|
André Diethelm
André Diethelm (3 July 1896 – 11 January 1954) was born in Bourg-en-Bresse (Ain department) and was a French Resistance fighter and politician. As an Inspector General of Finance, he joined General de Gaulle and Free France during the Second World War, and presided over the Rally of the French People political party ( (RPF)) under the French Fourth Republic, Fourth Republic. Early life and education He pursued a secondary education in Foix. He was admitted to the prestigious École normale supérieure (Paris), École normale supérieure in Paris in 1914, but the war interrupted his studies just as they began. Career Diethelm fought in the First World War, in Alsace, on the Eastern front, and in Greece. After the war, he returned to the École normale supérieure but in 1919 he gave up taking the Agrégation, competitive civil service exam, preferring to go for the competitive exam for the Inspectorate General of Finances, in which he came in second. He was in charge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
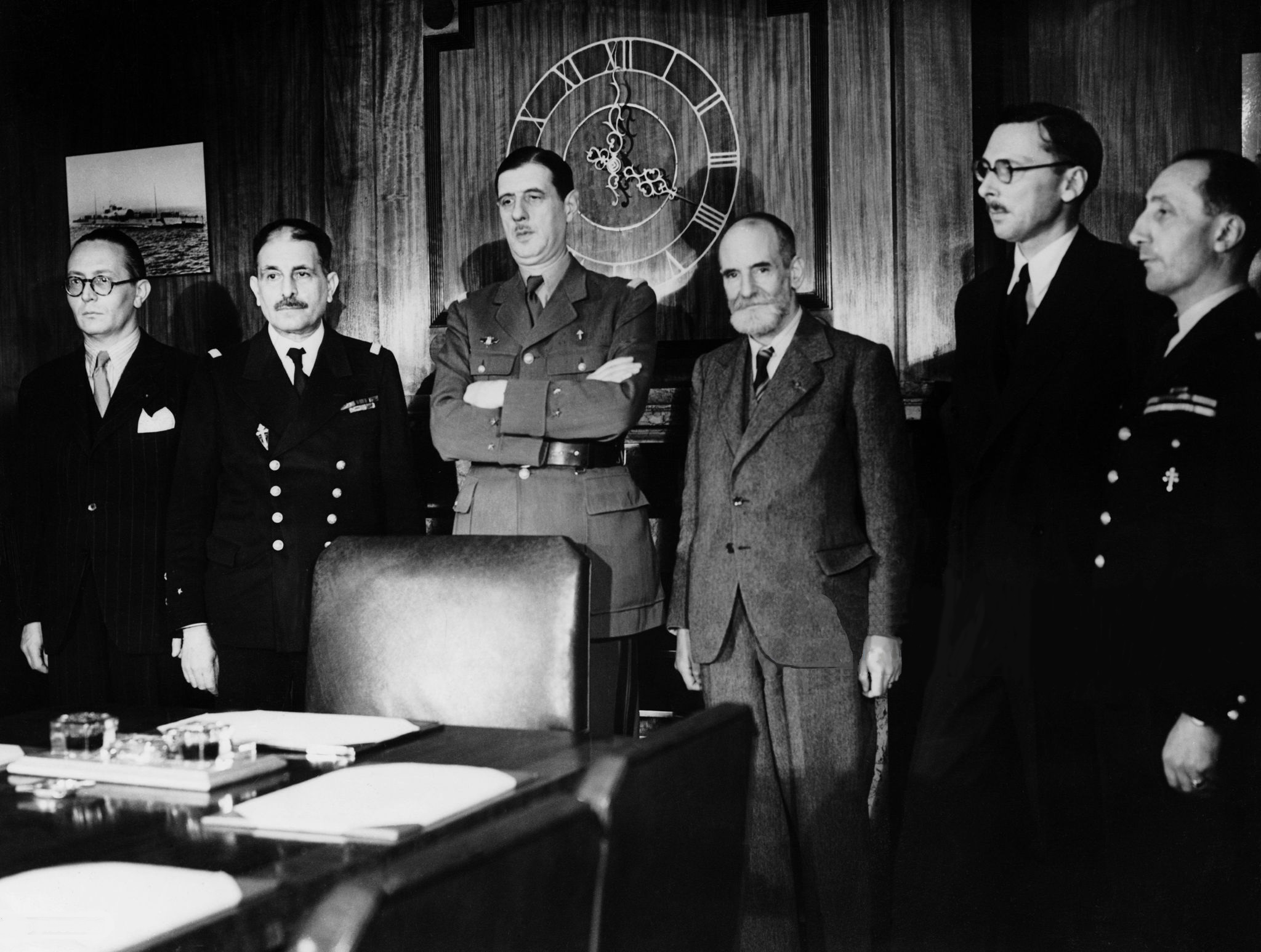
French National Committee
The French National Committee (french: Comité national français, CNF) was the coordinating body created by General Charles de Gaulle which acted as the government in exile of Free France from 1941 to 1943. The committee was the successor of the smaller Empire Defense Council. It was Winston Churchill who suggested that de Gaulle create a committee, in order to lend an appearance of more constitutionally based and less dictatorial authority. According to historian , De Gaulle went on to accept his proposal, but took care to exclude all his adversaries within the Free France movement, such as Émile Muselier, André Labarthe and others, retaining only "yes men" in the group. The CNF was founded 24 September 1941 by an edict signed by General de Gaulle in London. The committee remained active until 3 June 1943, when it merged with the French Civil and Military High Command headed by Henri Giraud, becoming the new French Committee of National Liberation. Composition The Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Mandel
Georges Mandel (5 June 1885 – 7 July 1944) was a French journalist, politician, and French Resistance leader. Early life Born Louis George Rothschild in Chatou, Yvelines, he was the son of a tailor and his wife. His family was Jewish, originally from Alsace. They moved into France in 1871 to preserve their French citizenship when Alsace-Lorraine was annexed by the German Empire at the end of the Franco-Prussian War. Early career Mandel began working life as a journalist for ''L'Aurore'', a literary and socialist newspaper founded in 1897 by Émile Zola and Georges Clemenceau. They notably defended Alfred Dreyfus during the Dreyfus Affair of the 1890s. The paper continued until 1916. As Minister of the Interior, Clemenceau later brought Mandel into politics as his aide. Described as "Clemenceau's right-hand man," Mandel helped Clemenceau control the press and the trade union movement during the First World War. Clemenceau said of him: "I fart and Mandel stinks". Inter-war per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free French Africa
Free French Africa (french: Afrique française libre, sometimes abbreviated to AFL) was the political entity which collectively represented the colonial territories of French Equatorial Africa and Cameroon under the control of Free France in World War II. It provided a political and territorial base for Free France and strengthened General Charles de Gaulle's international position. It made a major contribution to the war effort by financing the French Resistance, by the contribution of its many soldiers to the Free French Forces, and by the military exploitation of its installations and territories. Because of its geographical location, Free French Africa offered a considerable asset to the Allies, favoring military operations from Chad in the Western Desert Campaign in Egypt and Libya, as well as facilitating communications across the continent, thus giving British colonies the ability to communicate with each other. History and territories During the Second World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Policy Of Charles De Gaulle
The Foreign policy of Charles de Gaulle covers the diplomacy of Charles de Gaulle as French leader 1940–46 and 1958–1969, along with his followers. Status of France 1940-44 Prime Minister Winston Churchill and his top aides Foreign Minister Anthony Eden, and Chief of the Imperial General Staff General Alan Brooke in 1940-41 moved quickly to establish a base for in London. Control of the overseas French Empire was seen as the central issue, In the British government was prepared to use military support to help regain control. De Gaulle set up a shadow government, including a French National Council and a Resistance movement inside both Vichy France and German-controlled France. To establish his own leadership over like-minded Frenchmen, de Gaulle began broadcasting to France using BBC facilities. De Gaulle was especially keen to set up a Resistance movement inside France, However, many top British officials, as well as Roosevelt and sometimes even Churchill, still hoped fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Muselier
Émile Henry Muselier (Marseilles, 17 April 1882 – Toulon, 2 September 1965) was a French admiral who led the Free French Naval Forces ('' Forces navales françaises libres'', or FNFL) during World War II. He was responsible for the idea of distinguishing his fleet from that of Vichy France by adopting the Cross of Lorraine, which later became the emblem of all of the Free French. After entering the French Naval Academy (''École Navale'') in 1899, he embarked on a brilliant and eventful military career. He ran unsuccessfully in the legislative elections of 1946 as vice-president of the Rally of Republican Lefts (''Rassemblement des gauches républicaines'') and then entered private life as a consulting engineer before his retirement in 1960. He is buried in the cemetery of St. Pierre, at Marseilles. Early career Muselier's career started with a campaign in the Far East, several others in the Adriatic, one in Albania, which overlapped with a stay in Toulon. During World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Philip
André Philip (28 June 1902 – 5 July 1970) was a SFIO member who served in 1942 as Interior Minister under the Free French provisional government of General Charles de Gaulle. He also served as a finance minister in 1946 and part of 1947 in the Socialist‐led governments of Felix Gouin, Leon Blum and Paul Ramadier Paul Ramadier (17 March 1888 in La Rochelle – 14 October 1961 in Rodez) was a French statesman. Biography The son of a psychiatrist, Ramadier graduated in law from the University of Toulouse and started his profession as a lawyer in Par .... References External links * 1902 births 1970 deaths People from Pont-Saint-Esprit French Protestants Politicians from Occitania (administrative region) French Section of the Workers' International politicians Unified Socialist Party (France) politicians French Ministers of Finance French interior ministers Members of the 16th Chamber of Deputies of the French Third Republic Members of the Constitue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China. Membership in the Allies varied during the course of the war. When the conflict broke out on 1 September 1939, the Allied coalition consisted of the United Kingdom, France, and Poland, as well as their respective dependencies, such as British India. They were soon joined by the independent dominions of the British Commonwealth: Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Consequently, the initial alliance resembled that of the First World War. As Axis forces began invading northern Europe and the Balkans, the Allies added the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Greece, and Yugoslavia. The Soviet Union, which initially had a nonaggression pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincent Auriol
Vincent Jules Auriol (; 27 August 1884 – 1 January 1966) was a French politician who served as President of France from 1947 to 1954. Early life and politics Auriol was born in Revel, Haute-Garonne, as the only child of Jacques Antoine Auriol (1855–1933), a baker nicknamed Paul, and Angélique Virginie Durand (1862–1945).See Auriol's extensive biography by Jacques Batigne olauragais-patrimoine.fr His great-grandmother, Anne Auriol, was a first cousin of English engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel. He earned a law degree at the Collège de Revel in 1904 and began his career as a lawyer in Toulouse. A committed socialist, Auriol co-founded the newspaper '' Le Midi Socialiste'' in 1908; he was head of the Association of Journalists in Toulouse at this time. In 1914, Auriol entered the Chamber of Deputies as a Socialist Deputy for Muret, a position he retained until 1942.See the list of his mandates as a deputy oassembleenationale.fr He also served as Mayor of Muret from 3 May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Chaban-Delmas
Jacques Chaban-Delmas (; 7 March 1915 – 10 November 2000) was a French Gaullist politician. He served as Prime Minister under Georges Pompidou from 1969 to 1972. He was the Mayor of Bordeaux from 1947 to 1995 and a deputy for the Gironde ''département'' between 1946 and 1997. Biography Jacques Chaban-Delmas was born Jacques Michel Pierre Delmas in Paris. He studied at the Lycée Lakanal in Sceaux, before attending the École Libre des Sciences Politiques (''"Sciences Po"''). In the resistance underground, his final nom de guerre was ''Chaban''; after World War II, he formally changed his name to ''Chaban-Delmas''. As a general of brigade in the resistance, he took part in the Parisian insurrection of August 1944, with general de Gaulle. He was the youngest French general since François Séverin Marceau-Desgraviers, during the First French Empire. A member of the Radical Party, he finally joined the Gaullist Rally of the French People (RPF), which opposed the Fourth R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Soustelle
Jacques Soustelle (3 February 1912 – 6 August 1990) was an important and early figure of the Free French Forces, a politician who served in the French National Assembly and at one time served as Governor General of Algeria, an anthropologist specializing in Pre-Columbian civilizations, and vice-director of the Musée de l'Homme in Paris in 1939. Soustelle and his followers opposed any compromise with anticolonial activists in Algeria in the Algerian War. As Governor-General of Algeria, he helped the rise of Charles de Gaulle to the presidency of the Fifth Republic, but broke with De Gaulle over Algerian independence, joined the OAS in their efforts to overthrow De Gaulle and lived in exile between 1961 and 1968. On returning to France he resumed political and academic activity and was elected to the Académie française in 1983. Biography Jacques Soustelle was born in Montpellier, into a Protestant working-class family. A brilliant high school student, he was admitted to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine-et-Oise
Seine-et-Oise () was the former department of France encompassing the western, northern and southern parts of the metropolitan area of Paris. ''La Dépêche'' (in French), 2014-07-10. Its was and its administrative number was 78. Seine-et-Oise was disbanded in 1968 as part of the reorganisation of the departments of the Paris metropolitan area. The newly-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of The Republic (France)
The Council of the Republic (french: Conseil de la République) was the upper house of the French parliament under the Fourth Republic, with the National Assembly being the lower house. It was established by the Constitution of 1946, dissolved by the Constitution of 1958 and replaced with the Senate. History The constitution of the Fourth Republic, which came into force in 1946, stipulated that parliament was bicameral. The upper house was named the "Council of the Republic" (as opposed to the Senate of the Third Republic) and was granted greatly diminished powers. Role The council did not have the power to make laws, which was the responsibility of the National Assembly. The council was mainly consultative, and bills were only given a single reading at the council before being passed. However, it did share responsibility should the need arose to amend the constitution in matters regarding the election of the President of the Republic. A formal notice to the council was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |