|
Annesley Railway Station
Annesley railway station was a station in Annesley, Nottinghamshire. It was opened in 1874, to serve the mining village of Annesley which had grown following the opening of Annesley colliery in 1865. It was closed in 1953 as part of the post-war cutback, and the line closed to passengers in 1964. The station did not reopen as part of the Robin Hood Line project in the 1990s. History Opened by the Midland Railway, it became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923. The station then passed on to the London Midland Region of British Railways on nationalisation in 1948, closing five years later under the control of the British Railways Board. Stationmasters *R. Grice 1874 - 1878 *Henry Harding 1878 - 1888 *Henry Robinson 1889 - 1919 *W.C. Stephenson 1935 - 1942 (formerly station master at Asfordby, afterwards station master at Codnor Park and Ironville) *F.J. Toghill 1942 *B.V.Wall 1953 (Subsequently Swanwick Junction Station, then 1959 Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annesley
Annesley is a village and civil parish in the Ashfield district of Nottinghamshire, England, between Hucknall and Kirkby-in-Ashfield. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 1,162 (including Annesley Woodhouse to the west). Annesley Hall is a grade two listed building, once owned by the Chaworth-Musters family, which has connections to the Byron family of nearby Newstead Abbey. Annesley Old Church was mentioned by Lord Byron and D. H. Lawrence. There is also close by the earthworks of Annesley Castle. The Misk Hills lie to the south of the village. Annesley is part of Nottinghamshire's Hidden Valleys area. The parish is grouped with the neighbouring parish of Felley to elect a joint parish council. The old church of Annesley was dedicated to All Saints. It was allowed to become derelict in the 1940s. Features of interest included the east window of the south aisle, the 13th century sedilia and the 17th century royal arms in stucco.Pevsner, N. (1951) ''Nottinghamshire''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets or to assets owned by lower levels of government (such as municipalities) being transferred to the state. Nationalization contrasts with privatization and with demutualization. When previously nationalized assets are privatized and subsequently returned to public ownership at a later stage, they are said to have undergone renationalization. Industries often subject to nationalization include the commanding heights of the economy – telecommunications, electric power, fossil fuels, railways, airlines, iron ore, media, postal services, banks, and water – though, in many jurisdictions, many such entities have no history of private ownership. Nationalization may occur with or without financial compensation to the former owners. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Midland Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
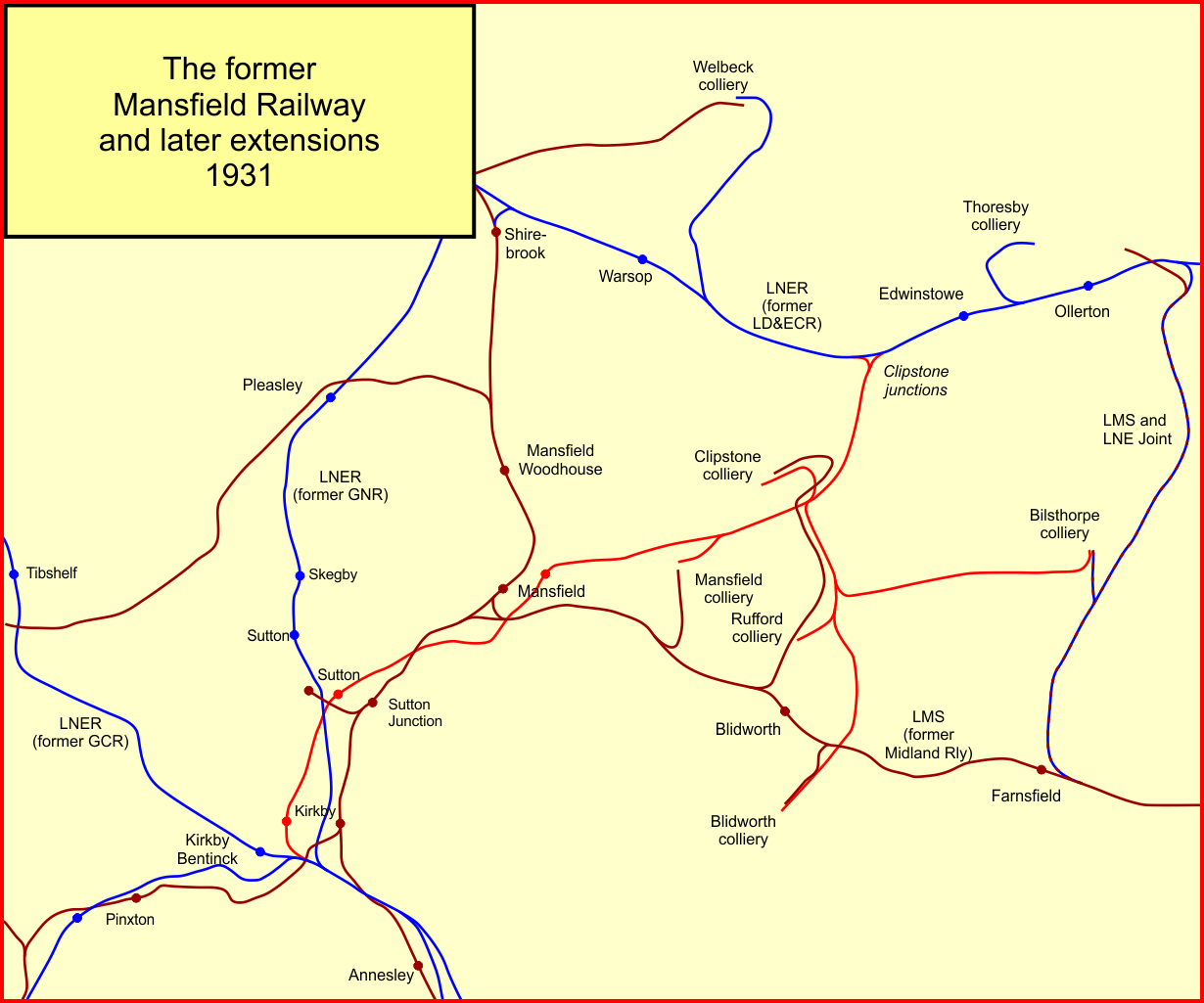
Mansfield Railway
The Mansfield Railway was an eleven-mile railway line in Nottinghamshire, England. It was built to serve collieries opening in the coalfield around Mansfield, and ran between junctions at Clipstone and Kirkby-in-Ashfield on the Great Central Railway. It opened in 1916 and was worked by the GCR. Passenger stations were opened on the line, although, at the date of opening, road bus competition was already dominant. The passenger service was withdrawn in 1956 and the line closed in stages as collieries ceased work, completely ending operation in 2003. Prior railways Railways had existed in the immediate area of Mansfield for many years. The first proper railway had been the Mansfield and Pinxton Railway of 1819, built for the purpose of conveying coal from Pinxton Basin on the Cromford Canal. It was a horse-drawn edge railway.Vanags, John, ''The Mansfield and Pinxton Railway'', The Old Mansfield Society, Mansfield, 2001, , pages 17 and 23 The Midland Railway established a prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkby-in-Ashfield Central Railway Station
Kirkby-in-Ashfield Central is a former railway station that served the town of Kirkby-in-Ashfield, Nottinghamshire. History The station was opened in 1917 by the Mansfield Railway along with Mansfield Central and Sutton-in-Ashfield Central. The line, including its stations, was worked by the Great Central Railway and became part of the LNER in 1923 and subsequently British Rail British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British rai ...ways in 1948. The station was conventional and spacious. Most passenger services plied between Nottingham Victoria and Mansfield Central, with some extending to Edwinstowe and Ollerton. Goods and timetabled passenger services ceased on 3 January 1956, though Summer weekend excursion traffic to Scarborough, Cleethorpes, Skegness and Mablethorpe cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkby-in-Ashfield East Railway Station
Kirkby-in-Ashfield East railway station was a station in Kirkby-in-Ashfield, Nottinghamshire. It was opened in 1848, and was located on the Midland Railway's Mansfield Branch Line (Now the Robin Hood Line). It was one of three stations that served the town. The others were both Kirkby-in-Ashfield Central and Kirkby Bentinck. The station was replaced by the modern-day station of the same name (minus the East name). History Opened by the Midland Railway, it became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923. The station then passed on to the London Midland Region of British Railways on nationalisation in 1948, the station survived use until 1965. Stationmasters *S. Osman 1873 - 1874 (resigned 30 June 1874) *John Mercer 1874 - 1890 (formerly station master at Worthington) *William Tunn 1890 - 1896 (formerly station master at Fiskerton) *Henry St. John Newell 1896 - 1901 (committed suicide 23 October 1901) *Albert William Niblett 1902 - 1910 *A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newstead Railway Station
Newstead railway station serves the village of Newstead in Nottinghamshire, England. Newstead was the original terminus of the Robin Hood Line when it was re-opened in 1993 by British Rail, under the Regional Railways sector. The line has since been extended to Mansfield and Worksop. Annesley, just to the north of Newstead, did not re-open. Newstead Abbey, the ancestral home of Lord Byron George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the ... is about two to three miles away and is served by this station. Services All services at Newstead are operated by East Midlands Railway. During the weekday off-peak and on Saturdays, the station is generally served by an hourly service northbound to and southbound to . During the peak hours, the station is also served by an additional tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways Board
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Midland Region Of British Railways
The London Midland Region (LMR) was one of the six regions created on the formation of the nationalised British Railways (BR), and initially consisted of ex-London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) lines in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The region was managed first from buildings adjacent to Euston station, and later from Stanier House in Birmingham. It existed from the creation of BR in 1948, ceased to be an operating unit in its own right in the 1980s, and was wound up at the end of 1992. Territory At its inception, the LMR's territory consisted of ex-LMS lines in England and Wales. The Mersey Railway, which had avoided being "Grouped" with the LMS in 1923, also joined the LMR. The LMR's territory principally consisted of the West Coast Main Line (WCML), the Midland Main Line (MML) south of Carlisle, and the ex-Midland Cross Country route from Bristol to Leeds. During the LMR's existence there were a number of transfers of territory to and from other regions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashfield, Nottinghamshire
Ashfield () is a local government district in Nottinghamshire, England. The population of Ashfield was 127,200 in 2018. The district is mostly urban and forms part of both the Nottingham and Mansfield Urban Areas. There are three towns in the district; Sutton-in-Ashfield, Kirkby-in-Ashfield and Hucknall. The district was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, by the merger of urban districts of Hucknall, Kirkby-in-Ashfield, Sutton-in-Ashfield and parts of Basford Rural District, namely the parishes of Annesley, Felley and Selston. The largest settlement is Sutton-in-Ashfield. Towns and villages in the district include the following: * Annesley * Annesley Woodhouse * Hucknall * Huthwaite * Jacksdale * Kirkby-in-Ashfield * Selston * Skegby * Sutton-in-Ashfield * Stanton Hill * Teversal * Underwood Politics Elections to the district are held every 4 years, with currently 35 councillors being elected from 23 wards. Since 2018 the council has been l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |