|
Andrew Cordier
Andrew Wellington Cordier (March 1, 1901 – July 11, 1975) was a United Nations official and President of Columbia University. Early life Cordier was born on a farm near Canton, Ohio and attended high school in Hartville, Ohio where he became quarterback of the football team and valedictorian of his graduating class. He graduated in 1922 from Manchester University and went on to earn a Ph.D. in Medieval History at the University of Chicago in 1927. He married the former Dorothy Butterbaugh in 1924. He studied at the Graduate Institute of International Studies in Switzerland in 1930–1931 where he made surveys of the situations in the Sudetenland, Danzig, and the Chaco War. He returned to Manchester University to teach in the Department of History and Political Science and at Indiana University extension. He became an international security advisor at the U.S. State Department in 1944 and was part of the U.S. delegation to the San Francisco Conference. The State Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Columbia University
The president of Columbia University is the chief officer of Columbia University in New York City. The position was first created in 1754 by the original royal charter for the university, issued by George II, and the power to appoint the president was given to an autonomous board of trustees. The university suspended operations upon the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, during which no individual served as president. When it was resuscitated by the New York State Legislature, the university was placed directly under the control of the Board of Regents of the University of the State of New York; its chancellor, George Clinton, served as the ''de facto'' president of Columbia University. Through the efforts of Alexander Hamilton and John Jay, control of the university was returned to a private board of trustees in 1787, which has to this day maintained the right to appoint or remove the president, who also serves on the board ''ex officio''. The university's first presi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy of the United States, foreign policy and foreign relations of the United States, relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nations, its primary duties are advising the President of the United States, U.S. president on international relations, administering List of diplomatic missions of the United States, diplomatic missions, negotiating international treaties and agreements, and representing the United States at the United Nations Security Council, United Nations conference. Established in 1789 as the first administrative arm of the Executive branch of the U.S. Government, U.S. executive branch, the State Department is considered among the most powerful and prestigious executive agencies. It is headed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Political Scientists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester University
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity , established = 2004 – University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 – UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 – Victoria University of Manchester 1880 – Victoria University 1851 – Owens College 1824 – Manchester Mechanics' Institute , endowment = £242.2 million (2021) , budget = £1.10 billion (2020–21) , chancellor = Nazir Afzal (from August 2022) , head_label = President and vice-chancellor , head = Nancy Rothwell , academic_staff = 5,150 (2020) , total_staff = 12,920 (2021) , students = 40,485 (2021) , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Manchester , country = England, United Kingdom , campus = Urban and suburban , colours = Manchester Purple Manchester Yellow , free_label = Scarf , free = , website = , logo = UniOfManchesterLogo.svg , affiliations = Universities Research Association Sutton 30 Russell Group EUA N8 Group NWUA ACUUniversities UK The University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrice Lumumba
Patrice Émery Lumumba (; 2 July 1925 – 17 January 1961) was a Congolese politician and independence leader who served as the first prime minister of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (then known as the Republic of the Congo) from June until September 1960. A member of the Congolese National Movement (MNC), he led the MNC from 1958 until his execution in January 1961. Ideologically an African nationalist and pan-Africanist, he played a significant role in the transformation of the Congo from a colony of Belgium into an independent republic. Shortly after Congolese independence in 1960, a mutiny broke out in the army, marking the beginning of the Congo Crisis. Lumumba appealed to the United States and the United Nations for help to suppress the Belgian-supported Katangan secessionists led by Moïse Tshombe. Both refused, due to suspicions among the Western world that Lumumba secretly held pro-communist views. These suspicions deepened when Lumumba turned to the Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of The Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo river. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to its northwest by Cameroon and its northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to its south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda Province, Cabinda and to its southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. The region was dominated by Bantu peoples, Bantu-speaking tribes at least 3,000 years ago, who built trade links leading into the Congo River basin. Congo was formerly part of the French colonial empire, French colony of French Equatorial Africa, Equatorial Africa. The Republic of the Congo was established on 28 November 1958 and gained independence from France in 1960. It was a Marxist–Leninist state from 1969 to 1992, under the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Neck, New York
Great Neck is a region on Long Island, New York, that covers a peninsula on the North Shore (Long Island), North Shore and includes nine villages, among them Great Neck (village), New York, Great Neck, Great Neck Estates, New York, Great Neck Estates, Great Neck Plaza, New York, Great Neck Plaza, Kings Point, New York, Kings Point, and Russell Gardens, and a number of unincorporated areas, as well as an area south of the peninsula near Lake Success, New York, Lake Success and the border territory of Queens. The incorporated village of Great Neck had a population of 9,989 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, while the larger Great Neck area comprises a residential community of some 40,000 people in nine villages and Hamlet (New York), hamlets in the town of North Hempstead, New York, North Hempstead, of which Great Neck is the northwestern quadrant. Great Neck has five ZIP Codes (11020–11024), which are united by Great Neck Park District, a park district, one library di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Malik
Yakov Alexandrovich Malik (russian: Яков Александрович Малик) (11 February 1980) was a Soviet diplomat. Biography Born in Ostroverkhovka village, Kharkov Governorate, Malik was educated at Kharkiv Institute of National Economy (1930). Then, he worked as an economist and the Communist Party's functionary in Kharkiv, since 1935 – in foreign affairs service in Moscow. He served as Ambassador in Japan from 1942 until 1945, the moment the Soviet government declared war on the Japanese Empire on Aug. 9. Malik was the Soviet ambassador to the United Nations from 1948 to 1952, and from 1968 to 1976. At the time of the United Nations Security Council Resolution 82 on 25 June 1950, Malik was boycotting the presence of a Nationalist Chinese representative. His absence enabled the resolution to pass unanimously with a 9–0 vote. On the floor of the United Nations on 23 June 1951, he proposed an armistice in the Korean War between Red China and North Kore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dean Rusk
David Dean Rusk (February 9, 1909December 20, 1994) was the United States Secretary of State from 1961 to 1969 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, the second-longest serving Secretary of State after Cordell Hull from the Franklin Roosevelt administration. He had been a high government official in the 1940s and early 1950s, as well as the head of a leading foundation. He is cited as one of the two officers responsible for dividing the two Koreas at the 38th parallel. Born to a poor farm family in Cherokee County, Georgia, Rusk graduated from Davidson College and was a Rhodes Scholar at Oxford University, where he immersed himself in English history and customs. After teaching at Mills College in California, he became an army officer in the war against Japan. He served as a staff officer in the China Burma India Theater, becoming a senior aide to Joseph Stilwell, the top American general. As a civilian he became a senior official in 1945 at the State Dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congo Crisis
The Congo Crisis (french: Crise congolaise, link=no) was a period of political upheaval and conflict between 1960 and 1965 in the Republic of the Congo (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The crisis began almost immediately after the Congo became independent from Belgium and ended, unofficially, with the entire country under the rule of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu. Constituting a series of civil wars, the Congo Crisis was also a proxy conflict in the Cold War, in which the Soviet Union and the United States supported opposing factions. Around 100,000 people are believed to have been killed during the crisis. A nationalist movement in the Belgian Congo demanded the end of colonial rule: this led to the country's independence on 30 June 1960. Minimal preparations had been made and many issues, such as federalism, tribalism, and ethnic nationalism, remained unresolved. In the first week of July, a mutiny broke out in the army and violence erupted between black and whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
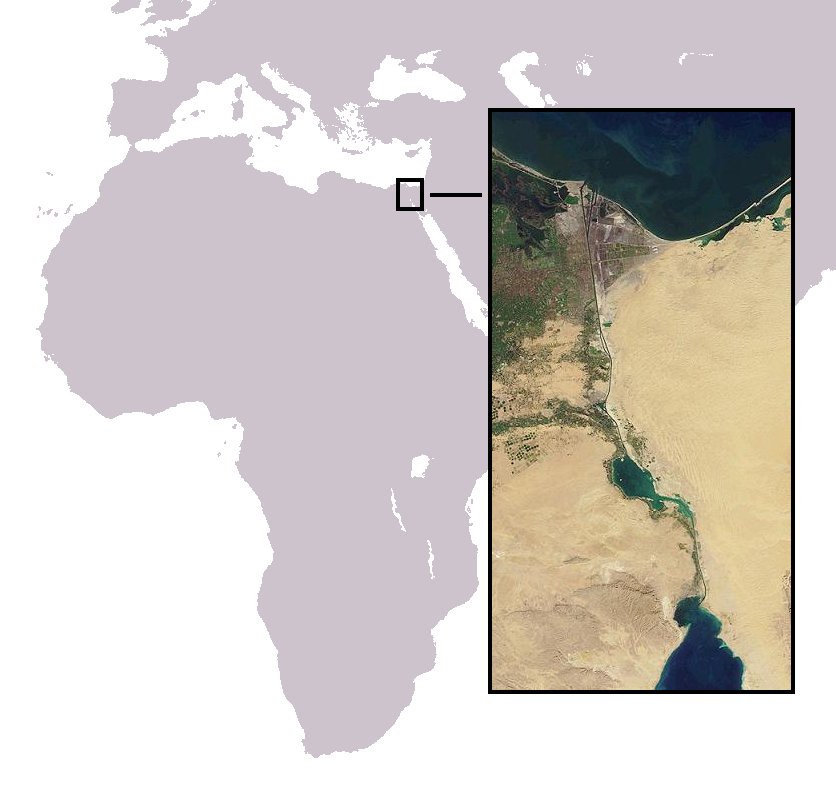
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 War; other names include the ''Sinai war'', ''Suez–Sinai war'', ''1956 Arab–Israeli war'', the Second Arab–Israeli war, ''Suez Campaign'', ''Sinai Campaign'', ''Kadesh Operation'' and ''Operation Musketeer'' was an invasion of Egypt in late 1956 by Israel, followed by the United Kingdom and France. The aims were to regain control of the Suez Canal for the Western powers and to remove Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had just swiftly nationalised the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company, which administered the canal. Israel's primary objective was to re-open the blocked Straits of Tiran. After the fighting had started, political pressure from the United States, the Soviet Union and the United Nations led to a withdrawal by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950) , place = Korean Peninsula, Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan, Korea Strait, China–North Korea border , territory = Korean Demilitarized Zone established * North Korea gains the city of Kaesong, but loses a net total of {{Convert, 1506, sqmi, km2, abbr=on, order=flip, including the city of Sokcho, to South Korea. , result = Inconclusive , combatant1 = {{Flag, First Republic of Korea, name=South Korea, 1949, size=23px , combatant1a = {{Plainlist , * {{Flagicon, United Nations, size=23px United Nations Command, United Nations{{Refn , name = nbUNforces , group = lower-alpha , On 9 July 1951 troop constituents were: US: 70.4%, ROK: 23.3% other UNC: 6.3%{{Cite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |