|
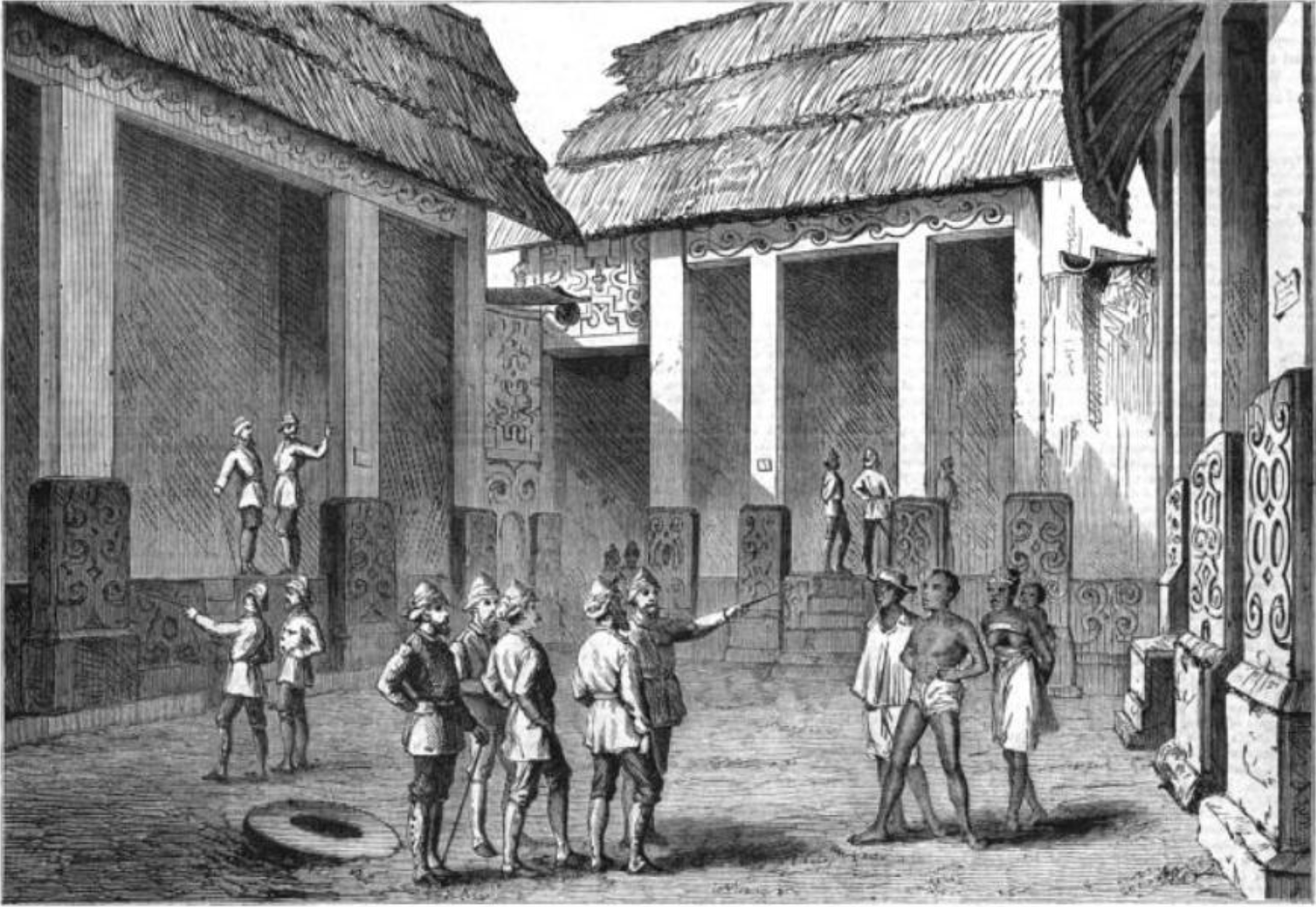
Anglo-Ashanti Wars
The Anglo-Ashanti wars were a series of five conflicts that took place between 1824 and 1900 between the Ashanti Empire—in the Akan people, Akan interior of the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast—and the British Empire and its African allies. Despite initial Ashanti victories, the British ultimately prevailed in the conflicts, resulting in the complete annexation of the Ashanti Empire by 1900. Earlier wars The British fought three earlier wars in the Gold Coast: In the Ashanti–Fante War of 1806–07, the British refused to hand over two rebels pursued by the Ashanti, but eventually handed one over (the other escaped). In the Ga–Fante War of 1811, the Ashanti sought to aid their Ga people, Ga allies in a war against the Fante and their British allies. The Ashanti army won the initial battles but was forced back by guerrilla fighting from the Fante. The Ashanti captured a British fort at Tantamkweri. In the Ashanti–Akim–Akwapim War of 1814–16 the Ashanti def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonisation Of Africa
External colonies were first founded in Africa Colonies in antiquity, during antiquity. Ancient Greece, Ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans established colonies on the African continent in North Africa, similar to how they established settler-colonies in parts of Eurasia. Some of these endured for centuries; however, popular parlance of colonialism in Africa usually focuses on the history of colonialism, European conquests of List of kingdoms in Africa throughout history, African states and Indigenous peoples of Africa, societies in the Scramble for Africa (1884–1914) during the age of New Imperialism, followed by gradual decolonisation of Africa, decolonisation after World War II. The principal powers involved in the modern colonisation of Africa were British Empire, Britain, French colonial empire, France, German colonial empire, Germany, Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Spain, Belgian Empire, Belgium, and Italian Empire, Italy. European rule had Analysis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofi Karikari
Kofi Karikari (–) Cameron Duodu"Obituary of Beryl Karikari" ''The Guardian'', 5 March 2007. was the tenth King of the Ashanti Empire, and grandnephew of Kwaku Dua I, whose sudden death in April 1867 sparked internal strife about the succession. Kofi Karikari was chosen by an electoral majority, reigning from 28 May 1867 until his forced abdication on 26 October 1874.T. C. McCaskie, ''State and Society in Pre-Colonial Asante'', Cambridge University Press, 2003, pp. 69–70. Karikari was the son of Afua Kobi. A notable achievement of Karikari was the intentional neglect of the armed forces, a step taken to avoid the escalation of war. A golden trophy head, owned by Karikari can be found at the Wallace Collection in London, acquired by Sir Richard Wallace in May 1874 for £500. Wallace Collection The Wallace Collection is a museum in London occupying Hertford House in Manchester Square, the former townhouse (Great Britain), townhouse of the Seymour family, Marquess of Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the north Atlantic Ocean.* * * Metropolitan Denmark, also called "continental Denmark" or "Denmark proper", consists of the northern Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands. It is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying southwest of Sweden, south of Norway, and north of Germany, with which it shares a short border. Denmark proper is situated between the North Sea to the west and the Baltic Sea to the east.The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. The Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has roughly List of islands of Denmark, 1,400 islands greater than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashanti–Akim–Akwapim War
The Ashanti–Akim–Akwapim War, also known as the Ashanti Invasion of the Gold Coast, was the expansion of West African Empire of Ashanti against the alliance of Akyem and Akuapem people, Akuapem tribes from 1814 until 1816 for access to the coast. This battle was not a direct war on Akyem states, which were never subdued by any power, but a war to get access to the coasts in which the Akyem along with Akuapem forces allied for. In 1814 the Ashanti, under the leadership of List of rulers of Asante, Asantehene Osei Bonsu, defeated the outnumbered Akim-Akwapim alliance. After attacking the Fante Confederacy, Fante during this period, the Ashanti seized Accra and took over Fante country, turning it into an Ashanti province. After the war and with access to the coast the Ashanti followed up their victory by pillaging the coastal Ga people. See also *Empire of Ashanti *Ashanti-Fante War *Ga-Fante War *Anglo-Asante Wars *History of Ghana References External linksSanderson Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ga People
The Ga-Dangbe, Ga-Dangme, Ga-Adangme or Ga-Adangbe are an ethnic group in Ghana, Togo and Benin. The Ga or Gan and Dangbe or Dangme people are grouped as part of the Ga–Dangme ethnolinguistic group. The Ga-Dangmes are one ethnic group that lives primarily in the Greater Accra region of Ghana. Ethnic Ga family names (surnames) include Nikoi, Amon, Kotey, Kotei, Adei, Adjei, Kutorkor, Okantey, Oblitey, Lartey, Nortey, Aryee, Obodai, Oboshi, Torgbor, Torshii and Lante. The following are names derived from the ethnic Dangme and common among the Ningos Tettey, Tetteh, Teye, Narh, Narteh, Nartey, Kwei, Kweinor, Kwetey, Dugbatey, Martey, Addotey, Addo, Siaw, Saki, Amanor, Djangba, Kabu, Kabutey, Koranteng, Nortse, Horminor. These are aligned to the ethnic Ga as well: Lomo, Lomotey, Tetteh, Ankrah, Tetteyfio, Laryea, Ayitey, Okai, Bortey, Quaye, Quaynor, Ashong, Kotei, Sowah, Odoi, Ablor, Adjetey, Dodoo, Darku and Quartey. (Dawhenya royal family name: Darpoh) Under their leader Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ga–Fante War
The Ga–Fante War in 1811 was a war fought by the Ashanti Empire. The war was started when an Ashanti ally started a war against the Fante Confederacy, and resulted in victory, albeit an inconclusive one, for the Ashanti. The Fante enjoyed significant material and military support from the British throughout the early stages of the war. It involved a series of battles between the Ashanti, also known as Asante, and their allies, the Ga people of Accra, against an alliance of the rival Akan states of the Fante. In a series of conflicts, the Ashanti won the initial battles but were unable to hold their gains due to the adoption of asymmetrical tactics by the Fante. Despite being eventually forced to withdraw, the Ashanti managed to capture a British British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashanti–Fante War
The Ashanti–Fante War (1806–1807) was a war fought between the Ashanti Empire and the Fante Confederacy in the region of what is currently the Republic of Ghana. Background and the course of the war In 1806, the Asantehene, Osei Bonsu, brought charges of grave robbing on some of his subjects who ran from Kumasi to Assin. Fleeing Ashanti lands, these suspected grave robbers were granted refuge by the Fante. Osei Bonsu sent out envoys to the Fante state of Abura/Asebu/Kwamankese District, Abura for harboring fugitives. The last envoys were murdered by the Fante. Osei Bonsu declared war in response. The Ashanti sacked Abura in May 1806. The Ashanti later attacked the British fort at Anomabu on 15 June 1807 for protecting the Ashanti fugitives who had fled there. 8000 of the 1500 Fante at Anomabu were slain by 16 June. The Ashanti tried to capture the British fort with significant losses. List of governors of the Gold Coast, British governor Torrane surrendered the fort to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Coast (British Colony)
The Gold Coast was a British Empire, British Crown colony on the Gulf of Guinea in West Africa from 1821 until its independence in 1957 as Ghana. The term Gold Coast is also often used to describe all of the four separate jurisdictions that were under the administration of the Governor of the Gold Coast. These were the Gold Coast itself, Ashanti (Crown Colony), Ashanti, the Northern Territories of the Gold Coast, Northern Territories protectorate and the British Togoland, British Togoland trust territory. The first European explorers to arrive at the coast were the Portuguese in 1471. They encountered a variety of African kingdoms, some of which controlled substantial deposits of gold in the soil. In 1483, the Portuguese came to the continent for increased trade. They built the Castle of Elmina, the first European settlement on the Gold Coast. From here they acquired slavery, slaves and gold in trade for European goods, such as metal knives, beads, mirrors, rum, and guns. News ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan People
The Akan () people are a kwa languages, Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak languages within the Central Tano languages, Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano languages, Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family.''Languages of the Akan Area: Papers in Western Kwa Linguistics and on the Linguistic Geography of the Area of Ancient''. Isaac K. Chinebuah, H. Max J. Trutenau, Linguistic Circle of Accra, Basler Afrika Bibliographien, 1976, pp. 168. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Adansi, Agona, Akuapem people, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi people, Anyi, Ashanti people, Asante, Baoulé people, Baoulé, Bono people, Bono, Chakosi people, Chakosi, Fante people, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi people, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta people, Ahanta, Denkyira and Nzema people, Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashanti Empire
The Asante Empire ( Asante Twi: ), also known as the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted from 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana and also parts of Ivory Coast and Togo. Due to the empire's military prowess, wealth, architecture, sophisticated hierarchy and culture, the Asante Empire has been extensively studied and has more historic records written by European, primarily British, authors than any other indigenous culture of sub-Saharan Africa. Starting in the late 17th century, the Asante king Osei Tutu ( – 1717) and his adviser Okomfo Anokye established the Asante Kingdom, with the Golden Stool of Asante as a sole unifying symbol. Osei Tutu oversaw a massive Asante territorial expansion, building up the army by introducing new organisation and turning a disciplined royal and paramilitary army into an effective fighting machine. In 1701, the Asante army conquered Denkyira, giving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |