|
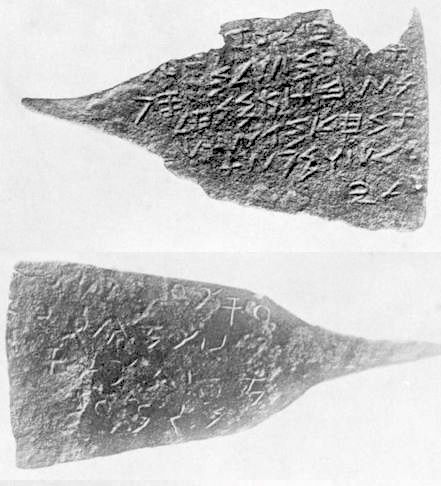
Ankh-Hapy Stele
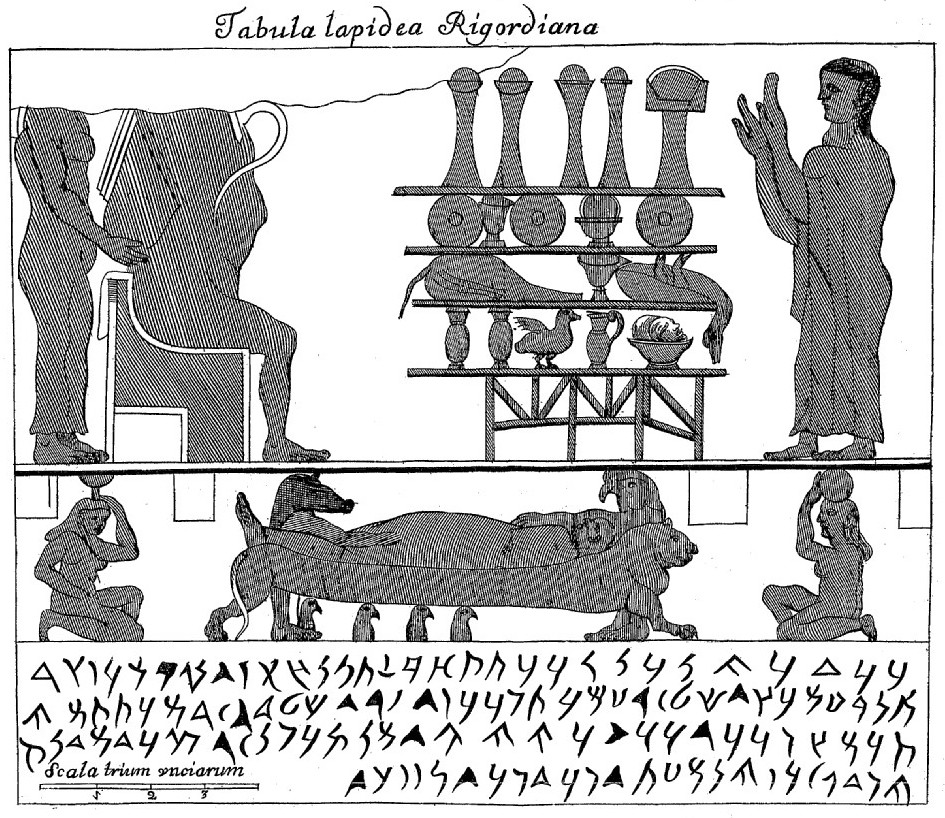
The Ankh-Hapy stele is an Egyptian-Aramaic stele dated to 525–404 BCE. It was first published in a letter from François Lenormant to Ernest Renan in the '' Journal asiatique''; Lenormant had noticed the stele in the Vatican collections and had brought a cast from Rome in 1860. Lenormant considered the stele to be reminiscent of the Carpentras Stele The Carpentras Stele is a stele found at Carpentras in southern France in 1704 that contains the first published inscription written in the Phoenician alphabet, and the first ever identified (a century later) as Aramaic. It remains in Carpentras, a .... The inscription was considered to be Aramaic, on the basis that it used the same style of writing and dialect as the Carpentras stele, the Turin papyri, the Blacas papyri and an Aramaic papyrus in the Louvre. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funerary Stele Of Ankh-Hapy, With Aramaic Inscription, Memphis, 27th Dynasty, 525-404 BC, Limestone - Museo Gregoriano Egizio - Vatican Museums - DSC00800
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect the dead, from interment, to various monuments, prayers, and rituals undertaken in their honor. Customs vary between cultures and religious groups. Funerals have both normative and legal components. Common secular motivations for funerals include mourning the deceased, celebrating their life, and offering support and sympathy to the bereaved; additionally, funerals may have religious aspects that are intended to help the soul of the deceased reach the afterlife, resurrection or reincarnation. The funeral usually includes a ritual through which the corpse receives a final disposition. Depending on culture and religion, these can involve either the destruction of the body (for example, by cremation or sky burial) or its preservat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Lenormant
François Lenormant (17 January 1837 – 9 December 1883) was a 19th-century French Hellenist, Assyriologist and archaeologist. Biography Early life Lenormant's father, Charles Lenormant, distinguished as an archaeologist, numismatist and Egyptologist, was anxious that his son should follow in his steps. He made him begin Greek at the age of six, and the child responded so well to this precocious scheme of instruction, that when he was only fourteen an essay of his, on the Greek tablets found at Memphis, appeared in the ''Revue Archéologique''. In 1856 he won the numismatic prize of the Académie des Inscriptions with an essay entitled ''Classification des monnaies des Lagides'' and in 1862 he became sub-librarian of the Institut de France. In 1858 he visited Italy and in 1859 accompanied his father on a journey of exploration to Greece, during which Charles succumbed to fever at Athens. Lenormant returned to Greece three times during the next six years, supervising excavations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Renan
Joseph Ernest Renan (; 27 February 18232 October 1892) was a French Orientalist and Semitic scholar, expert of Semitic languages and civilizations, historian of religion, philologist, philosopher, biblical scholar, and critic. He wrote influential and pioneering historical works on the origins of early Christianity, and espoused popular political theories especially concerning nationalism and national identity. Renan is known as being among the first scholars to advance the now-discredited Khazar theory, which held that Ashkenazi Jews were descendants of the Khazars, Turkic peoples who had adopted Jewish religion and migrated to Western Europe following the collapse of their khanate. Life Birth and family He was born at Tréguier in Brittany to a family of fishermen. His grandfather, having made a small fortune with his fishing smack, bought a house at Tréguier and settled there, and his father, captain of a small cutter and an ardent republican, married the daughter of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Asiatique
The ''Journal asiatique'' (full earlier title ''Journal Asiatique ou Recueil de Mémoires, d'Extraits et de Notices relatifs à l'Histoire, à la Philosophie, aux Langues et à la Littérature des Peuples Orientaux'') is a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal established in 1822 by the Société Asiatique covering Asian studies. It publishes articles in French and several other European languages. Cited texts are presented in their original languages. Each issue also includes news of the Société Asiatique and its members, obituaries of notable Orientalists, critical reviews, and books received. The journal is published by Peeters Publishers on behalf of the Société Asiatique and the editor-in-chief is Jean-Marie Durand. It is one of the oldest continuous French publications. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: Bibliographie linguistique/Linguistic Bibliography, ATLA Religion Database, Index to the Study of Religions Online, Index Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpentras Stele
The Carpentras Stele is a stele found at Carpentras in southern France in 1704 that contains the first published inscription written in the Phoenician alphabet, and the first ever identified (a century later) as Aramaic. It remains in Carpentras, at the Bibliothèque Inguimbertine, in a "dark corner" on the first floor. Rudolf Jaggi, (2012) " completely wrong, stele found in Égypt (MemphisDer "Stein von Carpentras" Kemet: Die Zeitschrift für Ägyptenfreunde, volume 21, issue 1, p.58-61: "So landet man über kurz oder lang vor der Bibliothèque Inguimbertine. Der 1745 von Malachie d'Inguimbert gegründeten Bibliothek ist heute die Musée Comtadin-Duplessis angeschlossen, ein kleines Museum mit Volkskunst und Werken einheimischer Maler. Im ersten Stock des schönen Gebäudes findet sich in einer finsteren Ecke die alte Vitrine mit dem sog. Stein von Carpentras." Older Aramaic texts were found since the 9th century BC, but this one is the first Aramaic text to be published in Europe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaanite And Aramaic Inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the society and history of the ancient Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription. The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician and Hebrew. Languages The old Aramaic period (850 to 612 BC) saw the production and dispersal of inscriptions due to the rise of the Arameans as a major force in Ancient Near East. Their language was adopted as an international language of diplomacy, particularly during the late stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanaanäische Und Aramäische Inschriften
Kanaanäische und Aramäische Inschriften (in English, Canaanite and Aramaic Inscriptions), or KAI, is the standard source for the original text of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions not contained in the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. It was first published from 1960 to 1964 in three volumes by the German Orientalists Herbert Donner and Wolfgang Röllig, and has been updated in numerous subsequent editions. The work attempted to "integrate philology, palaeography and cultural history" in the commented re-editing of a selection of Canaanite and Aramaic Inscriptions, using the "pertinent source material for the Phoenician, Punic, Moabite, pre-exile-Hebrew and Ancient Aramaic cultures." Röllig and Donner had the support of William F. Albright in Baltimore, James Germain Février in Paris and Giorgio Levi Della Vida in Rome during the compilation of the first edition. Editions The 4th edition was published between 1966-69, and a 5th edition was published in 2002. However, the 5t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum
The ("Corpus of Semitic Inscriptions", abbreviated CIS) is a collection of ancient inscriptions in Semitic languages produced since the end of 2nd millennium BC until the rise of Islam. It was published in Latin. In a note recovered after his death, Ernest Renan stated that: "Of all I have done, it is the Corpus I like the most." The first part was published in 1881, fourteen years after the beginning of the project. Renan justified the fourteen year delay in the preface to the volume, pointing to the calamity of the Franco-Prussian war and the difficulties that arose in the printing the Phoenician characters, whose first engraving was proven incorrect in light of the inscriptions discovered subsequently. A smaller collection – ("Repertory of Semitic Epigraphy", abbreviated RES) – was subsequently created to present the Semitic inscriptions without delay and in a deliberately concise way as they became known, and was published in French rather than Latin. The was for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textbook Of Aramaic Documents From Ancient Egypt
Textbook of Aramaic Documents from Ancient Egypt, often referred to as TAD or TADAE, is a four volume corpus of Aramaic inscriptions written during the period of ancient Egypt, written by Bezalel Porten and Ada Yardeni. Originally envisaged to be the ''Corpus Papyrorum Aramaicarum'', following the ''Corpus Papyrorum Judaicarum'', it grew to incorporate all Aramaic inscriptions from the region, not just on papyrus, so the title was changed – this time borrowing from J. C. L. Gibson's 1971 ''Textbook of Syrian Semitic Inscriptions''. Each of volumes 1-3 contains 40-50 texts (vol. 1 letters (A); vol. 2 contracts (B); vol. 3 literary texts (C)), and volume 4 contains 478 texts, including D1-5: 216 papyrus fragments; D6: 14 leather; D7-10: 87 ostraca. The collection does not include the Saqqarah papyri and most of the Clermont-Ganneau ostraca.Dion, P.-E. (2000). eview of Textbook of Aramaic Documents from Ancient Egypt. Newly Copied, Edited and Translated into Hebrew and English, Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the society and history of the ancient Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription. The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician and Hebrew. Languages The old Aramaic period (850 to 612 BC) saw the production and dispersal of inscriptions due to the rise of the Arameans as a major force in Ancient Near East. Their language was adopted as an international language of diplomacy, particularly during the late stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |