|
Android P
Android Pie ( codenamed Android P during development), also known as Android 9 (API 28) is the ninth major release and the 16th version of the Android mobile operating system. It was first released as a developer preview on March 7, 2018, and was released publicly on August 6, 2018. On August 6, 2018, Google officially announced the final release of Android 9 under the title "Pie", with the update initially available for current Google Pixel devices, and releases for Android One devices and others to follow "later this year". The Essential Phone was the first third-party Android device to receive an update to Pie, notably coming day-and-date with its final release. The Sony Xperia XZ3 was the first device with Android Pie pre-installed. As of December 2022, 9.17% of all Android devices ran Android 9 Pie (not receiving security updates), with 17.2% of tablets alone still running Pie, making it the 3rd most popular version to date. History Android Pie, then referred to as "And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example: from a television broadcast). Widely used as a form of data entry from printed paper data records – whether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized receipts, business cards, mail, printouts of static-data, or any suitable documentation – it is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed on-line, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech, key data and text mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacOS Mojave
macOS Mojave ( ; version 10.14) is the fifteenth software versioning, major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. Mojave was announced at Apple's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, Worldwide Developers Conference on June 4, 2018, and was released to the public on September 24, 2018. The operating system's name refers to the Mojave Desert, the home of the Mojave Rattlesnake, and is part of a series of California-themed names that began with OS X Mavericks. It succeeded macOS High Sierra and was followed by macOS Catalina. macOS Mojave brings several iOS apps to the desktop operating system, including Apple News, Voice Memos, and HomeKit, Home. It also includes a much more comprehensive "dark mode", is the final version of macOS to support 32-bit application software, and is also the last version of macOS to support the iPhoto app, which had already been superseded in OS X Yosemite (10.10) by the newer Apple Photos, Photos app. Moja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IOS 12
iOS 12 is the twelfth major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc. Aesthetically similar to its predecessor, iOS 11, it focuses more on performance than on new features, quality improvements and security updates. Announced at the company's Worldwide Developers Conference on June 4, 2018, iOS 12 was released to the public on September 17, 2018. It was succeeded for the iPhone and iPod Touch by iOS 13 on September 19, 2019 and for the iPad by iPadOS 13 on September 24, 2019. Security updates for iOS 12 have continued for four years following the release of iOS 13 for devices unable to run the newer operating system. The latest update, 12.5.6, was released on August 31, 2022. History Introduction and initial release iOS 12 was introduced by Craig Federighi at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference keynote address on June 4, 2018. The first developer beta version was released after the keynote presentation, with the first public beta released on Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android Go
Android Go, officially Android (Go Edition), is a stripped-down version of the Android operating system, designed for low-end and ultra-budget smartphones (but is also used by some tablets). However, it is intended for smartphones with less than 2 GB of RAM and was first made available for Android Oreo. This mode has platform optimizations designed to reduce mobile data usage (including enabling Data Saver mode by default), and a special suite of Google Mobile Services designed to be less resource and bandwidth-intensive. Google Play Services package was also modularized to reduce its memory footprint. The Google Play Store will highlight lighter apps suited for these devices. The operating system's interface differs from that of mainline Android, with the quick-settings panel giving greater prominence to information regarding the battery, mobile-data limit, and available storage; the recent apps menu using a modified layout and being limited to four apps (in order to redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNS Over TLS
DNS over TLS (DoT) is a network security protocol for encrypting and wrapping Domain Name System (DNS) queries and answers via the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. The goal of the method is to increase user privacy and security by preventing eavesdropping and manipulation of DNS data via man-in-the-middle attacks. The well-known port number for DoT is 853. While DNS-over-TLS is applicable to any DNS transaction, it was first standardized for use between stub or forwarding resolvers and recursive resolvers, in in May of 2016. Subsequent IETF efforts specify the use of DoT between recursive and authoritative servers ("Authoritative DNS-over-TLS" or "ADoT") and a related implementation between authoritative servers (Zone Transfer-over-TLS or "xfr-over-TLS"). Server software BIND supports DoT connections as of version 9.17. Earlier versions offered DoT capability by proxying through stunnel. Unbound has supported DNS over TLS since 22 January 2018. Unwind has supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Efficiency Image File Format
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a container format for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video. HEIF can store images encoded with multiple coding formats, for example both SDR and HDR images. HEVC is an image and video encoding format and the default image codec used with HEIF. HEIF files containing HEVC-encoded images are also known as HEIC files. Such files require less storage space than the equivalent quality JPEG. HEIF files are a special case of the ISO Base Media File Format (ISOBMFF, ISO/IEC 14496-12), first defined in 2001 as a shared part of MP4 and JPEG 2000. Introduced in 2015, it was developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) and is defined as Part 12 within the MPEG-H media suite (ISO/IEC 23008-12). HEIF was adopted by Apple in 2017 with the introduction of iOS 11. History The requirements and main use c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi Round Trip Time
Task Group mc (TGmc) of the IEEE 802.11 Working Group, sometimes referred to as IEEE 802.11mc, was the third maintenance/revision group for the IEEE 802.11 WLAN standards. Purpose was to incorporate accumulated maintenance changes (editorial and technical corrections) into IEEE Std 802.11-2012, and roll up approved amendments into the standard. The work by TGmc resulted in the publication of IEEE Std 802.11-2016 in 2016. TGmc has ceased its operation. Maintenance/revision for IEEE Std 802.11-2016 is being handled by TGmd. Amendments rolled-In Following amendments were incorporated by TGmc on top of IEEE Std 802.11-2012: * IEEE Std 802.11ae-2012 * IEEE Std 802.11aa-2012 * IEEE Std 802.11ad-2012 * IEEE Std 802.11ac-2013 * IEEE Std 802.11af-2013 Wi-Fi Round Trip Time While it is not the main purpose of the maintenance/revision group, some features deemed not big enough to require a full Task Group within the IEEE 802.11 WG are sometimes added to the IEEE 802.11 standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 802
IEEE 802 is a family of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards for local area networks (LAN), personal area network (PAN), and metropolitan area networks (MAN). The IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC) maintains these standards. The IEEE 802 family of standards has had twenty-four members, numbered 802.1 through 802.24, with a working group of the LMSC devoted to each. However, not all of these working groups are currently active. The IEEE 802 standards are restricted to computer networks carrying variable-size packets, unlike cell relay networks, for example, in which data is transmitted in short, uniformly sized units called cells. Isochronous signal networks, in which data is transmitted as a steady stream of octets, or groups of octets, at regular time intervals, are also outside the scope of the IEEE 802 standards. The number 802 has no significance: it was simply the next number in the sequence that the IEEE used for standards projects. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Play Store
Google Play, also known as the Google Play Store and formerly the Android Market, is a digital distribution service operated and developed by Google. It serves as the official app store for certified devices running on the Android operating system and its derivatives, as well as ChromeOS, allowing users to browse and download applications developed with the Android software development kit (SDK) and published through Google. Google Play has also served as a digital media store, offering games, music, books, movies, and television programs. Content that has been purchased on Google Play Movies & TV and Google Play Books can be accessed on a web browser and through the Android and iOS apps. Applications are available through Google Play either for free or at a cost. They can be downloaded directly on an Android device through the proprietary Google Play Store mobile app or by deploying the application to a device from the Google Play website. Applications utilizing the hardwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
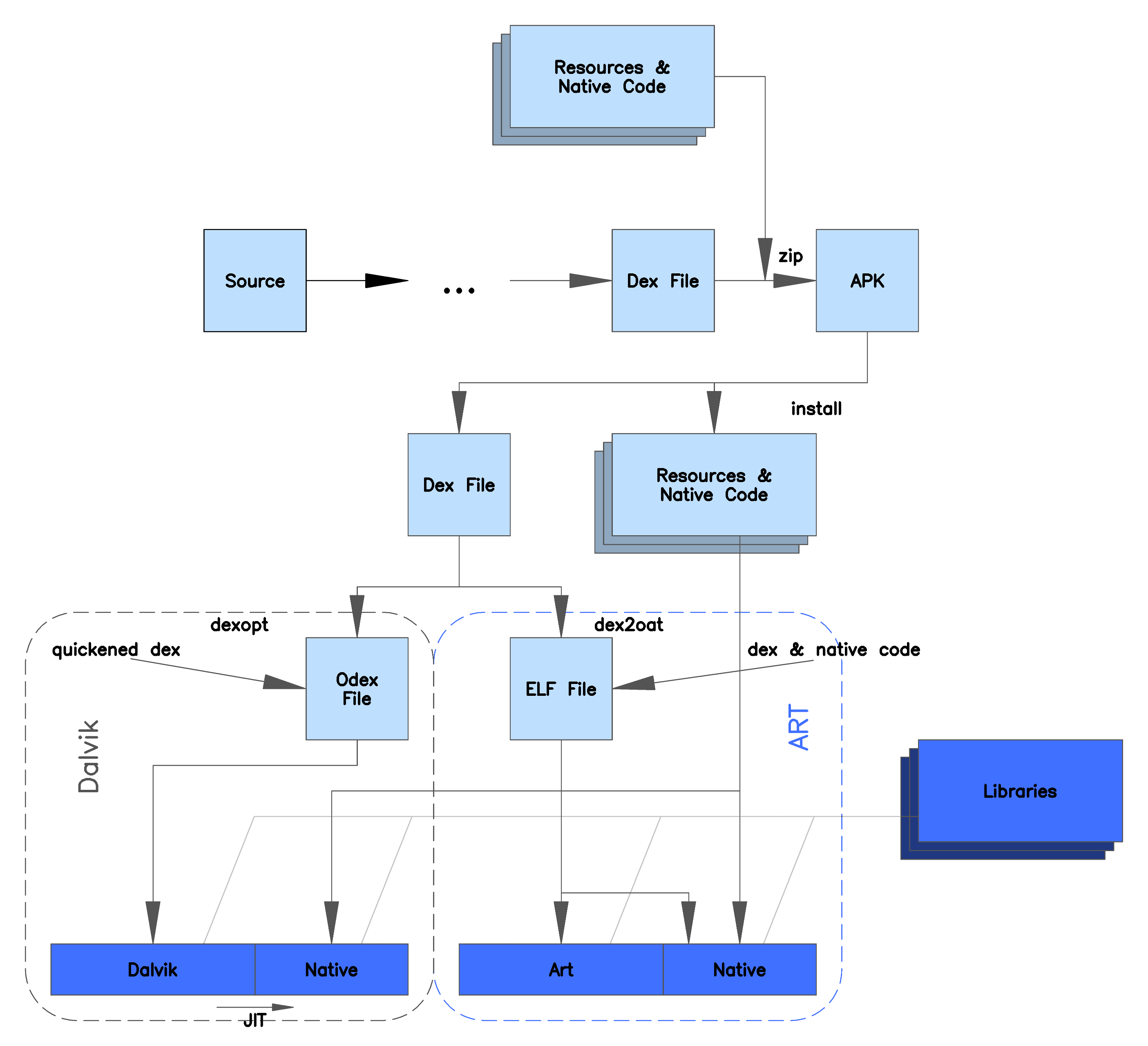
Android Runtime
Android Runtime (ART) is an application runtime environment used by the Android operating system. Replacing Dalvik, the process virtual machine originally used by Android, ART performs the translation of the application's bytecode into native instructions that are later executed by the device's runtime environment. Overview Android 2.2 "Froyo" brought trace-based just-in-time (JIT) compilation into Dalvik, optimizing the execution of applications by continually profiling applications each time they run and dynamically compiling frequently executed short segments of their bytecode into native machine code. While Dalvik interprets the rest of application's bytecode, native execution of those short bytecode segments, called "traces", provides significant performance improvements. Unlike Dalvik, ART introduces the use of ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation by compiling entire applications into native machine code upon their installation. By eliminating Dalvik's interpretation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android 4
Android 4 may refer to: * Android Ice Cream Sandwich (4.0 – 4.0.4) * Android Jelly Bean (4.1 – 4.3.1) * Android KitKat Android KitKat is the codename for the eleventh Android mobile operating system, representing release version 4.4. Unveiled on September 3, 2013, KitKat focused primarily on optimizing the operating system for improved performance on entry-level ... (4.4 – 4.4.4) {{Short pages monitor 4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |