|
Ansainiai
Ansainiai (formerly russian: Ганусевичи, pl, Hanusewicze) is a village in Kėdainiai district municipality, in Kaunas County, in central Lithuania. According to the 2011 census, the village had a population of 14 people. It is located from Labūnava, on the shore of the Labūnava Reservoir. There is a memorial for exiled local inhabitants during the Soviet era. History In the beginning of the 20th century, Ansainiai (''Hanusewicze'') was an ''okolica In Poland and Lithuania okolica szlachecka or akalica (in Lithuanian) is a kind of estate village (''neighbourhood of the nobility''), or a complex of several villages of the same first part of the name and different second part. In the past, it was ...'', a property of the Butkevičiai, Dautartai, Gineikiai, Hanusaučiai, Ivanaičiai, Jagėlavičiai, Jusevičiai, Kšešanavičiai, Stecevičiai, Uginskiai, Vencevičiai families. Demography left, 250px, Ansainiai memorial References Villages in Kaunas County Kė ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labūnava Reservoir
The Labūnava Reservoir is an artificial lake in Kėdainiai District Municipality, central Lithuania. It is located south from Kėdainiai, next to Labūnava village. It was created in 1977, when a dam on the Barupė The Barupė is a river of Jonava District Municipality and Kėdainiai District Municipality, Kaunas County, central Lithuania. It flows for and has a basin area of . It is a left tributary of the Nevėžis. The Barupė river starts next to Žin ... river had been built next to Labūnava village. In 2003, the dam was reconstructed and a small hydroelectric plant (of 160 kW) has been built. Shores of the reservoir are curvy, often grown by reed beds. The reservoir mostly is surrounded by agriculture lands, but a small section of the Labūnava Forest is located nearby. The water is used for irrigation. References Lakes of Kėdainiai District Municipality Reservoirs in Lithuania {{KaunasCounty-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
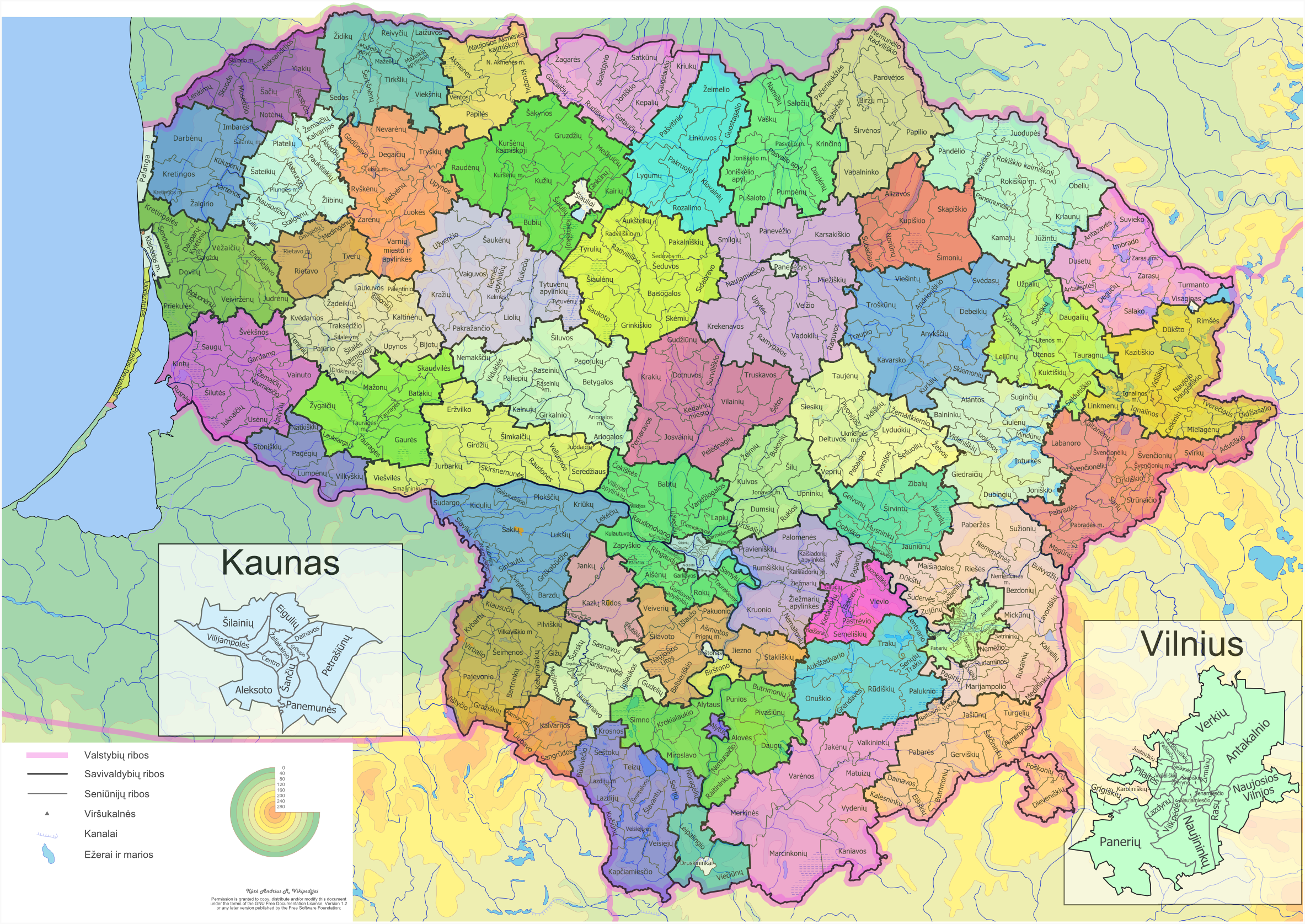
Pelėdnagiai Eldership
Pelėdnagiai Eldership ( lt, Pelėdnagių seniūnija) is a Lithuanian eldership, located in the south eastern part of Kėdainiai District Municipality. Eldership was created from the Pelėdnagiai ''selsovet'' in 1993. Geography The territory of Pelėdnagiai Eldership is located mostly in the Nevėžis Plain and the Nevėžis river valley. Relief is mostly flat, cultivated as agriculture lands. Forests cover about 40 % of the eldership. * Rivers: Nevėžis, Barupė, Urka, Mėkla, Lankesa, Ašarėna * Lakes and ponds: Labūnava Reservoir. * Forests: Labūnava Forest. * Protected areas: Barupė Hydrographical Sanctuary, Lankesa Botanical Sanctuary, Pelėdnagiai Botanical Sanctuary, Labūnava Forest Biosphere Polygon. Places of interest *Catholic church of the Divine in Labūnava *Juciūnai cemetery chapel *Aukupėnai cemetery tomb-chapel *Labūnava manor tower *Gelnai wayside chapel *Ancient burial site in Nociūnai and former cemetery site in Pašiliai *Soviet mosaic the "Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania shares land borders with Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and Russia to the southwest. It has a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west on the Baltic Sea. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.8 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities are Kaunas and Klaipėda. Lithuanians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, one of only a few living Baltic languages. For millennia the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united by Mindaugas, Monarchy of Lithuania, becoming king and founding the Kingdom of Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okolica
In Poland and Lithuania okolica szlachecka or akalica (in Lithuanian) is a kind of estate village (''neighbourhood of the nobility''), or a complex of several villages of the same first part of the name and different second part. In the past, it was a single settlement, but later it has split, as the property has been divided into several inheritors. Such localities were usually inhabited by yeomanry (''drobna szlachta''). They are common in the borderland of Mazovia and Podlachia in Poland and in central and north-west part of Lithuania. Many frequent toponymic (often noble) surnames are derived from their names. Examples *Łapy Łapy is a town in north-eastern Poland, in Białystok County (''powiat''), Podlaskie Voivodeship; the administrative centre of the urban-rural gmina Łapy. It is situated in the North Podlasie Lowland, on the river Narew. According to dat ... (nowadays a town), the nest of Łapiński family * Wyszonki, from where Wyszyński See also * zaściane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Transfer In The Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified into the following broad categories: deportations of "anti-Soviet" categories of population (often classified as "enemies of workers"), deportations of entire nationalities, labor force transfer, and organized migrations in opposite directions to fill ethnically cleansed territories. Dekulakization marked the first time that an entire class was deported, whereas the deportation of Soviet Koreans in 1937 marked the precedent of a specific ethnic deportation of an entire nationality. In most cases, their destinations were underpopulated remote areas (see Forced settlements in the Soviet Union). This includes deportations to the Soviet Union of non-Soviet citizens from countries outside the USSR. It has been estimated that, in their entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labūnava
Labūnava (formerly russian: Лабуновъ, Лабуново, pl, Łabunów) is a village in Kėdainiai district municipality, in Kaunas County, in central Lithuania. According to the 2011 census, the village had a population of 747 people. It is located from Kėdainiai, on the left bank of the Nevėžis river, by its tributary the Barupė. The Labūnava Reservoir on the Barupė is located next to the village. There is a kidergarden, a library, a school, a forestry, an agriculture cooperative, a Catholic church of the Divine, a cemetery, some relics of the former manor (two towers, hunter house). History During the 14th century, Labūnava was under attacks from the Teutonic Knights. It was mentioned for the first time in 1364, in the chronicle of Hermann von Wartberge. The Labūnava Manor has been known since the 16th century. Labūnava has been burnt during Napoleon's campaign in 1812. Labūnava developed greatly during the Soviet era. It became a center of the "Eastern Dawn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Time
Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer. A number of African countries use UTC+02:00 all year long, where it is called Central Africa Time (CAT), although Egypt and Libya also use the term ''Eastern European Time''. The most populous city in the Eastern European Time zone is Cairo, with the most populous EET city in Europe being Athens. Usage The following countries, parts of countries, and territories use Eastern European Time all year round: * Egypt, since 21 April 2015; used EEST ( UTC+02:00; UTC+03:00 with daylight saving time) from 1988–2010 and 16 May–26 September 2014. See also Egypt Standard Time. * Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia), since 26 October 2014; also used EET in years 1945 and 1991–2011. See also Kaliningrad Time. * Libya, since 27 October 2013; switched from Central European Time, which was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Summer Time
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is one of the names of the UTC+03:00 time zone, which is 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European and Middle Eastern countries, which makes it the same as Arabia Standard Time, East Africa Time, and Moscow Time. During the winter periods, Eastern European Time ( UTC+02:00) is used. Since 1996, European Summer Time has been applied from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Previously, the rules were not uniform across the European Union. Usage The following countries and territories use Eastern European Summer Time during the summer: * Belarus, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–89, regular EEST from 1991-2011 * Bulgaria, regular EEST since 1979 * Cyprus, regular EEST since 1979 ( Northern Cyprus stopped using EEST in September 2016, but returned to EEST in March 2018) * Estonia, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–88, regular EEST since 1989 * Finland, regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Lithuania
The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties (Lithuanian language, Lithuanian: singular ''apskritis'', plural ''apskritys''), all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into Municipalities of Lithuania, 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: singular ''savivaldybė'', plural ''savivaldybės''): 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities. Each municipality is then divided into elderates (Lithuanian: singular ''seniūnija'', plural ''seniūnijos''). This division was created in 1994 and slightly modified in 2000. Until 2010, the counties were administered by county governors (Lithuanian: singular – ''apskrities viršininkas'', plural – ''apskrities viršininkai'') appointed by the central government in Vilnius. Their primary duty was to ensure that the municipalities obey the laws and the Constitution of Lithuania. They did not have great powers vested in them, and so it was suggested that 10 counties are too much for Lithuania as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elderships Of Lithuania
A ''seniūnija'' (in English: eldership, elderate, ward, parish, or subdistrict) is the smallest administrative division of Lithuania. An eldership may comprise a very small region consisting of few villages, one single town, or a part of a big city. Elderships vary in size and population depending on their location and nature. A few elderships make up a municipality. Šilainiai (Kaunas) and Dainava (Kaunas) are the most populous elderates, with population counts over , exceeding the population of some entire municipalities. Elderships manage small-scale local matters, such as repairing pavements and dirt roads, and keep records on all families living in the eldership. The premise of the concept is that - unlike in higher administrative divisions - an elder (the leader of the eldership) could have time to talk to every person in the eldership who wants to. Modern Lithuania is divided into 10 counties, 60 municipalities, and 546 elderships. Elderships function as municip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |