root of the word is the Proto-Indo-European word ''*seu'', meaning "wet". The Austrian overflowing of the Gyö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
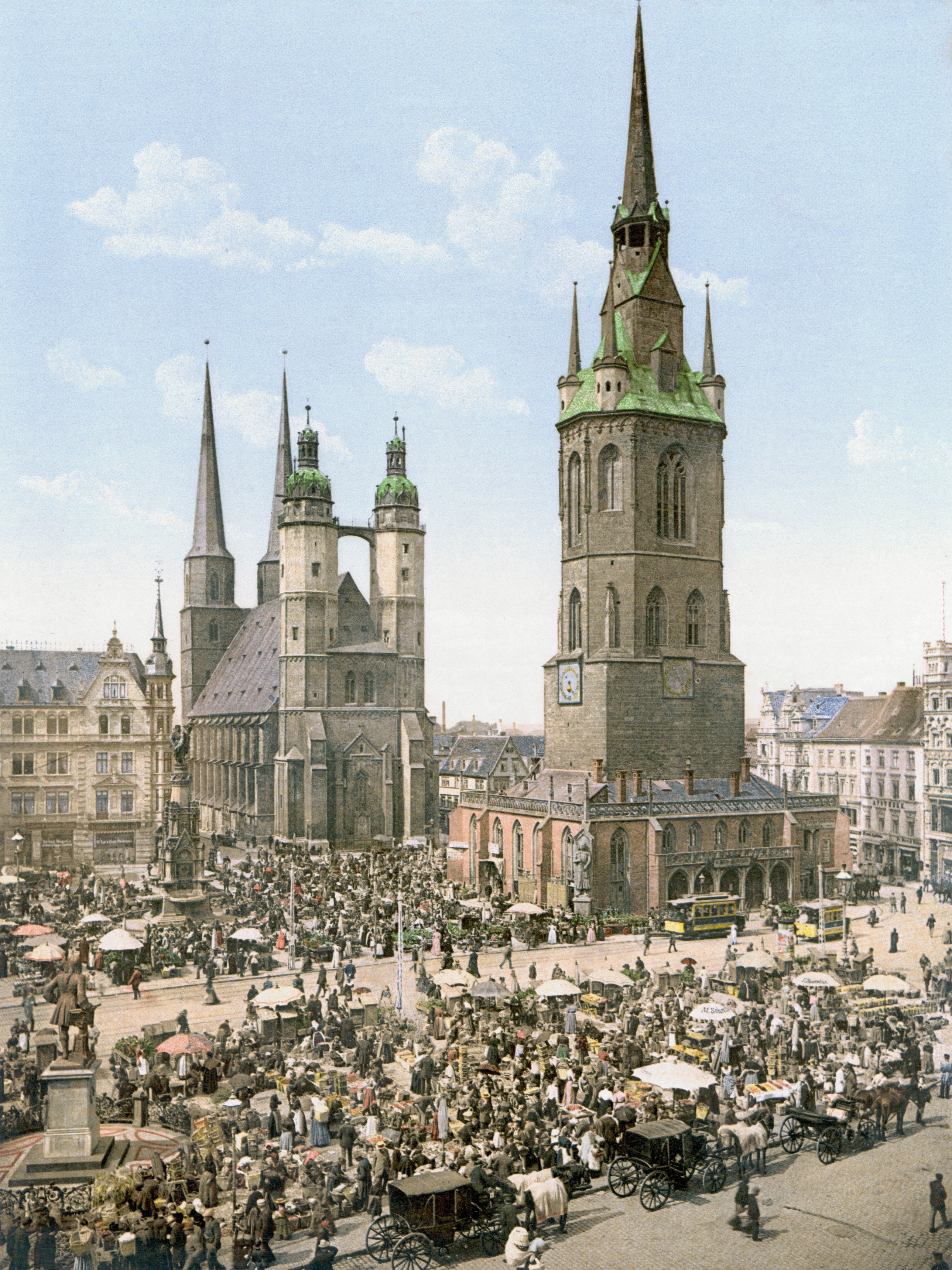
Halle (Saale)
Halle (Saale), or simply Halle (; from the 15th to the 17th century: ''Hall in Sachsen''; until the beginning of the 20th century: ''Halle an der Saale'' ; from 1965 to 1995: ''Halle/Saale'') is the largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Saxony-Anhalt, the fifth most populous city in the area of former East Germany after (East Berlin, East) Berlin, Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz, as well as the List of cities in Germany by population, 31st largest city of Germany, and with around 239,000 inhabitants, it is slightly more populous than the state capital of Magdeburg. Together with Leipzig, the largest city of Saxony, Halle forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle conurbation. Between the two cities, in Schkeuditz, lies Leipzig/Halle Airport, Leipzig/Halle International Airport. The Leipzig-Halle conurbation is at the heart of the larger Central German Metropolitan Region. Halle lies in the south of Saxony-Anhalt, in the Leipzig Bay, the southernmost part of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Emigrants To The United States
Hungarian may refer to: * Hungary, a country in Central Europe * Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946 * Hungarians, ethnic groups in Hungary * Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the assignment problem * Hungarian language, a Finno-Ugric language spoken in Hungary and all neighbouring countries * Hungarian notation, a naming convention in computer programming * Hungarian cuisine Hungarian or Magyar cuisine is the cuisine characteristic of the nation of Hungary and its primary ethnic group, the Magyars. Traditional Hungarian dishes are primarily based on meats, seasonal vegetables, fruits, bread, and dairy products. ..., the cuisine of Hungary and the Hungarians See also * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
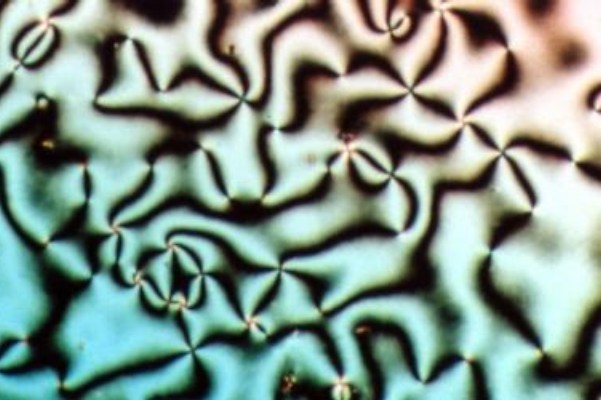
Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent State University Faculty
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties. Kent was one of the first British territories to be settled by Germanic tribes, most notably the Jutes, following the withdrawal of the Romans. Canterbury Cathedral in Kent, the oldest cathedral in England, has been the seat of the Archbishops of Canterbury since the conversion of England to Christianity that began in the 6th century with Saint Augustine. Rochester Cathedral in Medway is England's second-oldest cathedral. Located between London and the Strait of Dover, which separates England from mainl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1958 Births
Events January * January 1 – The European Economic Community (EEC) comes into being. * January 3 – The West Indies Federation is formed. * January 4 ** Edmund Hillary's Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition completes the third overland journey to the South Pole, the first to use powered vehicles. ** Sputnik 1 (launched on October 4, 1957) falls to Earth from its orbit, and burns up. * January 13 – Battle of Edchera: The Moroccan Army of Liberation ambushes a Spanish patrol. * January 27 – A Soviet-American executive agreement on cultural, educational and scientific exchanges, also known as the "Lacy-Zarubin Agreement, Lacy–Zarubin Agreement", is signed in Washington, D.C. * January 31 – The first successful American satellite, Explorer 1, is launched into orbit. February * February 1 – Egypt and Syria unite, to form the United Arab Republic. * February 6 – Seven Manchester United F.C., Manchester United footballers are among the 21 people killed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Saupe Prize
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *'' Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album ''Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England *Alfred Music, an American music publisher * Alfred University, New York, U.S. *The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario * Alfred Island, Nunavut * Mount Alfred, British Columbia United States * Alfred, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word ''piezoelectricity'' means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. It is derived from the Greek word ; ''piezein'', which means to squeeze or press, and ''ēlektron'', which means amber, an ancient source of electric charge. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process: materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an applied electrical field. For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measurable piezoelectricity when their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexoelectricity
Flexoelectricity is a property of a dielectric material whereby it exhibits a spontaneous electrical polarization induced by a strain gradient. Flexoelectricity is closely related to piezoelectricity, but while piezoelectricity refers to polarization due to uniform strain, flexoelectricity refers specifically to polarization due to strain that changes from point to point in the material. This nonuniform strain breaks centrosymmetry, meaning that unlike in piezoelectiricty, flexoelectric effects can occur in centrosymmetric crystal structures. Flexoelectricity is not the same as Ferroelasticity. Inverse flexoelectricity, quite intuitively can be defined as generation of strain gradient due to polarization. Similarly extending on that, Converse flexoelectricity would refer to the process where a polarization gradient induces strain in a material. The electric polarization due to mechanical stress in a dielectric is given by :P_i=e_\epsilon_+\mu_\frac where the first term correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrospinning
Electrospinning is a fiber production method that uses electric force to draw charged threads of polymer solutions or polymer melts up to fiber diameters in the order of some hundred nanometers. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers.Ziabicki, A. (1976) ''Fundamentals of fiber formation'', John Wiley and Sons, London, . The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry or high temperatures to produce solid threads from solution. This makes the process particularly suited to the production of fibers using large and complex molecules. Electrospinning from molten precursors is also practiced; this method ensures that no solvent can be carried over into the final product. Process When a sufficiently high voltage is applied to a liquid droplet, the body of the liquid becomes charged, and electrostatic repulsion counteracts the surface tension and the droplet is stretched; at a critical point a stream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal Institute
The former Glenn H. Brown Liquid Crystal Institute (LCI) at Kent State University is now renamed the Advanced Materials and Liquid Crystal Institute. The AMLCI is a center of study for liquid crystal technology and education, blending basic and applied research on liquid crystals. This approach has resulted in technological advances and new applications such as display tablets, optical shutters, variable transmission windows, projection display devices, and flexible display A flexible display or rollable display is an electronic visual display which is flexible in nature, as opposed to the traditional flat screen displays used in most electronic devices. In recent years there has been a growing interest from nume ...s. Established in 1965, the institute is now directed by Dr. Torsten Hegmann and is housed at KSU's Liquid Crystal and Materials Sciences building, completed in 1996. The LCI is home to the Chemical Physics Interdisciplinary Program, which offers masters and Ph.D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

