|
Anoplotheriidae
Anoplotheriidae is an extinct family of even-toed ungulates ( order Artiodactyla). They were endemic to Western Europe during the Eocene and Oligocene epochs about 48—23 million years ago (Mya), existing for about 25 million years. They disappeared at the end of the Oligocene, leaving no survivors today. Its name is derived from the grc, ἂνοπλος ("unarmed") and θήριον ("beast"), translating as "unarmed beast". They were most likely mid-sized terrestrial herbivores not too distantly related to camels, but smaller and low-slung with long and thick tails, and rather generalistic. The climate during their time was warmer than today, and their habitats were probably subtropical or even tropical, with plentiful rainfall and abundant vegetation. Tropical rainforest may at least initially have occurred all over the Anoplotheriidae's range. Ecologically, they may have resembled a large duiker of our time (e.g. the similarly sized yellow-backed duiker ''Cephalophus silvicu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
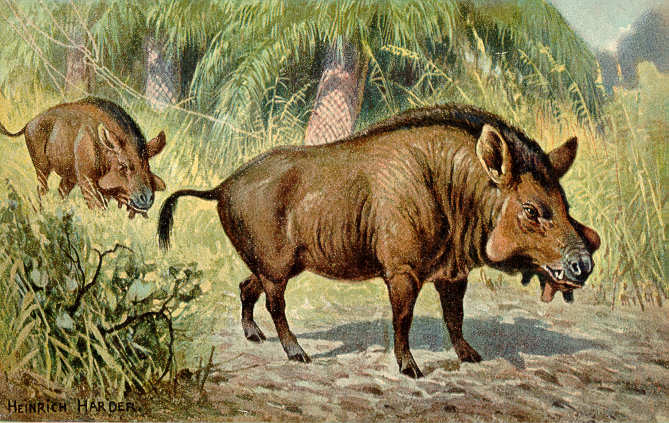
Anoplotherium
''Anoplotherium'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous artiodactyl mammal, possibly belonging to or a close relative of the suborder Tylopoda, which lived in Europe from the Late Eocene to the earliest Oligocene. Fossils of ''Anoplotherium'' were first discovered in the gypsum quarries of Paris in 1804 and were subsequently described by French naturalist Georges Cuvier. One of the first Paleogene mammals to be described, 19th Century reconstructions of ''Anoplotherium'' can be seen at Crystal Palace Park. Etymology The genus name ''Anoplotherium'' is a compound of the Greek prefixes αν ('an') meaning 'not', ὅπλον ('hóplon') meaning 'armor, large shield' and the suffix θήρ ('thēr') meaning beast or wild animal. Therefore, the genus name has a full meaning of 'Unarmed Beast', a reference to the lack of tusks or horns. Palaeontology Fossils attributed to the genus ''Anoplotherium'' have been found in Late Eocene to earliest Oligocene strata in the United Kingdom, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoplotherium Commune
''Anoplotherium'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous artiodactyl mammal, possibly belonging to or a close relative of the suborder Tylopoda, which lived in Europe from the Late Eocene to the earliest Oligocene. Fossils of ''Anoplotherium'' were first discovered in the gypsum quarries of Paris in 1804 and were subsequently described by French naturalist Georges Cuvier. One of the first Paleogene mammals to be described, 19th Century reconstructions of ''Anoplotherium'' can be seen at Crystal Palace Park. Etymology The genus name ''Anoplotherium'' is a compound of the Greek prefixes αν ('an') meaning 'not', ὅπλον ('hóplon') meaning 'armor, large shield' and the suffix θήρ ('thēr') meaning beast or wild animal. Therefore, the genus name has a full meaning of 'Unarmed Beast', a reference to the lack of tusks or horns. Palaeontology Fossils attributed to the genus ''Anoplotherium'' have been found in Late Eocene to earliest Oligocene strata in the United Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even-toed Ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain 36% of Earth's landmass. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family (biology), family, order (biology), order, class (biology), class, phylum (biology), phylum, kingdom (biology), kingdom, domain (biology), domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of phenotypic trait, traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William King Gregory
William King Gregory (May 19, 1876 – December 29, 1970) was an American zoologist, renowned as a primatologist, paleontologist, and functional and comparative anatomist. He was an expert on mammalian dentition, and a leading contributor to theories of evolution. In addition he was active in presenting his ideas to students and the general public through books and museum exhibits. Early life He was born in Greenwich Village, New York, on May 19, 1876 to George Gregory and Jane King Gregory. He attended Trinity School and then moved onto Columbia University in 1895, initially at the School of Mines but then transferring to Columbia College. He majored in zoology and vertebrate paleontology under Henry Fairfield Osborn. While still an undergraduate he became Osborn's research assistant and soon after married Laura Grace Foote. He received his undergraduate degree from Columbia in 1900, followed by a masters in 1905, and a doctorate in 1910. Academic career He developed an earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminantia
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science; he published his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope married his cousin and had one child; the family moved from Philadelphia to Haddonfield, New Jersey, although Cope would maintain a residence and museum in Philadelphia in his later years. Cope had little formal scientific training, and he eschewed a teaching position for field work. He made regular trips to the American West, prospecting in the 1870s and 1880s, often as a member of United States Geological Survey teams. A personal feud between Cope and paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh led to a period of intense fossil-finding competition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lucien Bonaparte
Charles Lucien Jules Laurent Bonaparte, 2nd Prince of Canino and Musignano (24 May 1803 – 29 July 1857), was a French naturalist and ornithologist. Lucien and his wife had twelve children, including Cardinal Lucien Bonaparte. Life and career Bonaparte was the son of Lucien Bonaparte and Alexandrine de Bleschamp. Lucien was a younger brother of Napoleon I, making Charles the emperor’s nephew. Born in Paris, he was raised in Italy. On 29 June 1822, he married his cousin, Zénaïde, in Brussels. Soon after the marriage, the couple left for Philadelphia in the United States to live with Zénaïde's father, Joseph Bonaparte (who was also the paternal uncle of Charles). Before leaving Italy, Charles had already discovered a warbler new to science, the moustached warbler, and on the voyage he collected specimens of a new storm-petrel. On arrival in the United States, he presented a paper on this new bird, which was later named after Alexander Wilson. Bonaparte then set about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
