|
Anima Locus
The anima loci or animus loci is the "soul" of a place, its essential personality. A concept linked to the supernatural spirits of nature as residing in stones, springs, mountains, islands, trees, etc.Pennick, Nigel (1996). ''Celtic Sacred Landscapes''. Thames & Hudson. . P. 13 - 15. This practice is found in religions that have gods that may be more animal than man, like the Japanese Shinto. These beliefs are held throughout some modern religions too. Some of the Catholic Church has some beliefs like these. A country that follows these beliefs is Ireland, "there are several sites sacred to St. Patrick, but investigation has revealed that these were sites devoted to the worship of various Celtic gods and spirits long before the Catholic Church co-opted the location." Witchcraft In witchcraft, the anima loci is often referred to a spirit of the place, sprite, fairy, guardian. Sites with strong anima loci Image:Duskwatergorge2.JPG, Image:Duskwatergorge1.JPG, Image:Carlinstonea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
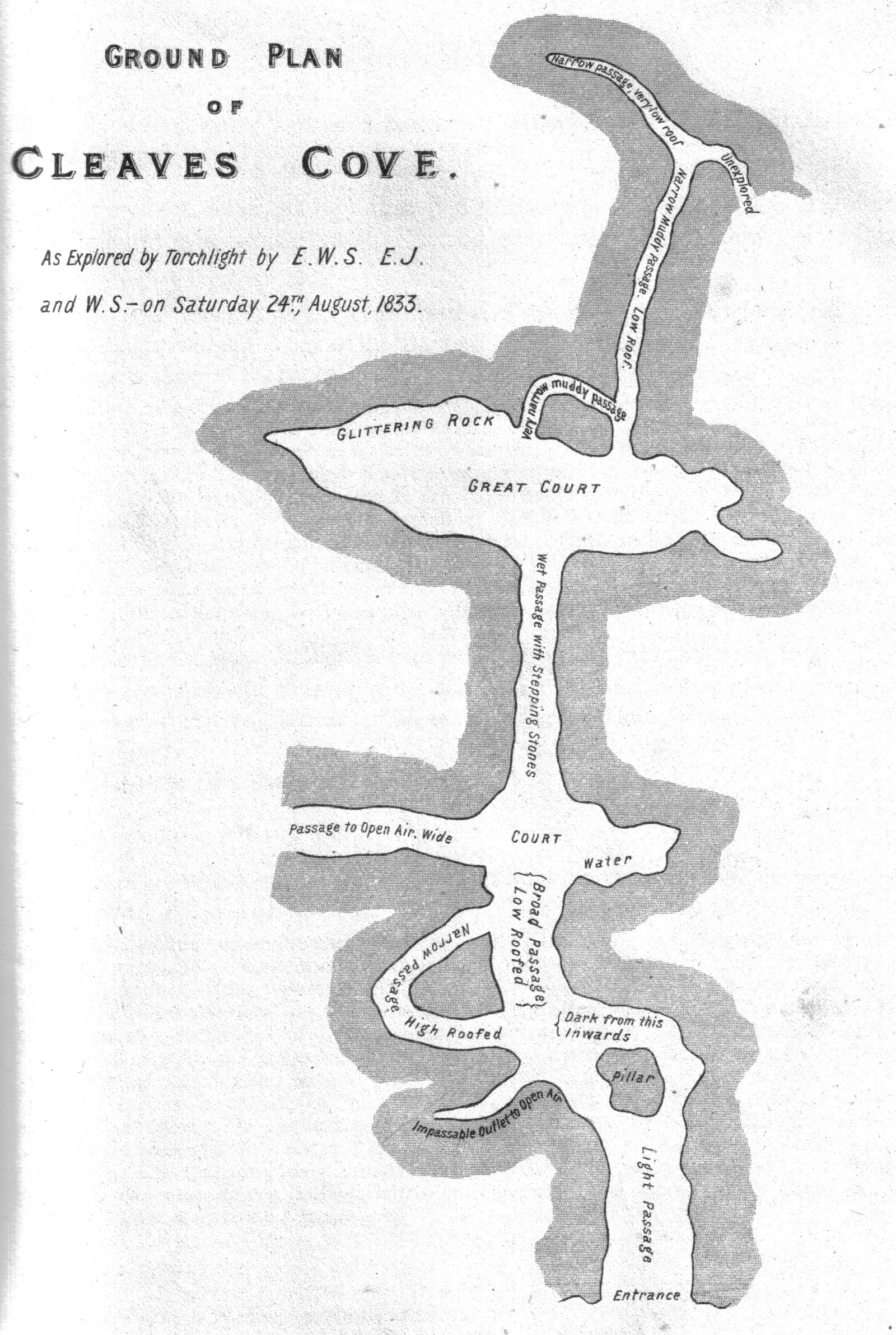
Cleeves Cove Cave
Cleeves Cove or Blair Cove is a solutional cave system on the Dusk Water in North Ayrshire, Scotland, close to the town of Dalry. Cave system The Cleeves, or Cleaves Cove (Scots) cave system is situated in the lower beds of Carboniferous limestone. It has a total passage length of around . The caves are now well above the level of the Dusk Water and lie close to Cleeves Farm and Blair Mill on the Blair Estate. Many of the stalactites and stalagmites have been damaged by visitors. The cave has three practical entrances facing onto the Dusk Water. A number of older books refer to ''the romantic sylvan dell of Auchenskeigh,'' now Auchenskeith, derived from ''Achadh-na-sgitheach'' - the field of thorns.Dobie, James D. (ed Dobie, J.S.) (1876). ''Cunninghame, Topographized by Timothy Pont'' 1604–1608, with continuations and illustrative notices. Pub. Glasgow : John Tweed. p. 49. The calcareous incrustations in these caves were compared with Gothic fretwork. A number of old limesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlin Stone
Carlin Stone or Carline Stane is the name given to a number of prehistoric standing stones and natural stone or landscape features in Scotland. The significance of the name is unclear, other than its association with old hags, witches, and the legends of the Cailleach. Etymology A 'Carle' in Scots is a commoner, a husband or in a derogatory sense, a churl or male of low birth. The name 'Carline', 'Cairlin', Carlin, 'Cyarlin', 'Kerlin' or 'Kerl' was also used in lowland Scots as a derogatory term for an old woman meaning an 'old hag'.Scots Dictionary It is from Old Norse ''Kerling'' or a corruption or equivalent in ScotsMcHardy, Stuart (1999), ''Scotland: Myth, Legend & Folklore''. Pub. Luath Press, Edinburgh. P. 24. of the Gaelic word “ |
Moot Hill
A moot hill or ''mons placiti'' (statute hill) is a hill or mound historically used as an assembly or meeting place, as a moot hall is a meeting or assembly building, also traditionally to decide local issues. In early medieval Britain, such hills were used for "moots", meetings of local people to settle local business. Among other things, proclamations might be read; decisions might be taken; court cases might be settled at a moot. Although some moot hills were naturally occurring features or had been created long before as burial mounds, others were purpose-built. Etymology Although the word ''moot'' or ''mote'' is of Old English origin, deriving from the verb ''to meet'', it has come to have a wider meaning throughout the United Kingdom; initially referring to any popular gathering. In England, the word '' folkmoot'' in time came to mean a more specific local assembly with recognised legal rights. In Scotland the term is used in the literature for want of any other single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giffordland, Ayrshire
Giffordland is in North Ayrshire, Parish of Dalry (Cunninghame) in the former Region of Strathclyde, Scotland. Background Giffordland was a small barony, but the families associated with it played an active part in the history of feudal Scotland. The name is given as just 'Gifford' on Armstrong's 1775 map Andrew Armstrong's map. and Ainslie's 1821 map and as 'Giffertland Mains' on the first 6 inch OS maps of 1840 - 1880. A Giffordland Mill, originally with stepping stones and now a bridge, lie at the (Keaff in 1747 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Researcher's Guide To Local History Terminology
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |