|
Andrianjaka Razakatsitakatrandriana
Andrianjaka Razakatsitakatrandriana or Andrianjakatsitakatrandriana was the King of Imerina in the central Highlands of Madagascar from 1670–1675. He was born in Analamanga as Lamboritakatra, eldest son of King Andriantsimitoviaminandriandehibe. During his father's lifetime, Andrianjakatsitakatrandriana was granted Antananarivo and the land west of it, including Ambohidrabiby, Ambohimanga and regions in the north, as his fief. Although his younger brother, Andrianjakanavalondambo, demonstrated a stronger capacity for wise leadership, Andrianjakatsitakatrandriana was selected to succeed upon the death of their father in 1670. Andriantsimitoviaminandriandehibe took this decision on the basis of the tradition established by their Vazimba ancestors Rafohy and Rangita, who declared that the elder must rule before the younger. In 1675 Andriamampandry and the nobles of Imerina deposed him in favor of his younger brother. Reign Andrianjakatsitakatrandriana married twice during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Imerina Monarchs
This article lists the Imerina monarchs, from the earliest origins of the Merina monarchy until the French conquest of the Merina Kingdom during the Second Madagascar expedition. Early monarchs in the Merina line Below is a list of the line of Merina monarchs that ruled in the Central Highlands of Madagascar and from whom were issued the first true monarchs of a united Madagascar in the 19th century. Before the uniting of Madagascar, succession was based on the current monarch's designation of an heir, typically from among his or her own children. As such, the list below represents a direct genealogical line from the last 19th-century queen of Madagascar to some of the earliest known rulers identified in the 15th century or before. Prior to the 16th century, detailed information about the names and dates of Merina rulers becomes less consistent. Genealogy in this early period are derived primarily from oral history, while later names and dates are verifiable from primary source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andriana
Andriana refers to both the noble class and a title of nobility in Madagascar. Historically, many Malagasy ethnic groups lived in highly stratified caste-based social orders in which the ''andriana'' were the highest strata. They were above the Hova (free commoner castes) and Andevo (slaves). The Andriana and the Hova were a part of ''Fotsy'', while the Andevo were ''Mainty'' in local terminology. The Andriana strata originally constituted the nobility, warrior, and land owning class of the Merina society. They were endogamous and their privileges were institutionally preserved. While the term and concept of Andriana is studied with the Merina people of Madagascar, the term is not limited to them. The use of the word "Andriana" to denote nobility occurs among numerous other Malagasy ethnic groups such as the Betsileo, the Betsimisaraka, the Tsimihety, the Bezanozano, the Antambahoaka and the Antemoro. ''Andriana'' often traditionally formed part of the names of Malagasy kings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Monarchs In Africa
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malagasy Monarchs
Malagasy may refer to: *Someone or something from Madagascar *Malagasy people *Malagasy language *Malagasy Republic *Related to the culture of Madagascar See also *Madagascar (other) Madagascar is an island country located off the eastern coast of Africa. Madagascar may also refer to: Places * Geography of Madagascar * Madagascar Plate Entertainment * ''Madagascar'' (1994 film), a Cuban film by Fernando Pérez * ''Madagas ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampy
A sampy is an amulet or idol of spiritual and political importance among numerous ethnic groups in Madagascar. Amulets and idols fashioned from assorted natural materials have occupied an important place among many Malagasy communities for centuries. ''Ody'', personal amulets believed to protect or allocate powers to the wearer, were commonplace objects possessed by anyone from slave children to kings. The name ''sampy'' was given to those amulets that, while physically indistinguishable from ''ody'', were distinct in that their powers extended over an entire community. The ''sampy'' were often personified - complete with a distinct personality - and offered their own house with keepers dedicated to their service. In the sixteenth century, King Ralambo of the Merina people amassed twelve of the most reputed and powerful ''sampy'' from neighboring communities. He furthermore transformed the nature of the relationship between ''sampy'' and ruler: whereas previously the ''sampy'' had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty hump on their shoulders, a large dewlap, and sometimes drooping ears. They are well adapted to withstanding high temperatures, and are farmed throughout the tropical countries, both as pure zebu and as hybrids with taurine cattle, the other main type of domestic cattle. Zebu are used as draught and riding animals, dairy cattle, and beef cattle, as well as for byproducts such as hides and dung for fuel and manure. Some small breeds such as the miniature zebu are also kept as pets. In 1999, researchers at Texas A&M University successfully cloned a zebu. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle, especially zebu, have significant religious meaning. Taxonomy and name The scientific name ''Bos indicus'' was introduced by Carl Linnae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakalava People
The Sakalava are an ethnic group of Madagascar. They are found on the western and northwest region of the island, in a band along the coast. The Sakalava are one of the smaller ethnic groups, constituting about 6.2 percent of the total population, that is over 1,210,000 in 2014. Their name means "people of the long valleys." They occupy the western edge of the island from Toliara in the south to the Sambirano River in the north. Ethnic identity The Sakalava denominate a number of smaller ethnic groups that once comprised an empire, rather than an ethnic group in its own right. The origin of the word ''Sakalava'' itself is still subject to controversy, as well as its actual meaning. The most common explanation is the modern Malagasy translation of Sakalava meaning long ravines, denoting the relatively flat nature of the land in western Madagascar. Another theory is that the word is possibly from the Arabic ''saqaliba'', which is in turn derived from Late Latin ''sclavus'', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antananarivo Madagascar Andohalo Plaza
Antananarivo ( French: ''Tananarive'', ), also known by its colonial shorthand form Tana, is the capital and largest city of Madagascar. The administrative area of the city, known as Antananarivo-Renivohitra ("Antananarivo-Mother Hill" or "Antananarivo-Capital"), is the capital of Analamanga region. The city sits at above sea level in the center of the island, the highest national capital by elevation among the island countries. It has been the country's largest population center since at least the 18th century. The presidency, National Assembly, Senate and Supreme Court are located there, as are 21 diplomatic missions and the headquarters of many national and international businesses and NGOs. It has more universities, nightclubs, art venues, and medical services than any city on the island. Several national and local sports teams, including the championship-winning national rugby team, the Makis are based here. Antananarivo was historically the capital of the Merina peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
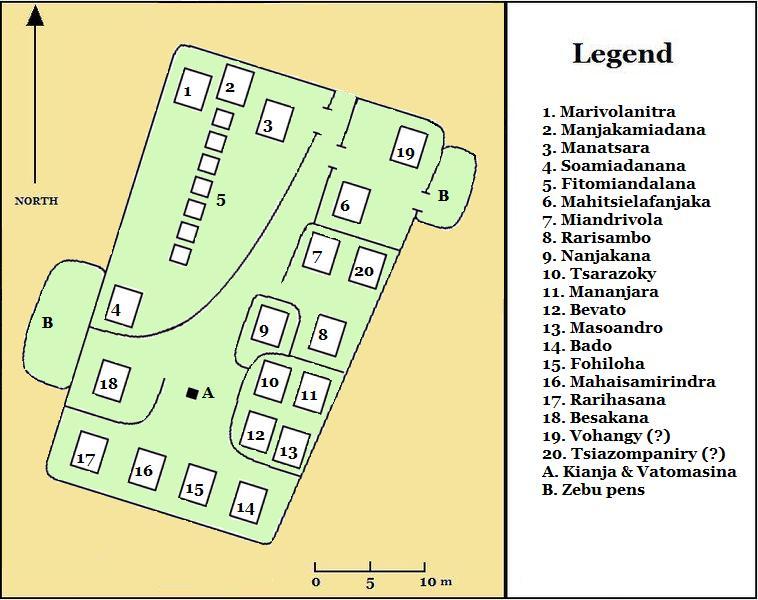
Rova Of Antananarivo
The Rova of Antananarivo ( mg, Rovan'i Manjakamiadana ) is a royal palace complex (''rova'') in Madagascar that served as the home of the sovereigns of the Kingdom of Imerina in the 17th and 18th centuries, as well as of the rulers of the Kingdom of Madagascar in the 19th century. Its counterpart is the nearby fortified village of Ambohimanga, which served as the spiritual seat of the kingdom in contrast to the political significance of the Rova in the capital. Located in the central highland city of Antananarivo, the Rova occupies the highest point on Analamanga, formerly the highest of Antananarivo's many hills. Merina king Andrianjaka, who ruled Imerina from around 1610 until 1630, is believed to have captured Analamanga from a Vazimba king around 1610 or 1625 and erected the site's first fortified royal structure. Successive Merina kings continued to rule from the site until the fall of the monarchy in 1896, frequently restoring, modifying or adding royal structures within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merina People
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina people Ethnic Groups of Madagascar Encyclopædia Britannica They are the "highlander" Malagasy ethnic group of the African island and one of the country's eighteen official ethnic groups. Their origins are mixed, predominantly with |
Rangita
Queen Rangita (died 1530), also known as Rangitamanjakatrimovavy, was a Vazimba sovereign who ruled at Merimanjaka in the central highlands of Madagascar after her father, King Andrianmpandramanenitra (Rafandramanenitra). She was succeeded upon her death by her daughter (some sources say her adopted sister), Queen Rafohy (1530-1540). Oral tradition is unclear about the roles and relations of Rangita and Rafohy to one another. This lack of clarity includes who was the mother to whom, who succeeded whom and which one was the mother of Andriamanelo Andriamanelo (Floruit, ''fl.'' 1540–1575) was king of Twelve sacred hills of Imerina#Hill of Alasora, Alasora in the central highlands region of Madagascar. He is generally considered by historians to be the founder of the Kingdom of Imeri .... According to one version of the oral tradition, Rangita had two sons, and possibly one daughter, Rafohy. These accounts relate that Rangita shared the stereotypical Vazimba physical charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andriantsimitoviaminandriandehibe
Andriantsimitoviaminandriandehibe ("the noble without equal among great nobles") was the King of Imerina in the central highlands of Madagascar from 1650 to 1670. He acceded to the throne on the death of his father, King Andriantsitakatrandriana. He had three wives: Ratompoimbahoaka of Ambohimalaza, Princess Ramahafoloarivo (granddaughter of King Andrianjaka), and Princess Rafaravavy Rampanananiamboninitany. He is responsible for establishing the rice paddies of the Betsimitatatra that lie to the west of Ankadimbahoaka.Callet (1908), p. 532 Reign Andriantsimitoviaminandriandehibe pledged to continue his father's work to transform the Bestimitatatra swamps into rice paddies to feed the growing population of Imerina. He selected two of his sons to oversee the labor. The two princes challenged one another to see who could complete their dike fastest. The king proceeded to traditionally divide the territory into northern and southern halves along the Ikopa River and assigned Andrianjaka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |