|
Anak Ng Espada
Anak (; he, , homophone to a word for "giant, long neck, necklace"; ) is a figure in the Hebrew Bible. His descendants are mentioned in narratives concerning the conquest of Canaan by the Israelites. According to the Book of Numbers, Anak was a forefather of the Anakim. Ten of the twelve Israelite spies described them as very tall descendants of Anak, compare . The text states that the giant stature of the Anakim was the standard by which other giant races were measured, such as the Rephaites, and that Anak was a son of Arba. Etymology L. Nesiolowski-Spano proposed a hypothesis that his name is derived from the Greek ' wanax', 'ruler'. In the Bible The sons of Anak are first mentioned in . The Israelite leader Moses sends twelve spies representing the Twelve Tribes of Israel to scout out the land of Canaan. The spies enter from the Negev desert and journey northward through the Judaean hills until they arrive at the brook of Eshcol near Hebron, where reside Sheshai, Ahima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy ( grc, Δευτερονόμιον, Deuteronómion, second law) is the fifth and last book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called (Hebrew: hbo, , Dəḇārīm, hewords Moses.html"_;"title="f_Moses">f_Moseslabel=none)_and_the_fifth_book_of_the_Christian_Old_Testament.html" ;"title="Moses">f_Moses.html" ;"title="Moses.html" ;"title="f Moses">f Moses">Moses.html" ;"title="f Moses">f Moseslabel=none) and the fifth book of the Christian Old Testament">Moses">f_Moses.html" ;"title="Moses.html" ;"title="f Moses">f Moses">Moses.html" ;"title="f Moses">f Moseslabel=none) and the fifth book of the Christian Old Testament. Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to the Israelites by Moses on the Plains of Moab, shortly before they enter the Promised Land. The first sermon recounts the Moses#The years in the wilderness, forty years of wilderness wanderings which had led to that moment, and ends with an exhortation to observe the law. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American people, American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are ''Moby-Dick'' (1851); ''Typee'' (1846), a romanticized account of his experiences in Polynesia; and ''Billy Budd, Billy Budd, Sailor'', a posthumously published novella. Although his reputation was not high at the time of his death, the 1919 centennial of his birth was the starting point of a #Melville revival and Melville studies, Melville revival, and ''Moby-Dick'' grew to be considered one of the great American novels. Melville was born in New York City, the third child of a prosperous merchant whose death in 1832 left the family in dire financial straits. He took to sea in 1839 as a common sailor on a merchant ship and then on the whaler ''Acushnet'', but he jumped ship in the Marquesas Islands. ''Typee'', his first b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Greek Myths
''The Greek Myths'' (1955) is a mythography, a compendium of Greek mythology, with comments and analyses, by the poet and writer Robert Graves. Many editions of the book separate it into two volumes. Abridged editions of the work contain only the myths and leave out Graves's commentary. Each myth is presented in the voice of a narrator writing under the Antonines, such as Plutarch or Pausanias, with citations of the classical sources. The literary quality of his retellings is generally praised. Following each retelling, Graves presents his interpretation of its origin and significance, influenced by his belief in a prehistoric Matriarchal religion, as discussed in his book ''The White Goddess'' and elsewhere. Graves's theories and etymologies are rejected by most classical scholars. Graves argued in response that classical scholars lack "the poetic capacity to forensically examine mythology". Contents Graves interpreted Bronze Age Greece as changing from a matriarchal society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
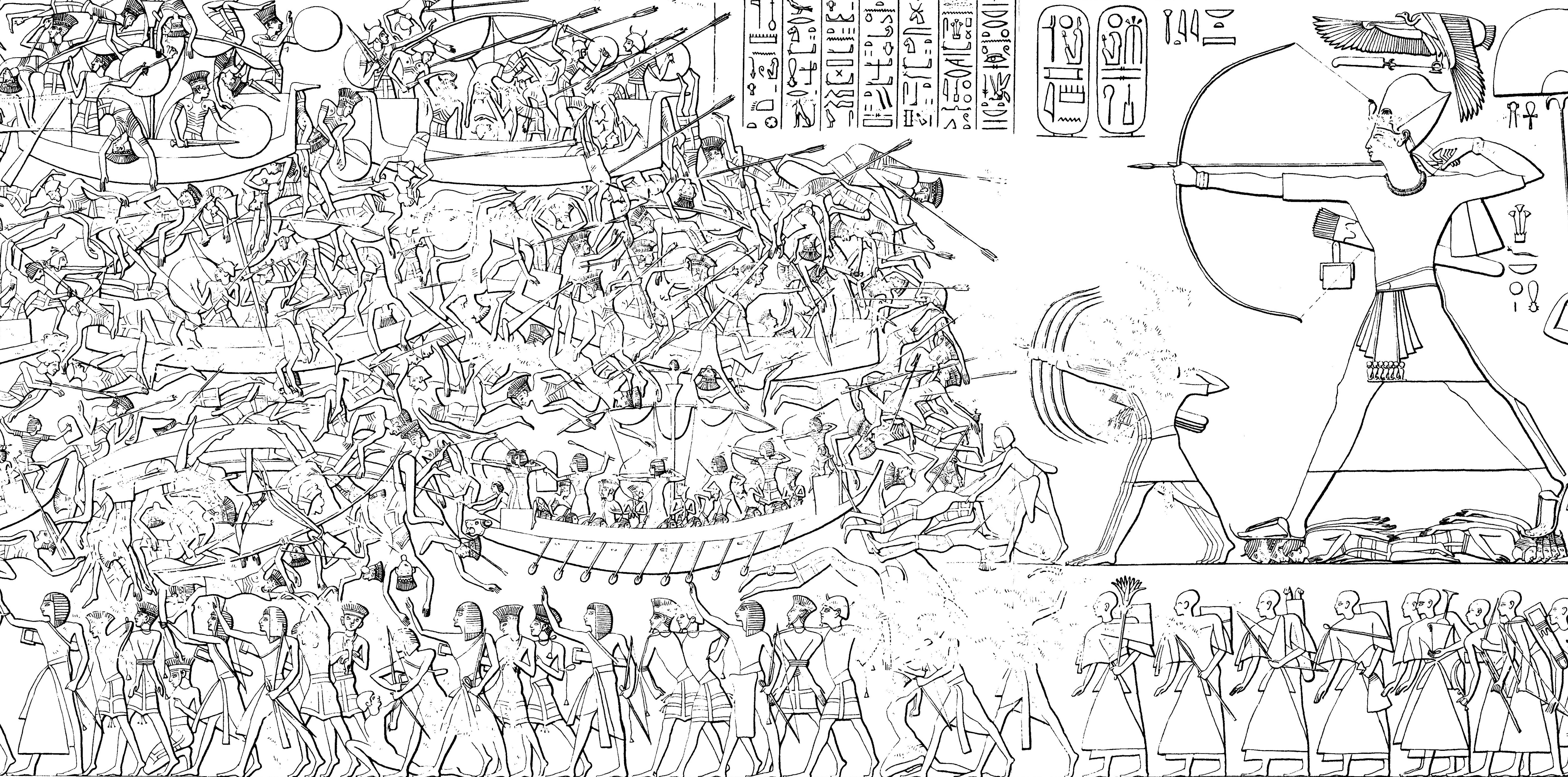
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world, the lives and activities of List of Greek mythological figures, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Ionia. Its ruins are located near the modern village of Balat in Aydın Province, Turkey. Before the Persian rule that started in the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered among the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities. Evidence of first settlement at the site has been made inaccessible by the rise of sea level and deposition of sediments from the Maeander. The first available evidence is of the Neolithic. In the early and middle Bronze Age the settlement came under Minoan influence. Legend has it that an influx of Cretans occurred displacing the indigenous Leleges, and the site was renamed Miletus after a place in Crete. Recorded history at Miletus begins with the records of the Hittite Empire, and the Mycenaean records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anax (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Anax (Ancient Greek: ; from earlier , ') was a king of Anactoria (Miletus). He was the son of Gaea (Earth) and father of Asterius. Anax' name means "tribal chief, lord, (military) leader". Mythology According to the Milesians in Asia Minor, their land was called Anactoria for two generations, during the reigns of the eponymous founder Anax and his son Asterius who succeeded him in the throne. But later on, Miletus who was fleeing from King Minos, with a Cretan army in Anactoria, occupied the country and called it after himself.Pausanias7.2.5/ref> See also * Anax (word) * Anak * Giants * Anakim Notes References * Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to: *Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium'' *Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC * Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ..., ''Description of Greece'' with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistia
Philistia (; Koine Greek (LXX): Γῆ τῶν Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''gê tôn Phulistieìm''), also known as the Philistine Pentapolis, was a confederation of cities in the Southwest Levant, which included the cities of Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, Gath, Gaza, and for a time, Jaffa. The population, according to the most recent assessments, was, in all probability, formed basically from Canaanite stock going back to the Bronze Age,Benjamin M. Sulliva'In the Shadow of Phoenicia,' The Journal of Hellenic Studies, 2018, Vol. 138 pp.67-79 p.70 tinged with an Indo-European admixture of people from an Aegean background from roughly 1200 BCE onwards, and came to be known as ''Peleset'', or Philistines. At its maximum territorial expansion, its territory may have stretched along the Canaanite coast from Arish in the Sinai (today's Egypt) to the Yarkon River (today's Tel Aviv), and as far inland as Ekron and Gath. Nebuchadnezzar II invaded Philistia in 604 BC, burned Ashkelon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was a British poet, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were both Celticists and students of Irish mythology. Graves produced more than 140 works in his lifetime. His poems, his translations and innovative analysis of the Greek myths, his memoir of his early life—including his role in World War I—''Good-Bye to All That'', and his speculative study of poetic inspiration ''The White Goddess'' have never been out of print. He is also a renowned short story writer, with stories such as "The Tenement" still being popular today. He earned his living from writing, particularly popular historical novels such as ''I, Claudius''; '' King Jesus''; ''The Golden Fleece''; and ''Count Belisarius''. He also was a prominent translator of Classical Latin and Ancient Greek texts; his versions of ''The Twelve Caesars'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
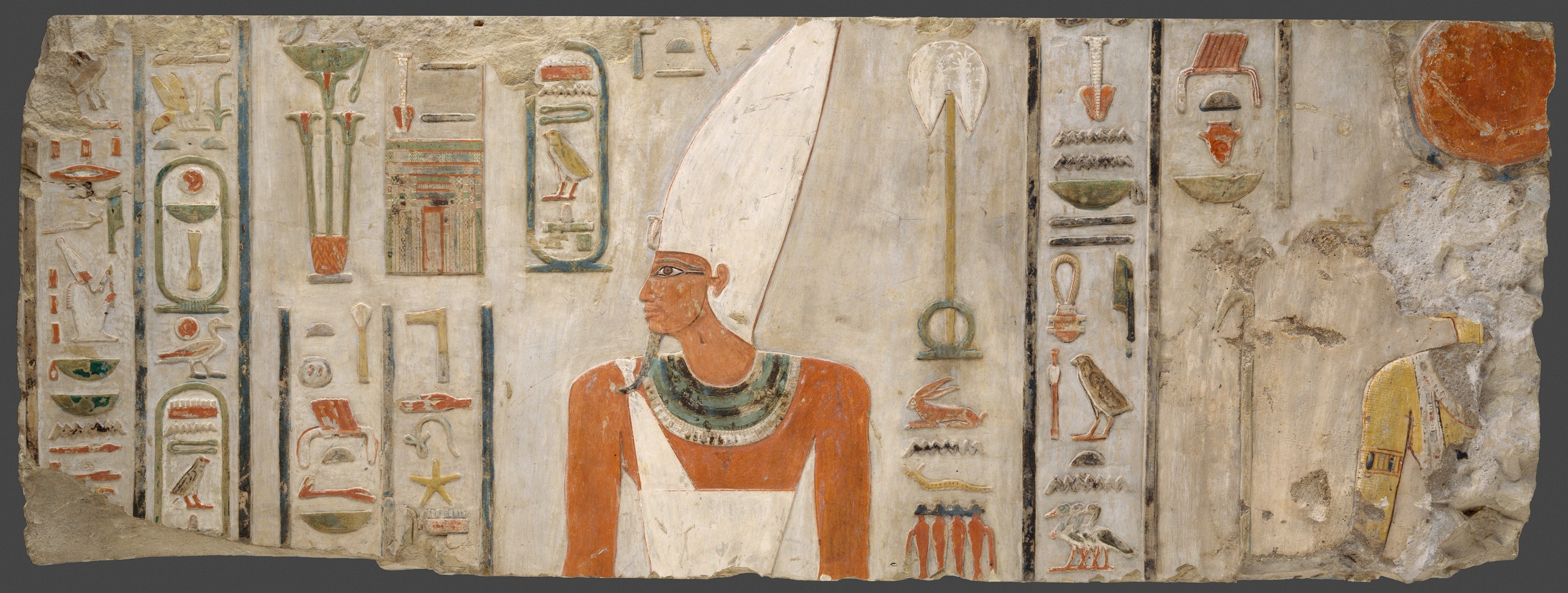
Middle Kingdom Of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht. The concept of the Middle Kingdom as one of three golden ages was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition evolved significantly throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. Some scholars also include the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt wholly into this period, in which case the Middle Kingdom would end around 1650 BC, while others only include it until Merneferre Ay around 1700 BC, last king of this dynasty to be attested in both Upper and Lower Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Execration Texts
Execration texts, also referred to as proscription lists, are ancient Egyptian hieratic texts, listing enemies of the pharaoh, most often enemies of the Egyptian state or troublesome foreign neighbors. The texts were most often written upon statuettes of bound foreigners, bowls, or blocks of clay or stone, which were subsequently destroyed. The ceremonial process of breaking the names and burying them was intended to be a sort of sympathetic magic that would affect the persons or entities named in the texts. The fragments were usually placed near tombs or ritual sites. This practice was most common during times of conflict with the Asiatic neighbors of Egypt. Historical periods of execration texts Execration texts are attested from the late Old Kingdom ( 2686–2160 BCE) up into the New Kingdom (c. 1550–1069). The earliest execration texts date to the 6th dynasty (24th–22nd century BCE) during Egypt's Old Kingdom. They are statuettes made from unbaked clay and fashioned i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |