|
Ancient Roman Freedmen
The Roman practice of slavery utilized slaves for both production and domestic labour, overseen by their wealthy masters. Urban and domestic slaves especially could achieve high levels of education, acting as agents and representatives of their masters' affairs and finances. Within Roman law there was a set of practices for freeing trusted slaves, granting them a limited form of Roman Citizenship or Latin Rights. These freed slaves were known in Latin as ''liberti'' (freedmen), and formed a class set apart from freeborn Romans. While freedmen were barred from most forms of social mobility in Roman society, many achieved high levels of wealth and status. The legal and social status of freedmen remained a point of cultural and legal contention throughout the Republic and Empire. Manumission Freedmen in Ancient Rome existed as a distinct social class, with former slaves granted freedom and rights through the legal process of manumission. Manumission was codified during the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
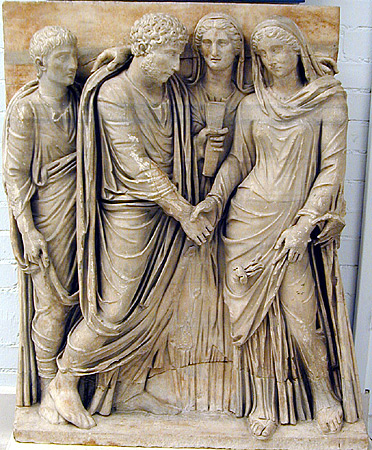
Relief Of Publius Aiedius Amphio And Aiedia Fausta Melior Antikensammlung Berlin
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς, ; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime. Dionysius' opinion of the necessity of a promotion of paideia within education, from true knowledge of classical sources, endured for centuries in a form integral to the identity of the Greek elite. Life He was a Halicarnassian. At some time after the end of the civil wars he moved to Rome, and spent twenty-two years studying Latin and literature and preparing materials for his history. During this period, he gave lessons in rhetoric, and enjoyed the society of many distinguished men. The date of his death is unknown. In the 19th century, it was commonly supposed that he was the ancestor of Aelius Dionysius of Halicarnassus. Works His major work, entitled ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Constantius Chlorus, Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrians, Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helena, was a Greeks, Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Sasanian Empire, Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Roman Britain, Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonia (Roman)
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''. Characteristics Under the Roman Republic, which had no standing army, bodies of their own citizens were planted in conquered towns as a kind of garrison. There were two types: * Roman colonies, ''coloniae civium Romanorum'' or ''coloniae maritimae'', as they were often built near the sea, e.g. Ostia (350 BC) and Rimini (268 BC). The colonists consisted of about three hundred Roman families and were given a small plot of land so were probably small business owners. * Latin colonies (''coloniae Latinae'') were considerably larger than Roman colonies. They were military strongholds near or in enemy territory. The colonists were given large estates up to 35 hectares. They lost their citizenship which they could regain if they returned to Rome. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italia (Roman Empire), Italy. Nonetheless, Claudius was an Italian of Sabine origins. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to sickness at a young age, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his Roman consul, consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate. The Principate is characterised by the reign of a single emperor (''princeps'') and an effort on the part of the early emperors, at least, to preserve the illusion of the formal continuance, in some aspects, of the Roman Republic. Etymology and anticipations *'Principate' is etymologically derived from the Latin word ''princeps'', meaning ''chief'' or ''first'', and therefore represents the political regime dominated by such a political leader, whether or not he is formally head of state or head of government. This reflects the principate emperors' assertion that they were merely "first among equals" among the citizens of Rome. *Under the Republic, the ''princeps senatus'', traditionally the oldest or most honoured member of the Senate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodales Augustales
The Sodales or Sacerdotes Augustales (''singular'' Sodalis or Sacerdos Augustalis), or simply Augustales,Tacitus, ''Annales'' 1.54 were an order ('' sodalitas'') of Roman priests originally instituted by Tiberius to attend to the maintenance of the cult of Augustus and the Julii. Their establishment in 14 A.D. was described by Tacitus in his first book of the ''Annales''. Augustales or ''seviri Augustales'' became institutions throughout the cities of the western Roman empire and were usually selected by the town councillors. Up to 95% of Augustales were freedmen as has been attested in inscriptions. They were rich and acted as benefactors, funding public entertainments and new buildings. In Rome the ''sodales'' were chosen by lot among the principal persons of Rome, and were twenty one in number, to which were added Tiberius, Drusus, Claudius, and Germanicus, as members of the imperial family. Women might be appointed priestesses of Augustus, a practice probably originating in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father was the politician Tiberius Claudius Nero and his mother was Livia Drusilla, who would eventually divorce his father, and marry the future-emperor Augustus in 38 BC. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus' two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus' successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat, and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for the empire's northern frontier. Early in his career, Tiberius was happily married to Vipsania, daughter of Augustus' friend, distinguished general and intended heir, Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa. They had a son, Drusus Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Julia
A ''lex Julia'' (plural: ''leges Juliae'') was an ancient Roman law that was introduced by any member of the gens Julia. Most often, "Julian laws", ''lex Julia'' or ''leges Juliae'' refer to moral legislation introduced by Augustus in 23 BC, or to a law related to Julius Caesar. ''Lex Julia de civitate'' (90 BC) During the Social War, a conflict between the Italians and the Romans over the withholding of Italian citizenship, the consul Lucius Julius Caesar passed a law to grant all Italians not under arms citizenship. At the instruction of the Senate, Lucius Caesar proposed a law providing that each Italian community would decide as to whether they would take Roman citizenship and establish new tribes – possibly eight – in the Tribal Assembly for the new citizens. This grant to citizenship had the effect of almost tripling the number of Roman citizens and annexing large swathes of Italy into the republic proper. The offer would be open to all Italian towns which were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Papia Poppaea
The ''Lex Papia et Poppaea'' was a Roman law introduced in 9 AD to encourage and strengthen marriage. It included provisions against adultery and against celibacy after a certain age and complemented and supplemented Augustus' ''Lex Iulia de maritandis ordinibus'' of 18 BC and the '' Lex Iulia de adulteriis coercendis'' of 17 BC. The law was introduced by the suffect consuls of that year, Marcus Papius Mutilus and Quintus Poppaeus Secundus, although they themselves were unmarried. History Tacitus mentions several '' leges Iuliae'' (Julian Laws) pertaining to morals and marriage, and the ''Lex Papia Poppaea'' as a separate later law, refining the Julian Laws (''Annals'', 3.25) Some writers conclude from the passage in Suetonius (Suet. Aug. 14) that the ''Lex Julia de maritandis ordinibus'' of 18/17 BC was rejected, and add that it was not enacted until 4 AD. In the year 9 AD, and in the consulship of Marcus Papius Mutilus and Quintus Poppaeus Secundus (consules suffecti) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Aelia Sentia
''Lex Aelia Sentia'' was a law established in ancient Rome in 4 AD. It was one of the laws that the Roman assemblies had to pass (after they were asked to do so by emperor Augustus). This law (as well as ''Lex Fufia Caninia''), has made limitations on manumissions. Manumission, or the freeing of a slave, became increasingly important by the early empire. Augustus sought to enact a series of restrictions on the practice. This law stated that for a manumission to be valid a master had to be at least twenty years old and a slave at least thirty. These limitations on manumissions were made when the number of manumissions were so large (at the end of Republic and the beginning of Empire), that they even questioned the social system of the time. This law had several provisions. One such provision stated that certain slaves who were manumitted could not become full Roman citizens, but rather would become members of a lower class of freedmen (''Peregrini dediticii''). If a manumitted slave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |