|
Anatoli Zhelezniakov
Anatoli Grigorievich Zhelezniakov (May 2, 1895 - July 26, 1919) was a Russian anarchist, Baltic sailor and revolutionary best known for dispersing the short-lived Russian Constituent Assembly on Bolshevik orders during the October Revolution. Life Early years Anatoli Zhelezniakov was born in the village of Fedoskino, in the Moscow Governorate, where his father worked as an employee on a landowner's estate. He had an older sister Alexandra and two brothers - Nikolai and Victor. Nikolai was a sailor and a notorious anarchist, Victor graduated from the Petrograd Naval School and served as the commander of the ship in the Baltic Fleet. His father died of a heart attack in May 1918 and his mother died in 1927. Anatoli enrolled in the Lefortovo military paramedic school, but in April 1912 he refused to go to the parade in honor of the empress's name day, provoking his expulsion. He also failed at admission to the Kronstadt Naval College and began working in a pharmacy at a we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Governorate
Moscow Governorate (russian: Московская губерния; pre-reform Russian: ), or the Government of Moscow, was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the Russian SFSR, which existed in 1708–1929. Administrative division Moscow Governorate consisted of 13 uyezds (their administrative centres in brackets): * Bogorodsky Uyezd ( Bogorodsk/Noginsk) * Bronnitsky Uyezd (Bronnitsy) * Vereysky Uyezd (Vereya) * Volokolamsky Uyezd (Volokolamsk) * Dmitrovsky Uyezd (Dmitrov) * Zvenigorodsky Uyezd (Zvenigorod) * Klinsky Uyezd (Klin) * Kolomensky Uyezd (Kolomna) * Mozhaysky Uyezd (Mozhaysk) * Moskovsky Uyezd (Moscow) * Podolsky Uyezd (Podolsk) * Ruzsky Uyezd ( Ruza) * Serpukhovsky Uyezd (Serpukhov) History Moscow Governorate, together with seven other governorates, was established on , 1708, by Tsar Peter the Great's edict. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Pavlunovsky
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgarian tsar Ivan Vladislav. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is Иван, while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is Іван. The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English '' John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Ilyin-Genevsky
Alexander Fyodorovich Ilyin (russian: Алекса́ндр Фёдорович Ильи́н-Жене́вский; November 28, 1894 – September 3, 1941), known with the party name Zhenevsky, "the Genevan" because he joined the Bolshevik group of Russian émigrés while exiled in that city, was a Soviet chess master and organizer, one of founders of the Soviet chess school, an Old-Guard Bolshevik cadre, a writer, a military organizer, a historian and a diplomat. He was born in Saint Petersburg and was the younger brother of Red Navy leader Fedor Raskolnikov. Ilyin-Zhenevsky promoted chess as an educational vehicle for developing tactical and strategical comprehension during military training, and, within the Soviet Union, he was the main person responsible for the spreading of the idea of chess as a way to teach the basics of scientific and rational thought. The All-Russian Chess Olympiad (retroactively recognized as the first Soviet Championship) in 1920 and the 1933 match Mikh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Khovrin
Nikolai Alexandrovich Khovrin (1891 – 1972) was a Russian and Soviet military leader who headed Baltic sailor formations during the October Revolution. Life and career Born on 7 October 1891 in Saint Petersburg, since 1912 Khovrin served in the Baltic Fleet, and he was a member of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party since 1915. In 1917 he participated in the February Revolution and was a member of the Bolsheviks Gelsingfors Committee, one of founders and a member of the Central Committee of the Baltic Fleet (Tsentrobalt). During the October Revolution, Khovrin was a commissar of the Tsentrobalt, participated in the assault of the Winter Palace, destroying the Kerensky–Krasnov uprising, and was a member of the 2nd All-Russian Congress of Soviets. On 13 November 1917 he led his sailors to crush anti-Bolshevik resistance in Moscow. In 1918 Khovrin was appointed a commander of the Petrograd Naval Base and participated in Soviet invasion of Ukraine as part of the Ukrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerensky–Krasnov Uprising
The Kerensky–Krasnov uprising was an attempt by Alexander Kerensky to crush the October Revolution and regain power after the Bolsheviks overthrew his government in Petrograd. It took place between . Following the October Revolution, Kerensky fled Petrograd, which fell to the Bolshevik-controlled Petrograd Soviet and went to Pskov, the headquarters of the Northern Front command. He did not get the support of its commander, General Vladimir Cheremisov, who prevented his attempts to gather units to march on Petrograd, but he did get the support of General Pyotr Krasnov, who advanced on the capital with about 700 Cossacks. In Petrograd, opponents of the October Revolution were preparing a revolt that would coincide with the attack on the city by Kerensky's forces. The Soviets had to improvise the defense of the hills south of the city and wait for the attack of Kerensky's troops, who, despite the efforts of the high command, received no reinforcements. The clash in the Pulkovo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Executive Committee Of The Navy
The Central Executive Committee of the Navy (Centroflot) was the main collegial governing body of the navy, created as part of the democratization of the navy in 1917 in order to coordinate the activities of the committees of the fleets and flotillas. The Centroflot was formed by the First All-Russian Congress of Soviets of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies in June 1917 on the basis of delegates of the Maritime Section of the Petrograd Soviet.Centroflot – Article from the (3rd Edition) Most members of the Centroflot were moderate socialists – the Mensheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. By the fall of 1917, in parallel with the process of |
Assault On The Winter Palace
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment in the larger Russian Revolution of 1917–1923. It was the second revolutionary change of government in Russia in 1917. It took place through an armed insurrection in Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg) on . It was the precipitating event of the Russian Civil War. The October Revolution followed and capitalized on the February Revolution earlier that year, which had overthrown the Tsarist autocracy, resulting in a liberal provisional government. The provisional government had taken power after being proclaimed by Grand Duke Michael, Tsar Nicholas II's younger brother, who declined to take power after the Tsar stepped down. During this time, urban workers began to organize into councils (soviets) wherein revolutionaries criticized the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Congress Of Soviets
The All-Russian Congress of Soviets evolved from 1917 to become the supreme governing body of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic from 1918 until 1936, effectively. The 1918 Constitution of the Russian SFSR mandated that Congress shall convene at least twice a year, with the duties of defining (and amending) the principles of the Soviet Constitution and ratifying peace treaties. The October Revolution ousted the provisional government of 1917, making the Congress of Soviets the sole, and supreme governing body. It is important to note that this Congress was not the same as the Congress of Soviets of the Soviet Union which governed the whole Soviet Union after its creation in 1922. For the earlier portion of its life, the Congress was a democratic body. Over Russia there were hundreds of soviets, democratic local governing bodies in which the surrounding population could participate. The soviets elected the delegates to the Congress, and then in turn the Congress hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Berkman
Alexander Berkman (November 21, 1870June 28, 1936) was a Russian-American anarchist and author. He was a leading member of the anarchist movement in the early 20th century, famous for both his political activism and his writing. Berkman was born into a wealthy Jewish family in Vilna in the Russian Empire (present-day Vilnius, Lithuania) and immigrated to the United States in 1888. He lived in New York City, where he became involved in the anarchist movement. He was the one-time lover and lifelong friend of anarchist Emma Goldman. In 1892, undertaking an act of propaganda of the deed, Berkman made an unsuccessful attempt to assassinate businessman Henry Clay Frick during the Homestead strike, for which he served 14 years in prison. His experience in prison was the basis of his first book, '' Prison Memoirs of an Anarchist''. After his release from prison, Berkman served as editor of Goldman's anarchist journal, '' Mother Earth'', and later established his own jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Mooney
Thomas Joseph Mooney (December 8, 1882 – March 6, 1942) was an American political activist and labor leader, who was convicted with Warren K. Billings of the San Francisco Preparedness Day Bombing of 1916. It quickly became apparent that Mooney and Billings had been convicted based on falsified evidence and perjured testimony and the Mooney case and campaigns to free him became an international cause célèbre for two decades, with a substantial number of publications demonstrating the falsity of the conviction; these publications and the facts of the case are surveyed in Richard H. Frost, The Mooney Case (Stanford University Press, 1968). Mooney served 22 years in prison before finally being pardoned in 1939. Early life The son of Irish immigrants, Mooney was born in Chicago, Illinois on December 8, 1882. His father, Bernard, had been a coal miner and a militant organizer for the Knights of Labor in struggles so intense that after one fight he was left for dead. Bernard Moo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparedness Day Bombing
The Preparedness Day Bombing was a bombing in San Francisco, California, United States, on July 22, 1916, of a parade organised by local supporters of the Preparedness Movement which advocated American entry into World War I. During the parade a suitcase bomb was detonated, killing ten and wounding 40 in the worst terrorist attack in San Francisco's history. Two labor leaders, Thomas Mooney and Warren K Billings, were convicted in separate trials and sentenced to death, later commuted to life in prison. Later investigations found the convictions to have been based on false testimony, and the men were released in 1939 and eventually pardoned. The identity of the bombers has never been determined. Prelude By mid-1916, after viewing the carnage in Europe, the United States saw itself poised on the edge of participation in World War I. Isolationism remained strong in San Francisco, not only among radicals such as the Industrial Workers of the World ("the Wobblies"), but also amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_p6.jpg)

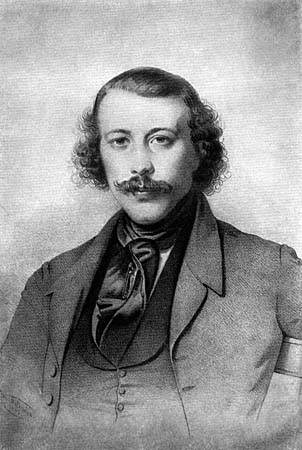
.jpg)




