|
Analytic Signal
In mathematics and signal processing, an analytic signal is a complex-valued function that has no negative frequency components. The real and imaginary parts of an analytic signal are real-valued functions related to each other by the Hilbert transform. The analytic representation of a real-valued function is an ''analytic signal'', comprising the original function and its Hilbert transform. This representation facilitates many mathematical manipulations. The basic idea is that the negative frequency components of the Fourier transform (or spectrum) of a real-valued function are superfluous, due to the Hermitian symmetry of such a spectrum. These negative frequency components can be discarded with no loss of information, provided one is willing to deal with a complex-valued function instead. That makes certain attributes of the function more accessible and facilitates the derivation of modulation and demodulation techniques, such as single-sideband. As long as the manip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler's Formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for any real number : e^ = \cos x + i\sin x, where is the base of the natural logarithm, is the imaginary unit, and and are the trigonometric functions cosine and sine respectively. This complex exponential function is sometimes denoted ("cosine plus i sine"). The formula is still valid if is a complex number, and so some authors refer to the more general complex version as Euler's formula. Euler's formula is ubiquitous in mathematics, physics, and engineering. The physicist Richard Feynman called the equation "our jewel" and "the most remarkable formula in mathematics". When , Euler's formula may be rewritten as , which is known as Euler's identity. History In 1714, the English mathematician Roger Cotes presented a geometrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passband Signal
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all the radio waves picked up by its antenna. The passband of a receiver is the range of frequencies it can receive when it is tuned into the desired frequency (channel). A bandpass-filtered signal (that is, a signal with energy only in a passband), is known as a bandpass signal, in contrast to a baseband signal. Filters In telecommunications, optics, and acoustics, a passband (a band-pass filtered signal) is the portion of the frequency spectrum that is transmitted (with minimum relative loss or maximum relative gain) by some filtering device. In other words, it is a ''band'' of frequencies which ''pass''es through some filter or a set of filters. The accompanying figure shows a schematic of a waveform being filtered by a bandpass filter consisting of a highpass and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is an analog of the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency. A baseband signal may have frequency components going all the way down to DC, or at least it will have a high ratio bandwidth. A modulated baseband signal is called a passband signal. This occupies a higher range of frequencies and has a lower ratio and fractional bandwidth. Various uses Baseband signal A ''baseband signal'' or ''lowpass signal'' is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest frequency (for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (signal strength) of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the sidebands a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
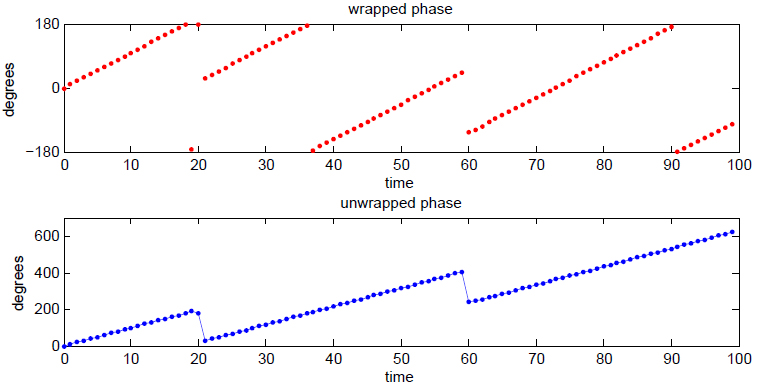
Instantaneous Phase
Instantaneous phase and frequency are important concepts in signal processing that occur in the context of the representation and analysis of time-varying functions. The instantaneous phase (also known as local phase or simply phase) of a ''complex-valued'' function ''s''(''t''), is the real-valued function: :\varphi(t) = \arg\, where arg is the complex argument function. The instantaneous frequency is the temporal rate of change of the instantaneous phase. And for a ''real-valued'' function ''s''(''t''), it is determined from the function's analytic representation, ''s''a(''t''): :\begin \varphi(t) &= \arg\ \\ pt &= \arg\, \end where \hat(t) represents the Hilbert transform of ''s''(''t''). When ''φ''(''t'') is constrained to its principal value, either the interval or , it is called ''wrapped phase''. Otherwise it is called ''unwrapped phase'', which is a continuous function of argument ''t'', assuming ''s''a(''t'') is a continuous function of ''t''. Unless oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envelope (waves)
In physics and engineering, the envelope of an oscillating signal is a smooth curve outlining its extremes. The envelope thus generalizes the concept of a constant amplitude into an instantaneous amplitude. The figure illustrates a modulated sine wave varying between an ''upper envelope'' and a ''lower envelope''. The envelope function may be a function of time, space, angle, or indeed of any variable. In beating waves A common situation resulting in an envelope function in both space ''x'' and time ''t'' is the superposition of two waves of almost the same wavelength and frequency: : \begin F(x, \ t) & = \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f + \Delta f )t \right) \right+ \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f - \Delta f )t \right) \right\\ pt& \approx 2\cos \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - \Delta f \ t \right) \right\ \sin \left 2 \pi \left( \frac - f \ t \right) \right\end which uses the trigonometric formula for the addition of two sine waves, and the approximation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |