|
Anomalous Scattering
Anomalous X-ray scattering (AXRS or XRAS) is a non-destructive determination technique within X-ray diffraction that makes use of the anomalous dispersion that occurs when a wavelength is selected that is in the vicinity of an absorption edge of one of the constituent elements of the sample. It is used in materials research to study nanometer sized differences in structure. Atomic scattering factors In X-ray diffraction the scattering factor ''f'' for an atom is roughly proportional to the number of electrons that it possesses. However, for wavelengths that approximate those for which the atom strongly absorbs radiation the scattering factor undergoes a change due to anomalous dispersion. The dispersion not only affects the magnitude of the factor but also imparts a phase shift in the elastic collision of the photon. The scattering factor can therefore best be described as a complex number : f= fo + Δf' + i.Δf" Contrast variation The anomalous aspects of X-ray scattering have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Diffraction
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous Dispersion
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
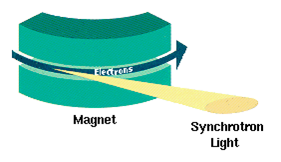
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonant Anomalous X-ray Scattering
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy. Note that X-ray diffraction is now often considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the distinction has not always existed. Thus Guinier's classic text from 1963 is titled "X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies" so 'diffraction' was clearly not restricted to crystals at that time. Scattering techniques Elas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-wavelength Anomalous Dispersion
Multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction (sometimes Multi-wavelength anomalous dispersion; abbreviated MAD) is a technique used in X-ray crystallography that facilitates the determination of the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules (e.g. DNA, drug receptors) via solution of the phase problem. MAD was developed by Wayne Hendrickson while working as a postdoctoral researcher under Jerome Karle at the United States Naval Research Laboratory. The mathematics upon which MAD (and progenitor Single wavelength anomalous dispersion) were based were developed by Jerome Karle, work for which he was awarded the 1985 Nobel Prize in Chemistry (along with Herbert Hauptman). See also * Single wavelength anomalous dispersion Single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) is a technique used in X-ray crystallography that facilitates the determination of the structure of proteins or other biological macromolecules by allowing the solution of the phase problem In physics, ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Wavelength Anomalous Dispersion
Single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) is a technique used in X-ray crystallography that facilitates the determination of the structure of proteins or other biological macromolecules by allowing the solution of the phase problem In physics, the phase problem is the problem of loss of information concerning the phase that can occur when making a physical measurement. The name comes from the field of X-ray crystallography, where the phase problem has to be solved for the de .... In contrast to multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction, SAD uses a single dataset at a single appropriate wavelength. One advantage of the technique is the minimization of time spent in the beam by the crystal, thus reducing potential radiation damage to the molecule while collecting data. SAD is sometimes called "single-wavelength anomalous dispersion", but no dispersive differences are used in this technique since the data are collected at a single wavelength. Today, selenium-SAD is commonly used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Techniques
A scientific technique is any systematic way of obtaining information about a scientific nature or to obtain a desired material or product. Scientific techniques can be divided in many different groups, e.g.: # Preparative techniques ## Synthesis techniques, e.g. the use of Grignard reagents in organic chemistry ## Growth techniques, e.g. crystal growth or cell cultures in biology ## Purification techniques e.g. those in chemistry # Measurement techniques ## Analysis techniques, e.g. ones that reveal atomic or molecular composition. ## Characterization techniques, e.g. ones that measure a certain property of a material. ## Imaging techniques, e.g. microscopy In some cases these methods have evolved into instrumental techniques that require expensive equipment. This is particularly true in sciences like physics, chemistry, and astronomy. It is customary to abbreviate the names of techniques into acronyms, although this does not hold for all of them. Particularly the advent of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |