|
Andrei Krasnov
Andrei Nikolaevich Krasnov (–Р–љ–і—А–µ—П –Э–Є–Ї–Њ–ї–∞–µ–≤–Є—З –Ъ—А–∞—Б–љ–Њ–≤, 27 October 1862 вАУ 19 December 1914) was a Russian botanist who explored the plants of Turkestan, Altai, Nizhny Novgorod, Tian Shan and the Caucasus regions. He was a professor at the University of Kharkov. His major contribution was in phytogeography, identifying combinations of species found in different regions and contributing to the study of global vegetation patterns and their links to the K√ґppen climate classification. Life and work Krasnov was born in a Don Cossack family in St. Petersburg. His brother Pyotr became a noted General. He went to the St Petersburg Gymnasium before joining St Petersburg University where he studied under V. V. Dokuchaev and A.N. Beketov. A contemporary was V. I. Vernadsky. He took an interest in geography, soils, and the distributions of plants. In 1883, he joined on an expedition into the Nizhny Novgorod region. This was followed by other regions during whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Krasnov (1862вАУ1914)
Andrei Nikolaevich Krasnov (–Р–љ–і—А–µ—П –Э–Є–Ї–Њ–ї–∞–µ–≤–Є—З –Ъ—А–∞—Б–љ–Њ–≤; 27 October 1862 вАУ 19 December 1914) was a Russian botanist who explored the plants of Turkestan, Altai, Nizhny Novgorod, Tian Shan and the Caucasus regions. He was a professor at the University of Kharkov. His major contribution was in phytogeography, identifying combinations of species found in different regions and contributing to the study of global vegetation patterns and their links to the K√ґppen climate classification. Life and work Krasnov was born in a Don Cossack family in St. Petersburg. His brother Pyotr became a noted General. He went to the St Petersburg Gymnasium before joining St Petersburg University where he studied under V. V. Dokuchaev and A.N. Beketov. A contemporary was V. I. Vernadsky. He took an interest in geography, soils, and the distributions of plants. In 1883, he joined on an expedition into the Nizhny Novgorod region. This was followed by other regions during whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
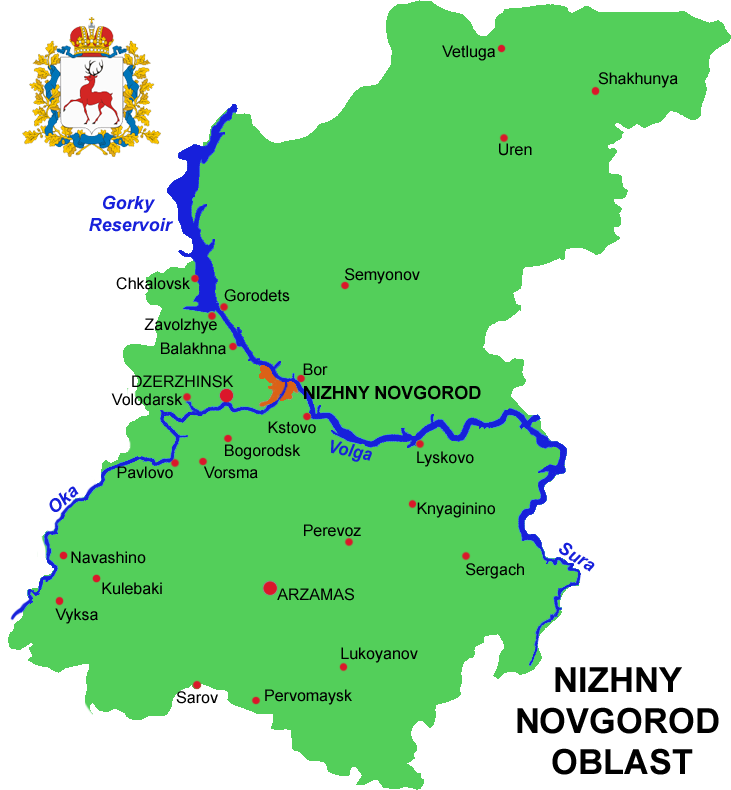
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast (russian: link=no, –Э–Є–ґ–µ–≥–Њ—А–Њ–і—Б–Ї–∞—П –Њ–±–ї–∞—Б—В—М, ''Nizhegorodskaya oblast''), is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Nizhny Novgorod. It has a population of 3,310,597 as of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. From 1932 to 1990 it was known as Gorky Oblast. The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area (including Dzerzhinsk, Russia, Dzerzhinsk, Bor, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Bor and Kstovo) the biggest city is Arzamas. Near the town of Sarov there is the Serafimo-Diveyevsky Monastery, one of the largest convents in Russia, established by Seraphim of Sarov, Saint Seraphim of Sarov. The Makaryev Monastery opposite of the town of Lyskovo, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Lyskovo used to be the location of the largest fair in Eastern Europe. Other historic towns include Gorodets, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914 Deaths
This year saw the beginning of what became known as World War I, after Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir to the Austrian throne was Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassinated by Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip. It also saw the first airline to provide scheduled regular commercial passenger services with heavier-than-air aircraft, with the St. PetersburgвАУTampa Airboat Line. Events January * January 1 – The St. PetersburgвАУTampa Airboat Line in the United States starts services between St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg and Tampa, Florida, becoming the first airline to provide scheduled regular commercial passenger services with heavier-than-air aircraft, with Tony Jannus (the first federally-licensed pilot) conveying passengers in a Benoist XIV flying boat. Abram C. Pheil, mayor of St. Petersburg, is the first airline passenger, and over 3,000 people witness the first departure. * January 11 – The Sakurajima volcano in Japan b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1862 Births
Year 186 ( CLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Glabrio (or, less frequently, year 939 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 186 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Peasants in Gaul stage an anti-tax uprising under Maternus. * Roman governor Pertinax escapes an assassination attempt, by British usurpers. New Zealand * The Hatepe volcanic eruption extends Lake Taup≈Н and makes skies red across the world. However, recent radiocarbon dating by R. Sparks has put the date at 233 AD ¬± 13 (95% confidence). Births * Ma Liang, Chinese official of the Shu Han state (d. 222) Deaths * April 21 – Apollonius the Apologist, Christian martyr * Bian Zhang, Chinese official and gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Grigorevich Popov
Mikhail Grigorevich Popov (russian: –Ь–Є—Е–∞–Є–ї –У—А–Є–≥–Њ—А—М–µ–≤–Є—З –Я–Њ–њ–Њ–≤) (5(17) April 1893 вАУ 18 December 1955) was a Soviet Union, Soviet botanist. He is known for developing a theory on the role of hybridization in plant evolution, and studying the flora of the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe. Eponyms *''Popoviocodonia'' Andrey A. Fedorov, Fed. 1957 Campanulaceae *''Popoviolimon'' Igor Lintchevski, Lincz. Plumbaginaceae References {{DEFAULTSORT:Popov, Mikhail Grigorevich Soviet botanists 1893 births 1955 deaths Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv faculty University of Lviv faculty Burials at Serafimovskoe Cemetery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnovia
''Krasnovia'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae. Its only described species is ''Krasnovia longiloba'', native to Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Xinjiang. The genus was first described in 1950, and was named after Andrei Krasnov by M.G. Popov. The species was first described in 1842 as ''Sphallerocarpus longilobus''. A 2001 study using ribosomal DNA found that '' Neoconopodium'', ''Krasnovia'' and ''Kozlovia'' were closely related within tribe Scandiceae subtribe Scandicinae, and proposed that they be combined into '' Kozlovia''. , this proposal had been accepted by the Germplasm Resources Information Network, but not by Plants of the World Online Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. It was launched in March 2017 with the ultimate aim being "to enable users to access information on all the world's known seed-bearing plants by .... References Apioideae Monotypic Apioideae genera< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batumi
Batumi (; ka, бГСбГРбГЧбГ£бГЫбГШ ) is the second largest city of Georgia and the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara, located on the coast of the Black Sea in Georgia's southwest. It is situated in a subtropical zone at the foot of the Caucasus. Much of Batumi's economy revolves around tourism and gambling (it is nicknamed "The Las Vegas of the Black Sea"), but the city is also an important seaport and includes industries like shipbuilding, food processing and light manufacturing. Since 2010, Batumi has been transformed by the construction of modern high-rise buildings, as well as the restoration of classical 19th-century edifices lining its historic Old Town. History Early history Batumi is located on the site of the ancient Greek colony in Colchis called "''Bathus"'' or "''Bathys"'', derived from ( grc-gre, ќ≤ќ±ќЄѕНѕВ ќїќєќЉќµќљ, ; or , ; lit. the 'deep harbour'). Under Hadrian (), it was converted into a fortified Roman port and later deserted for the fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazan Federal University
Kazan (Volga region) Federal University (russian: –Ъ–∞–Ј–∞–љ—Б–Ї–Є–є (–Я—А–Є–≤–Њ–ї–ґ—Б–Ї–Є–є) —Д–µ–і–µ—А–∞–ї—М–љ—Л–є —Г–љ–Є–≤–µ—А—Б–Є—В–µ—В, tt-Cyrl, –Ъ–∞–Ј–∞–љ (–Ш–і–µ–ї –±—Г–µ) —Д–µ–і–µ—А–∞–ї—М —Г–љ–Є–≤–µ—А—Б–Є—В–µ—В—Л) is a public research university located in Kazan, Russia. Founded in 1804 as Imperial Kazan University, astronomer Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky served there as the rector from 1837 until 1876. In 1929, the university was renamed in honour of its student Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov (Lenin). The university is known as the birthplace of organic chemistry due to works by Aleksandr Butlerov, Vladimir Markovnikov, Aleksandr Arbuzov, and the birthplace of electron spin resonance discovered by Evgeny Zavoisky. In 2011, Kazan University received a federal status. It is also one of 18 Russian universities that were initially selected to participate in the Project 5-100, coordinated by the Government of the Russian Federation and aimed to improve their international competit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernozem
Chernozem (from rus, —З–µ—А–љ–Њ–Ј—С–Љ, p=t…Х…™rn…РЋИz ≤…µm, r=chernozyom; "black ground"), also called black soil, is a black-colored soil containing a high percentage of humus (4% to 16%) and high percentages of phosphorus and ammonia compounds. Chernozem is very fertile soil and can produce high agricultural yields with its high moisture storage capacity. Chernozems are a Reference Soil Group of the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB). Distribution The name comes from the Russian terms for black and soil, earth or land (''chorny'' + ''zemlya''). The soil, rich in organic matter presenting a black color, was first identified by Russian geologist Vasily Dokuchaev in 1883 in the tallgrass steppe or prairie of European Russia. Chernozem cover about 230 million hectares of land. There are two "chernozem belts" in the world. One is the Eurasian steppe which extends from eastern Croatia (Slavonia), along the Danube (northern Serbia, northern Bulgaria ( Danubian Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Vernadsky
Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky (russian: link=no, –Т–ї–∞–і–ЄћБ–Љ–Є—А –Ш–≤–∞ћБ–љ–Њ–≤–Є—З –Т–µ—А–љ–∞ћБ–і—Б–Ї–Є–є) or Volodymyr Ivanovych Vernadsky ( uk, –Т–Њ–ї–Њ–і–ЄћБ–Љ–Є—А –Ж–≤–∞ћБ–љ–Њ–≤–Є—З –Т–µ—А–љ–∞ћБ–і—Б—М–Ї–Є–є; вАУ 6 January 1945) was a Russian, Ukrainian and Soviet mineralogist and geochemist who is considered one of the founders of geochemistry, biogeochemistry, and radiogeology. He was one of the founders and the first president of the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences (now National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine). Vladimir Vernadsky is most noted for his 1926 book ''The Biosphere'' in which he inadvertently worked to popularize Eduard Suess' 1885 term biosphere, by hypothesizing that life is the geological force that shapes the earth. In 1943 he was awarded the Stalin Prize. Vernadsky's portrait is depicted on the Ukrainian вВі1,000 hryvnia banknote. Early life Vernadsky was born in Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire, on in the family of the native Kyiv residents Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National University Of Kharkiv
The Kharkiv University or Karazin University ( uk, –Ъ–∞—А–∞–Ј—Ц–љ—Б—М–Ї–Є–є —Г–љ—Ц–≤–µ—А—Б–Є—В–µ—В), or officially V. N. Karazin Kharkiv National University ( uk, –•–∞—А–Ї—Ц–≤—Б—М–Ї–Є–є –љ–∞—Ж—Ц–Њ–љ–∞–ї—М–љ–Є–є —Г–љ—Ц–≤–µ—А—Б–Є—В–µ—В —Ц–Љ–µ–љ—Ц –Т. –Э. –Ъ–∞—А–∞–Ј—Ц–љ–∞), is one of the major universities in Ukraine, and earlier in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union. It was founded in 1804 through the efforts of Vasily Karazin becoming the second oldest university in modern-day Ukraine. History Russian Empire On , the Decree on the Opening of the Imperial University in Kharkiv came into force. The university became the second university in the south of the Russian Empire. It was founded on the initiative of the local community with Vasily Karazin at the fore, whose idea was supported by the nobility and the local authorities. Count Seweryn Potocki was appointed the first supervisor of the university, the first rector being the philologist and philosopher Ivan Rizhsky. In 1811 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Beketov
Andrey Nikolayevich Beketov (russian: –Р–љ–і—А–µ–є –Э–Є–Ї–Њ–ї–∞–µ–≤–Є—З –С–µ–Ї–µ—В–Њ–≤, 8 December 1825, Saratov Governorate, Russian Empire вАФ 1 July 1902, Shakhmatovo, Moscow Governorate) was a prominent Russian Imperial botanist, an Honourable member of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences. Beketov, the Meritorious Professor of Saint Petersburg University (which he was the head of in 1876-1883) was also a famous pedagogue and lecturer; among his best-known students were Andrey Krasnov, Vladimir Vernadsky, Kliment Timiryazev and Ivan Shmalhausen. Beketov initiated the inception of the High Women's Courses which he was the head of until 1889 when they were reorganized, to be known later as the Bestuzhev Courses. He edited the Works of Free Economical Society (for which he was for several years the secretary and, since 1891 its vice-president) and, in 1861вАФ1863, the Russian Geographical Society Herald (–Т–µ—Б—В–љ–Є–Ї –†—Г—Б—Б–Ї–Њ–≥–Њ –≥–µ–Њ–≥—А–∞—Д–Є—З–µ—Б–Ї–Њ–≥–Њ o–±—Й– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)