|
Anau Culture
The Anau culture was an ancient agricultural civilization of Central Asia centred in southern Turkmenistan. It started during the Chalcolithic period around 4000 BC, following the Neolithic Jeitun culture. It is named after its main site of Anau, Turkmenistan. The Namazga culture was contemporary to the Anau culture. Pottery similar to that of Anau (the earliest Anau IA phase) has been found as far as Shir Ashian Tepe in the Semnan Province of Iran. Site of Anau The settlement of Anau started around 4500 BC in the Neolithic period, before copper was used. Thus, it is earlier than Namazga-Tepe, the main site of the Namazga culture. Anau includes two mounds, north and south. Archaeological research here began in 1890. Raphael Pumpelly, Marushchenko, and Khurban Sokhatov were some of the researchers over the years. The lowest layers of the north mound in Anau provide some good evidence for the transition from the Neolithic to the Chalcolithic in the area. This archaeological s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapis Lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mines,David Bomford and Ashok Roy, ''A Closer Look- Colour'' (2009), National Gallery Company, London, () in Shortugai, and in other mines in Badakhshan province in northeast Afghanistan. Lapis lazuli artifacts, dated to 7570 BC, have been found at Bhirrana, which is the oldest site of Indus Valley civilisation. Lapis was highly valued by the Indus Valley Civilisation (7570–1900 BC). Lapis beads have been found at Neolithic burials in Mehrgarh, the Caucasus, and as far away as Mauritania. It was used in the funeral mask of Tutankhamun (1341–1323 BC). By the end of the Middle Ages, lapis lazuli began to be exported to Europe, where it was ground into powder and made into ultramarine, the finest and most expensive of all blue pigments. Ultra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Cultures Of Asia
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Central Asia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Turkmenistan
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Wang
Helen Kay Wang (; ; born 1965) is an English sinologist and translator. She works as curator of East Asian Money at the British Museum in London. She has also published a number of literary translations from Chinese, including an award-winning translation of a Chinese children's book. Biography Wang has a BA in Chinese from SOAS University of London (1988, including a year at the Beijing Language Institute, 1984–1985). She has a PhD in archaeology from University College London, titled "Money on the Silk Road: the evidence from Eastern Central Asia to c. AD 800", 2002. In 1991 Wang joined the British Museum staff as an assistant to Joe Cribb in the Asian section of the Department of Coins and Medals. She became Curator of East Asian Money in 1993. Her work mostly relates to the collections for which she is responsible, collection history and development of the field, in particular East Asian numismatics, Silk Road Numismatics, Sir Aurel Stein and his collections, and textiles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Tao (archaeologist)
Tao Wang (, born 1962) is a Chinese–British archaeologist and art historian specialising in early Chinese art. He is also known for his work on early inscriptions on oracle bones and ritual bronzes. He is married to numismatist and translator Helen Wang. Education Dr. Wang was born in Kunming in 1962. He studied Chinese literature at Yunnan Normal University and did postgraduate work at the China Academy of Art. Wang moved to London in 1986. He studied under Sarah Allan at SOAS University of London, earning his PhD in 1993. His thesis was titled ''Colour Symbolism in Late Shang China''. Academic career After obtaining his PhD, Wang took up a position as lecturer in Chinese archaeology at SOAS. He was Chair of the Centre of Chinese Studies at SOAS from 2005 to 2008. He was later appointed a senior lecturer at SOAS and University College London. He worked with Peter Ucko of the UCL Institute of Archaeology to develop links with archaeology departments in China, and helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (short BMAC) or Oxus Civilization, recently dated to c. 2250–1700 BC,Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilization between 2250 and 1700 BC, while its final phase extends until ca. 1500 BC..." is the modern archaeological designation for a Bronze Age civilization of Central Asia, previously dated to c. 2400–1900 BC, by Sandro Salvatori, in its urban phase or Integration Era. Though i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepe Hissar
Tepe Hissar (also spelled Tappeh Hesār) is a prehistoric site located in the village Heydarabad just south of Damghan in Semnan Province in northeastern Iran. The site is notable for its uninterrupted occupational history from the 5th to the 2nd millennium BCE. The quantity and elaborateness of its excavated artifacts and funerary customs position the site prominently as a cultural bridge between Mesopotamia and Central Asia. Archaeology The overall site covers 200 hectares including multiple mounds and several middle Islamic fortresses. The main tell has an extent of 12 hectares. The site was firstly discovered in 1877 by Albert Houtum-Schindler and then investigated in 1931 and 1932 by Erich Schmidt, on behalf of the University of Pennsylvania Museum (Schmidt 1933). A surface survey was carried out in 1972, while in 1976 a re-study project was performed, utilizing modern methods of stratigraphic assessments, ceramic typological analysis and radiocarbon dating, by the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
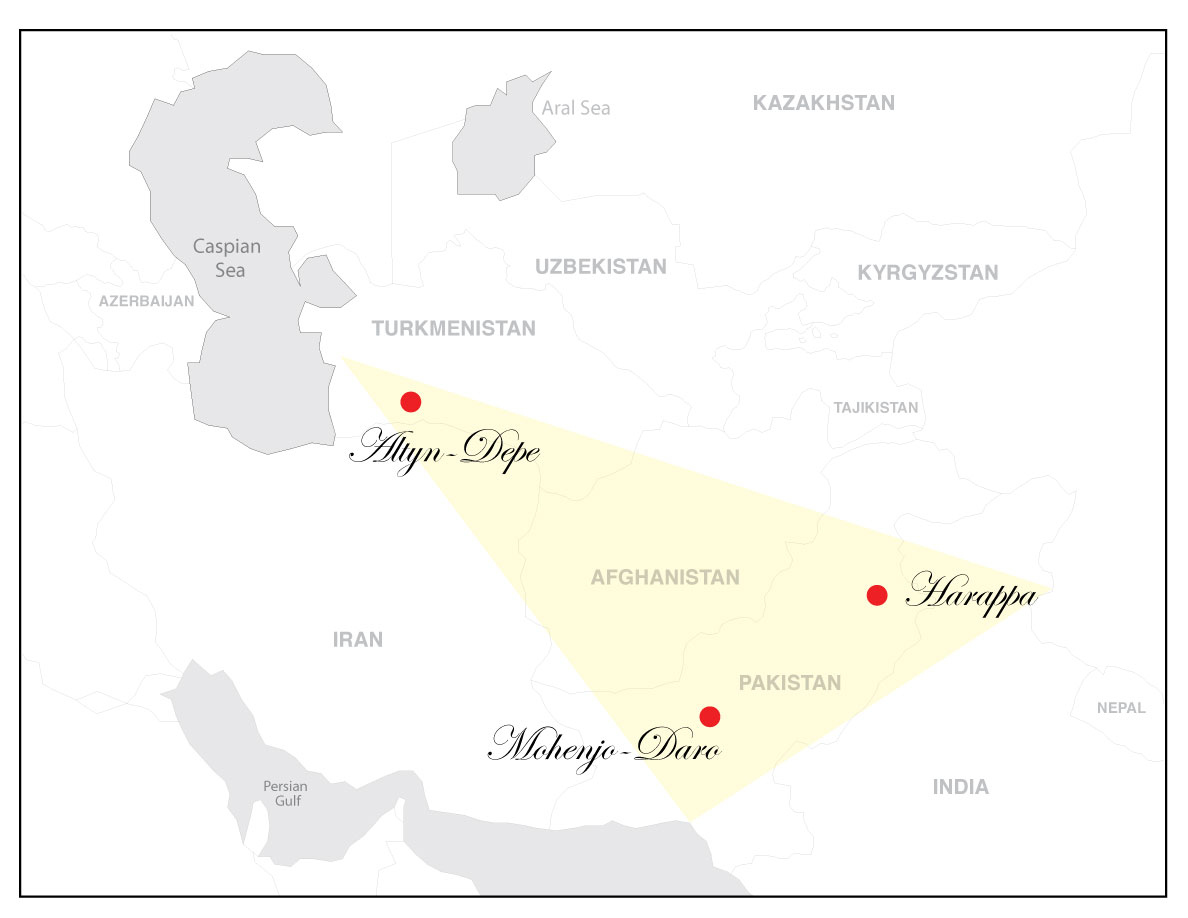
Altyndepe
(, sometimes Altyn Tepe, Turkmen "Golden Hill"), is a Bronze Age ( BMAC) archaeological site in Turkmenistan, near Aşgabat, inhabited first from c. 3200 to 2400 BCE in the Late Regionalization Era, and from c. 2400 to 2000 BCE in the Integration Era as a full urban site. Excavations Large-scale excavations at Altyn-depe started in 1965. During the late chalcolithic period Altyn Depe became a large-scale center with an area of 25 hectares. It was surrounded by an adobe wall with rectangular watch towers. Several living quarters were uncovered. The area called ''Excavation 9'' was a living quarter with several houses, many of them perhaps belonging to wealthy people. The houses had courtyards and street were running between them. People were often buried within houses. At ''Excavation 5'' and ''Excavation 10'' two other larger parts of living quarters were found. Those belong more likely to craftsmen. The houses are smaller and not so well built. Ziggurat The site is notable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepe Sialk
Tepe Sialk ( fa, تپه سیلک) is a large ancient archeological site (a ''tepe'', "hill, tell (archaeology), tell") in a suburb of the city of Kashan, Isfahan Province, in central Iran, close to Fin Garden. The culture that inhabited this area has been linked to the Zayandeh River Culture. History A joint study between Iran's Cultural Heritage Organization, the Louvre, and the Institut Francais de Recherche en Iran also verifies the oldest settlements in Sialk to date to around 6000–5500 BC. The Sialk ziggurat was built around 3000 BC. Sialk, and the entire area around it, is thought to have originated as a result of the pristine large water sources nearby that still run today. The Cheshmeh ye Soleiman ("Solomon's Spring") has been bringing water to this area from nearby mountains for thousands of years. The Fin garden, built in its present form in the 17th century, is a popular tourist attraction. It is here that the kings of the Safavid dynasty would spend their vacations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monjukli Depe
Monjukli Depe is an ancient settlement in south Turkmenistan, at the northern edge of the Kopet Dag mountains. Excavations reveal occupation from the late Neolithic period, starting about 6200 BC, to the early Chalcolithic period. The earliest layers belong to the Jeitun culture of Turkmenistan. The prehistoric settlement lies in an arid alluvial plain, which is bordered in the north by the Karakum desert and in the south by the slopes of the Kopet Dag. The mountains also mark today's political border with Iran. About two kilometers northwest of the site runs the dry bed of Meana river, where the modern village of Miana, Turkmenistan is located. The large Bronze Age settlement of Altyn Depe is located about 2km to the northeast. Excavations The first excavations by Aleksandr A. Marushchenko took place in 1959, and were later continued by his colleague O. K. Berdiev. The results of this first investigation were compiled in a preliminary report. In 2010, the potential of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)